Active Directory Federation Services (AD
FS) provides Internet-based clients a secure identity access solution
that works on both Windows and non-Windows operating systems.
Normally when a user from one network tries to
access an application in another network, they must have a secondary
username and password.
AD FS allows organizations to set up trust
relationships between networks and supports single sign-on (SSO), which
allows users to access applications on other networks without needing
secondary passwords. Security is improved and administrators spend less
time resetting passwords when users don't have to remember multiple
passwords.
AD FS requires an AD FS server on both ends of the
connection. For example, if company A is going to set up trust
relationship with company B, the AD FS server needs to be configured at
both company A and company B.
1. Installing AD FS
Exercise 1 shows you the steps you need to perform to install the AD FS through the Server Manager MMC.
Open the Server Manager MMC by selecting Start => Administrative Tools => Server Manager. In the left pane, click Roles. In the Roles Summary section of right pane, click Add Roles.
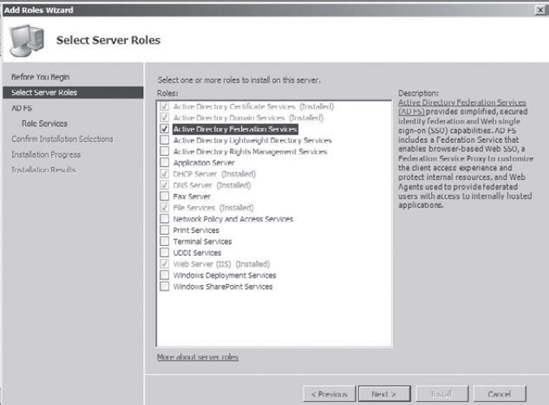
On the Select Server Roles screen, click the Active Directory Federation Services check box and click Next.
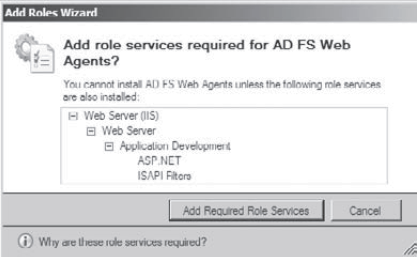
On the Introduction To AD FS screen, click Next. On
the Select Role Services screen, choose the AD FS Web Agent check box.
A dialog box appears asking you to confirm the additional services that
need to be installed. Click Add Required Role Services. When the Select
Role Services screen reappears, Click Next.
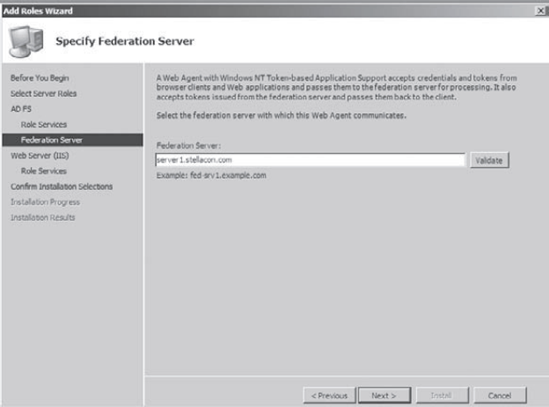
On the Specify Federation Server screen, type the name of your server and domain and click Validate.
You will see an error message
explaining that the other Federation server that you are trying to
connect to is unavailable. That is OK for this exercise. Click Next. At the Introduction To IIS screen, click Next. On
the Select Role Services screen, you see the additional services needed
to install IIS. All the required boxes are already checked. Click Next.
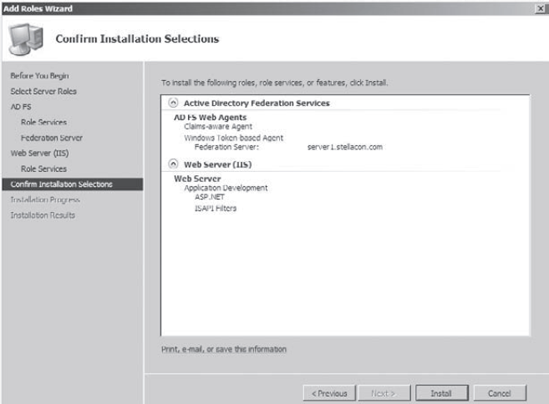
The Confirm Installation Selections screen shows you all the services and roles that you are about to install. Click Install.
After the installation is finished, click Close.
|
2. Configuring AD FS
Now that the AD FS is installed and running, you
need to learn how to configure some of the important options. In the AD
FS, you can configure trust policies, AD FS agents, and user and group
mapping.
AD FS Web Agents
Administrators have the ability to configure a
Windows NT token-based Web Agent. To support this new feature, Windows
Server 2008 AD FS includes a user interface for the AD FS Web Agent
role service. The Web Agent account is a service account that calls
upon other services.
Trust policies
The AD FS trust policy is a file that outlines
the set of rules that a Federation Service uses to recognize partners,
certificates, account stores, claims, and the other numerous properties
that are associated with the Federation Service.
User and group claim mapping
In basic terms, claims mean that each partnered
location agrees and appropriately maps the AD FS trust policy for
sharing between federation partner locations. A claim contains user
information and helps users connect to a partner's resources. Three
types of claims are supported by AD FS:
Identity claim
This claim type helps identify the user. The
identity claim is included within a security token. A security token
can contain up to three identity claims.
Group claim
This claim type indicates membership in a group or role.
Custom claim
This claim type provides any additional
information that needs to be sent. An example might be DepartmentID.
This is a custom field and then in turn would be a custom claim. A
custom claim can provide any attribute that is located in Active
Directory.