With Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), you
manage objects (users, computers, printers, etc.) on a network. Active
Directory is the database that stores all of your domain objects. In a
Windows Server 2000, 2003, or 2008 network, you can not have a domain
without Active Directory.
1. Introducing the New Domain Services Features in Windows Server 2008
Many new AD DS features have been added in Windows
Server 2008. These features improve the security and efficiency of
deploying and administering AD DS.
User interface improvements
Domain services are easier to install using the
updated Installation Wizard for AD DS. Administrators can set up domain
controllers anywhere in the organization. An improved AD DS user
interface offers additional installation options for domain
controllers. One of these is the ability to set up read-only domain
controllers (RODCs).
Read-only domain controllers
Windows Server 2008 supports a new type of domain controller, the read-only domain controller (RODC).
You can safely install an RODC in a location that has limited security,
such as a small offsite office. Offsite users no longer have to be
authenticated across a slow WAN connection.
Auditing
Previous versions of Microsoft Windows Server
supported auditing of successful or unsuccessful changes to Active
Directory objects; however, the nature of the change was not included
in the Security Log. In Microsoft Windows Server 2008, you can view the
new and old values of the object and its attributes.
Fine-grained password policies
In Microsoft Windows Server 2000 and 2003,
domain-based password policies and account lockout policies applied to
all users in the domain. There was no inexpensive way to implement
multiple such policies for individuals or groups. In Windows Server
2008, fine-grained password policies support multiple password and
account lockout policies in the same domain.
Restartable Active Directory Domain Services
With Microsoft Windows Server 2008,
administrators can stop or restart AD DS while other services not
dependent on Active Directory (DNS, DHCP, etc.) continue to operate.
For example, administrators can do an offline defragmentation of the
Active Directory database or apply security updates without needing to
restart the machine.
Database mounting tool
In previous versions of Active Directory, if an
object got deleted, an administrator had to load multiple online
backups until they found the object to restore. Windows Server 2008
Active Directory includes a database mounting tool (Dsamain.exe)
that makes it quicker and easier to find and restore specific data. The
tool supports online and Volume Shadow Copy Service (snapshot) backups.
2. Security Features Available for Domain Services
Two important security features are available for domain services in Windows Server 2008—RODCs and BitLocker Drive Encryption.
2.1. Read-Only Domain Controllers
As stated earlier, RODCs allow you to have a
non-editable copy of Active Directory in an area that may be a security
risk. RODCs hold an entire copy of Active Directory and the replication
traffic is unidirectional. Unidirectional replication means that other domain controllers can talk to an RODC but an RODC cannot talk to other domain controllers.
One advantage to having an RODC is that you can give
a normal user the administrator role for the RODC, and that user can do
any type of maintenance on it. The user does not need to be a domain
administrator; they are allowed to have the maintenance role for just
the one RODC. This concept is known as administrator role separation.
You can also load DNS on an RODC. This makes a
read-only copy of the DNS database. The downside to a read-only DNS
server is that it does not allow dynamic updates . The benefit is that you do not have to
worry about hackers or unauthorized domain users changing the DNS
database.
RODCs do not store account credentials. They allow
for authentication through credential caching, but not all accounts
have to be cached. You can decide which accounts to cache on an RODC by
using a password replication policy. This policy allows an administrator to determine which user groups will be allowed to use the RODC credential caching.
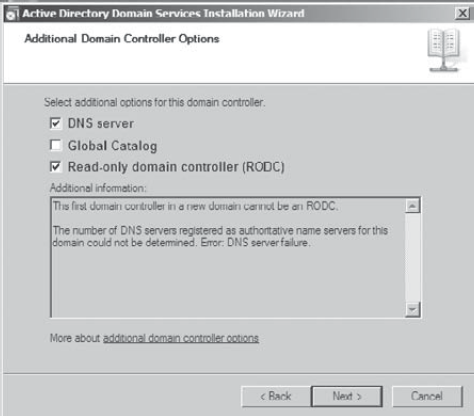
To install an RODC, use the dcpromo.exe application . In the Active Directory
Domain Services Installation Wizard, on the Additional Domain
Controller Options page, you check the box labeled Read-Only Domain
Controller (RODC) (see Figure 1).
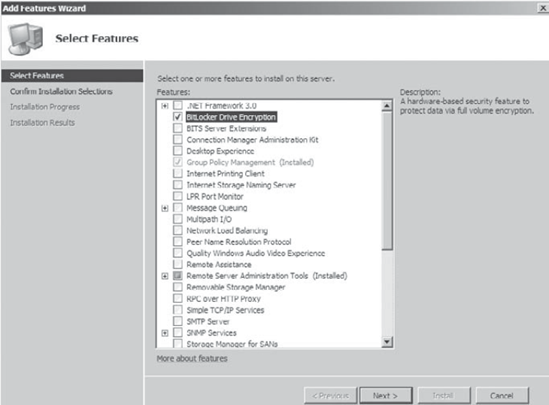
2.2. BitLocker Drive Encryption
Another way to add security in a non-secure location
is through the use of BitLocker Drive Encryption. The BitLocker
data-protection feature, new to Windows Server 2008, allows an IT
administrator to encrypt both the operating system volume and
additional data volumes within same server. However, BitLocker is not
installed by default. To install the BitLocker security, use Server
Manager (see Figure 2).