The Windows Firewall in Windows Server 2008 R2 is the same
basic firewall included in Windows 7 and adds many new features and
capabilities compared to the Windows Firewall included in previous versions. These
new features include outbound filtering; filtering based on SIDs; a
better management UI; configuration for local, remote, local port,
remote port, and protocol; and tight integration with IPsec. The other
big change is location-specific policies. There are three separate
firewall profiles: a domain profile, a private profile for
computers that aren’t domain members but are on secured networks, and
a public profile for computers that reside on publicly accessible
networks. And, finally, per-user rules are now supported. Although
these profiles aren’t terribly useful for the SBS server
itself, which uses only the Domain Profile, the same profiles are used
by Windows 7 and Windows Vista computers and can be enforced with
Group Policy.
In SBS, the Windows Firewall is on by default. All of the
wizards in SBS and Windows Server 2008 R2 that are used to add roles
and features will automatically set the necessary Windows Firewall
rule or rules to ensure proper functionality while still securing the
server.
SBS 2003 R2 had a built-in firewall, but most of the wizards
used to configure the server were not designed to configure the
firewall, and most environments had the Windows Firewall disabled on
servers, relying on an external firewall, or ISA 2004 on SBS Premium
servers, to protect the network. In SBS 2011, the expectation is that
the Windows Firewall remains enabled.
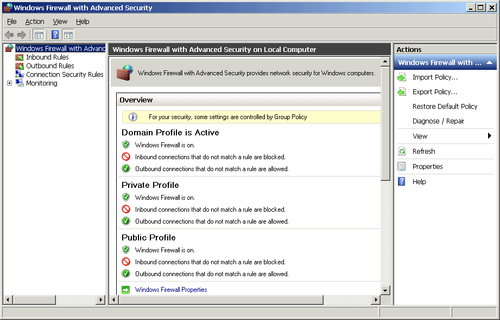
The Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Firewall allows more granular
control over the configuration and settings than previous versions. To
open the Windows Firewall With Advanced Security console, shown
in Figure 1, type
wf.msc at the command prompt, click Windows Firewall With
Advanced Security in the Administrative Tools folder, or open the
Firewall Settings in the Security page of the Windows SBS
Console.
Warning:
IMPORTANT SBS configures
the firewall automatically as part of the normal SBS wizards. You
should only make changes directly with extreme caution. Know not
only what problem you’re trying to solve, but why it isn’t
automatically handled by the SBS wizards. And be sure you understand
the security implications whenever you make a change.
Windows Firewall has three profiles: a Domain Profile, a Private Profile, and a Public Profile. Each profile can have different inbound
and outbound rules as needed. To build a specific rule, click Inbound
Rules or Outbound Rules and then click New Rule. Custom rules can be
set for programs or for ports. The SBS server uses only the Domain
Profile.
1. Setting Firewall Policies Using Group Policy
Use Group Policy to ensure a consistent application of
Windows Firewall policies across the domain. Use the built-in Windows Management
Instrumentation (WMI) filters of SBS Group Policy to set specific
policies for different types of clients and servers.
2. Firewall Rule Basics
When building Windows Firewall rules, there are three possible actions for a
connection that matches the rule:
The order of precedence for Windows Firewall rules is as follows:
Authenticated bypass
Block connection
Allow connection
Default profile behavior
This means that if you have a Block rule and an Allow rule,
and your connection meets both criteria, the block rule
will always win. By being as specific as possible with
your rules, you have less likelihood of conflict and more direct
control. Port rules are much more general than application rules and
should be avoided whenever possible.
2.1. Rule Definitions
Building rule definitions is the process of building a
combination of conditions and specific access types into a rule
that either allows or disallows a connection.
Rules can be defined for
Programs Specific
applications that are either allowed or disallowed by the
rule
Ports General allow or
disallow of a protocol through a port
Predefined Preconfigured
and well-known services and programs
Custom Can combine
programs, ports, and specific interfaces into a custom
rule
Rules can allow or disallow traffic to or from programs,
system services, computers, or users.
Rules can use protocol values of
Any
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) IP protocol
numbers
TCP
UDP
ICMPv4
ICMPv6
Others including IGMP, HOPOPT, GRE, IPv6-NoNxt,
IPV6-Opts, VRRP, PGM, L2TP, IPv6-Route, IPv6-Frag
Rules for local ports (UDP or TCP) can include
Rules for Remote Ports (TCP and UDP) can include
Rules for ICMP traffic (ICMPv4 and ICMPv6) can be
Rules can be for a Local IP address scope of
Specific IPv4 or v6 address or list of addresses
Range of IPv4 or v6 addresses or list of ranges
Entire IPv4 or v6 subnet or list of subnets
Rules can be for a remote IP address scope of
Specific IPv4 or v6 address or list of addresses
Range of IPv4 or v6 addresses or list of ranges
Entire IPv4 or v6 subnet or list of subnets
Predefined set of computers (local subnet, default
gateway, DNS servers, WINS servers, DNS servers or a list of
such items)
Rules can specify an interface type of
All interface types
Local area network
Remote access
Wireless
Rules can include program types of
Rules for services can
There are three predefined special local ports
Dynamic RPC is used by applications and services that
receive dynamic RPC traffic over TCP. (Does not include
traffic over named pipes.)
RPC Endpoint Mapper is used only with the RPCSS service
and allows traffic to the endpoint mapper.
Edge Traversal is used only with the iphlpsvc (Teredo)
service and allows the traffic to be decapsulated by the
Teredo service on a dynamic port.
Additional rules can be set to allow only secure
connections. For secure connections you can specify that the
connection
Warning:
Whenever
possible, resist the temptation to create specific Windows Firewall rules for specific computers or
users. Although it is technically possible, it can quickly
become a management and documentation nightmare. Use the SBS
security groups and OUs to control firewalls. This is flexible
and easy to maintain, and can be easily documented.