1. Blocking Inheritance
By default, GPO settings from GPOs at higher levels
are automatically inherited at lower levels. For example, each OU
automatically inherits all GPO settings set at the domain level. In
this context, each OU is a child of the domain. Similarly, children OUs
automatically inherit GPO settings from parent OUs; however, you can
block this behavior.
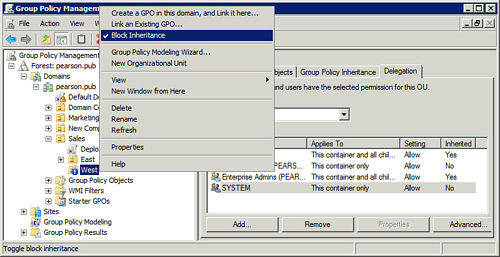
Figure 1 shows how to enable Block Inheritance for a child OU. The West OU is a child OU of the Sales OU. The exclamation icon next to the OU and the checkmark next to Block Inheritance show that Block Inheritance is enabled.
Note
You can set Block Inheritance on an OU but not on a GPO.
Tip
When Block Inheritance is selected, it blocks all GPOs with one exception. If a GPO from any parent is set to Enforced, the Enforced GPO is not blocked.
2. Enforcing GPOs
There are times when you want to ensure that
settings from a GPO take precedence no matter when they are applied.
For example, you might want to ensure that Group Policy settings set at
the domain level are not overwritten by settings at an OU level.
Similarly, you might want to ensure that GPOs are not blocked even if
an OU has Block Inheritance configured. You can do so by configuring Enforced on the GPO.
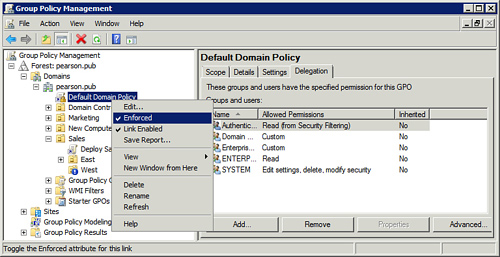
Figure 2 shows the setting as enforced for the Default Domain Policy.
Notice that the GPO has a lock icon indicating that it is enforced. Of
course, you can right-click it to see the checkmark next to Enforced.