When it comes to the actual installation of
Exchange 2007, an administrator can run setup manually or create an
unattended file so that the install can be automated for a branch
office with no onsite technical staff. There are also different
configurations of Exchange based on server roles such as Mailbox,
Client Access, Bridgehead, Unified Messaging, and Gateway. This section
covers the preinstallation tasks prior to installing the first typical
Exchange server in the environment.
There
are many changes in the Exchange 2007 setup program when compared to
Exchange 2003. These changes include the flexibility to install a
specific Exchange server role, prepare the AD schema and forest
automatically during the installation process as a single process, and
complete a more thorough health check on prerequisites such as AD.
Performing an Active Directory Health Check
If
AD is not being set up from scratch, it is beneficial to validate that
the existing AD environment is functioning correctly. Because Exchange
requires AD as a prerequisite, an administrator should conduct an
extensive health check on the directory structure with tools such as
DCDIAG, NETDIAG, and Replication Monitor to identify any anomalies that
will impact the installation of Exchange Server 2007. The Windows
Server 2003 support tools are required to conduct these tasks.
Alternatively,
the Exchange Server 2007 Installation Wizard also conducts a minor
health check automatically as a prerequisite task when installing
Exchange Server 2007. If an extensive AD health check is required, this
must be conducted manually as a separate task.
Tip
To
access the Windows Server 2003 support tools, install them from the
Windows Server 2003 CD. Go to the original CD, select Support, Tools,
and run the Suptools.msi installer, which installs the Windows Server 2003 support utilities into the \Program Files\Support Tools\ directory. It is also possible to download the latest support tools from the Microsoft website.
Preparing the Active Directory Domain and Forest
In
Exchange 2000 Server and Exchange Server 2003, it was necessary to run
two separate processes to prepare the forest and the domain before the
installation of Exchange. The first process was extending the AD schema
with ForestPrep and the second process was preparing all the domains
with DomainPrep.
With Exchange Server
2007, these prerequisite processes are eliminated and it is possible to
prepare both the forest and domain as part of the Exchange Server 2007
installation. During the installation, a new process, ADprep,
executes to prepare both the forest and domain with the appropriate
changes. Alternatively, the AD preparation can be conducted manually,
before the installation of Exchange similar to Exchange 2000 or 2003.
Preparing AD includes the following tasks:
Extending the AD schema
Creating the Exchange organization in AD
Creating the Microsoft Exchange System Objects container for the domain
Creating
the following Universal Security groups (USGs) for Exchange; Exchange
Organization Administrators, Exchange Mailbox Administrators, Exchange
ReadOnly Administrators, and Exchange Servers Group
Setting
the appropriate permissions on the global Exchange configuration
container, the Microsoft Exchange System Objects container, and the
Universal Security groups
To prepare AD for Exchange Server 2007 manually, use the following steps preferably on the Schema Master:
1. | Insert the Exchange Server 2007 CD or DVD (Standard or Enterprise).
|
2. | From the Start menu, select Run. Then type [CDDrive]:\setup.exe /prepareAD, and click OK.
|
Note
It
is easier to allow the Exchange Server Installation Wizard to prepare
the AD environment automatically. However, there might be a need to
conduct this task separately as a manual process. In addition, it is
common that a different AD administrator might conduct this task
because the Exchange administrator might not be a member of the
Enterprise and Schema Admins group, and a member of the local
Administrators group of that server.
Raising the Domain Functional Levels
To bring a Windows Server 2003 domain to Windows Server 2003 functional levels, perform the following steps:
1. | Ensure that all domain controllers in the forest are upgraded to Windows 2000 Server or Windows Server 2003.
|
2. | From the first domain controller, open AD Domains and Trusts from the Administrative Tools menu.
|
3. | In the left scope pane, right-click on the domain name, and then click Raise Domain Functional Level.
|
4. | On the Raise Domain Functional Level screen, shown in Figure 1, select Windows Server 2003, and then click Raise.
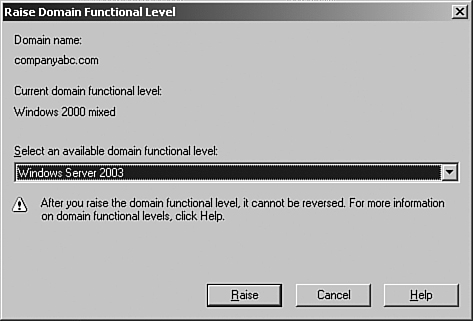
|
5. | Click OK and then click OK again to complete the task.
|
Reviewing All Log Files Before Proceeding
Each
of the utilities that have been executed has some form of output in its
respective log files. Review the log file after running each utility to
ensure no errors are encountered.