An index is a list
of significant terms or phrases that appear in a document, along with
the number of each page where the item appears. If you’re writing for a
specialized audience and your document contains a lot of key terms,
your readers will appreciate having an index.
Adding an Index to a Document
Indexing
is a time-consuming task, but Word makes it a simple one. To add a term
or phrase to an index, you mark the text (called an entry)
with a special code. When you’re done marking items, Word can compile
the index at your command. Of course, indexing can be a much more
complicated process, depending on how detailed you want the index to
be. Here, we’ll just hit the high spots to introduce you to the basics
of indexing.
Marking an Index Entry
You have to mark each word or phrase that you want to include in the index. Here’s how:
1. | Select a word or phrase.
|
2. | On the References tab, click Mark Entry. The Mark Index Entry dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 1. The selected text appears in the Main Entry text box.
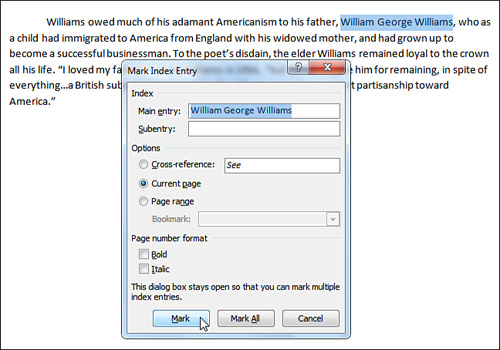
|
3. | To
add a subentry to the item, click the Subentry box and type a word or
short phrase that puts the main entry into some context. For example,
if your document
includes information about butterflies and their feeding habits, your
main entry might be “Monarch” and the subentry might be “Favorite
snacks.” |
4. | Do one of the following:
- Click Mark to mark the selected text.
- Click Mark All to mark every occurrence of the selected text in the document.
Either way, the Mark Index Entry dialog box remains open, so you can
continue marking entries. You can click outside the dialog box to
select other pieces of text in the document; then click the dialog box
to edit the entry. After you mark your first entry, the Cancel button
changes to a Close button. |
5. | When you are finished marking index entries, click Close.
|
When you mark an index entry, Word automatically
displays nonprinting characters, such as paragraph marks and tabs. This
enables you to see the actual indexing codes as they are added to the
text.