Although a Windows Server 2008 computer can
be used by itself without connecting to a network, you will not harness
much of the potential of the operating system without network
connectivity. Because the fundamental purpose of a network operating
system is to provide resources to users, you must verify network
connectivity.
1. Basic Connectivity Tests
Before you begin to install Active Directory, you
should perform several checks of your current configuration to ensure
that the server is configured properly on the network. You should test
the following:
Network adapter
At least one network adapter should be installed
and properly configured on your server. A quick way to verify that a
network adapter is properly installed is to use the Computer Management
administrative tool. Under Device Manager, Network Adapters branch, you
should have at least one network adapter listed. If you do not, use the
Add Hardware icon in the Control Panel to configure hardware.
TCP/IP
Make sure TCP/IP is installed, configured, and
enabled on any necessary network adapters. The server should also be
given a valid IP address and subnet mask. Optionally, you may need to
configure a default gateway, DNS servers, WINS servers, and other
network settings. If you are using DHCP, be sure that the assigned
information is correct. It is always a good idea to use a static IP
address for servers because IP address changes can cause network
connectivity problems if they are not handled properly.
NOTE
You must understand TCP/IP to use Windows Server 2008 and Active Directory. See MCTS: Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Study Guide (70-642), First Edition (Sybex, 2008) to learn more about TCP/IP.
Internet access
If the server should have access to the
Internet, verify that it is able to connect to external web servers and
other machines outside the large area network (LAN). If the server is
unable to connect, you might have a problem with the TCP/IP
configuration.
LAN access
The server should be able to view other servers
and workstations on the network. You can quickly verify this type of
connectivity by clicking Start => Network. If other machines are not visible, ensure that the network and TCP/IP configuration are correct for your environment.
Client access
Network client computers should be able to
connect to your server and view any shared resources. A simple way to
test connectivity is to create a share and test whether other machines
are able to see files and folders within it. If clients cannot access
the machine, ensure that both the client and server are configured
properly.
Wide area network (WAN) access
If you're working in a distributed environment,
you should ensure that you have access to any remote sites or users
that will need to connect to this machine. Usually, this is a simple
test that can be performed by a network administrator.
2. Tools and Techniques for Testing Network Configuration
In some cases, verifying network access can be quite
simple. You might have some internal and external network resources
with which to test. In other cases, it might be more complicated. You
can use several tools and techniques to verify that your network
configuration is correct:
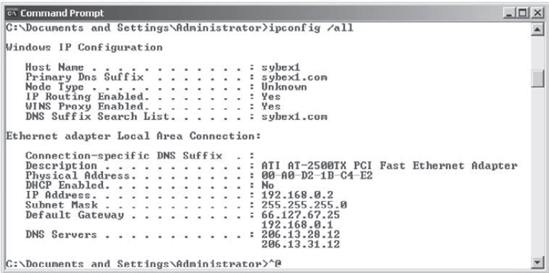
Using the ipconfig utility
By typing ipconfig/all at the command prompt, you can view information about the TCP/IP settings of a computer. Figure 1 shows the types of information you'll receive.
Using the ping
command
The ping command was designed to test connectivity to other computers. You can use the command by simply typing ping and then an IP address or hostname at the command line. The following are some steps for testing connectivity using the ping command.
Ping other computers on the same subnet.
You should start by pinging a known active IP
address on the network to check for a response. If you receive one,
then you have connectivity to the network.
Next, check to see if you can ping another machine using its hostname. If this works, then local name resolution works properly.
Ping computers on different subnets.
In order to ensure that routing is set up
properly, you should attempt to ping computers that are local on other
subnets (if any exist) on your network. If this test fails, try pinging
the default gateway. Any errors may indicate a problem in the network
configuration or a problem with a router.
NOTE
Some firewalls, routers, or servers on your
network or on the Internet might prevent you from receiving a
successful response from a ping command. This is usually for
security reasons (malicious users might attempt to disrupt network
traffic using excessive pings as well as redirects and smurf attacks).
If you do not receive a response, do not assume that the service is not
available. Instead, try to verify connectivity in other ways. For
example, you can use the TRACERT command to demonstrate
connectivity beyond your subnet, even if other routers ignore Internet
Control Message Protocol (ICMP) responses. Since the display of a
second router implies connectivity, the path to an ultimate destination
shows success even if it does not display the actual names and
addresses.
Browsing the network
To ensure that you have access to other computers on the network, be sure that they can be viewed by clicking Start =>
Network. This verifies that your name resolution parameters are set up
correctly and that other computers are accessible. Also, try connecting
to resources (such as file shares or printers) on other machines.
Browsing the Internet
You can quickly verify whether your server has access to the Internet by visiting a known website, such as www.microsoft.com.
Success ensures that you have access outside of your network. If you do
not have access to the Web, you might need to verify your proxy server
settings (if applicable) and your DNS server settings.
By performing these simple tests, you can
ensure that you have a properly configured network connection and that
other network resources are available.