1. Getting to Know Task Manager
Task Manager is a program that lets you view and
manage running programs and processes, as well as view performance data
for your computer and network. You can start Task Manager in several
ways:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and click Start Task Manager.
Right-click the clock or an empty spot on the taskbar and choose Start Task Manager.
Click Start and enter taskmgr.
|
If a program is hung (frozen), right-clicking the
taskbar might not work. But pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del might still work. If
Ctrl+Alt+Del doesn't work to bring up the Task Manager and the computer
is unresponsive, cycling power on the computer is generally the only way
to get it going again.
|
|
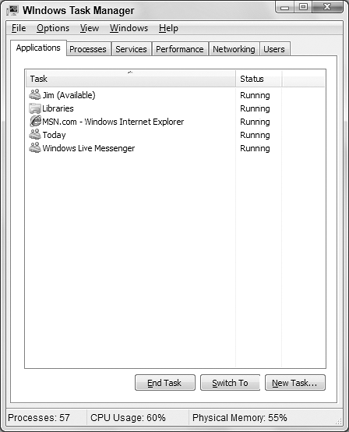
Figure 1
shows the Task Manager. It behaves much like any program window. It has
a button on the Windows taskbar when open. You can drag the program
window around by its title bar. Size it by dragging any corner or edge.
You can also configure it so it stays on the top of the stack of open
windows so you can always see it. You can change that by choosing
Options => Always On Top from its menu.
|
Regardless of how you start Task Manager, when it opens Task Manager displays whichever tab was open when it was last run.
|
|
Task Manager also has a mini-mode where the title bar, menu bar, and tabs are hidden, as in Figure 44-2.
When you're in that mode, double-click the empty space inside the
window border (such as to the left of the End Task button) to go to the
normal mode. Double-click that same area, or to the right of the tabs,
in the normal mode to go to mini-mode.
|
If you don't want Task Manager to show up on the Windows taskbar, click Options => Hide When Minimized. |
2. Choosing Task Manager Views
You can view and use Task Manager in several ways. On the Options menu in the menu bar, you have the following options:
Always On Top:
Choosing this option ensures that Task Manager is always on the top of
the stack when it's open, so no other program windows can cover it.
Minimize On Use:
If selected, this option just minimizes Task Manager whenever you
choose the Switch To option to switch to another running program.
Hide When Minimized:
Normally when you minimize Task Manager, only its taskbar button
remains visible. Choosing this option also hides the taskbar button when
you minimize Task Manager.
Whenever Task Manager is open, you'll see a small
green square in the Notification area unless Task Manager is configured
to show notifications only. Pointing to that icon displays the current
CPU (processor) usage, as shown in Figure 3. When Task Manager is minimized, you can double-click that little square to bring Task Manager back onto the desktop.
If you prefer to have Task Manager show only
notifications and remove it from the tray, click the Show Hidden Icons
button on the tray and choose Customize. In the Notification Area Icons
applet, find Windows Task Manager in the Icons list, choose Only Show
Notifications from the drop-down list, and click OK.
On the View menu in Task Manager, you have the following choices:
Refresh Now: Causes Task Manager to refresh all of its data immediately, regardless of the Update Speed setting.
Update Speed:
Task Manager needs to use some computer resources to keep itself up to
date with what's happening in the system at the moment. The Update Speed
option lets you choose how often Task Manager updates itself as
follows:
High: Updates Task Manager twice per second.
Normal: Updates Task Manager every two seconds.
Low: Updates Task Manager every four seconds.
Paused: Updates Task Manager only when you choose View => Refresh Now.