1. Understanding CDs and DVDs
Even though CDs and DVDs look exactly alike, there's
a big difference in capacity. A CD holds about 650–700 MB of data. A
DVD holds about 4.7 GB (or about 4,700 MB). In other words, one DVD can
hold more information than six CDs. This is also why albums are sold on
CDs and movies on DVDs — there isn't enough room on a CD to store a
feature-length movie.
The newest media type, Blu-ray, has the same
physical dimensions as CDs and standard DVDs, but uses a blue-violet
laser that has a shorter wavelength than the red laser used on older
formats. This shorter wavelength makes it possible for Blu-ray media to
hold up to 50 GB (using dual-layer media). Because of its higher
capacity, Blu-ray offers better image quality for movies than standard
DVD. However, you must have a Blu-ray drive to play Blu-ray media.
To complicate matters, many different kinds of CDs
and DVDs are available, including CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R, DVD-RW,
DVD+R, DVD+RW, and DVD-RAM. So let's untangle that mess, starting with
the most common types of disks — the CD-ROM and DVD-ROM.
|
CD and DVD drives have a top speed, indicated by an
"x" number, such as 52x. This is the top burn speed, measured as a
factor of the playback speed (which is 1x). Generally, the speed is
irrelevant unless you are burning a lot of CDs or DVDs and need to
reduce the amount of time it takes. If that's the case, buy a
high-speed drive and blank media that has an equivalent or higher
maximum burn rate.
|
|
1.1. CD-ROM and DVD-ROM
The ROM in CD-ROM and DVD-ROM stands for read-only memory. The term "read only" means you can read (or play) the contents of the disk whenever you want. The disk is not writable. You can't add new files to the disk, remove files from the disk, or change files that are already on the disk.
1.2. CD-R, DVD-R, and DVD+R
The R in CD-R, DVD-R, and DVD+R stands for recordable. These are often referred to as distribution media
because they're the blank disks that software companies, record
companies, and the movie industry use to stamp out thousands of copies
of the programs, albums, and movies they sell. In other words, they buy
-R disks to create the -ROM disks that they sell you.
1.3. CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW
The RW in CD-RW, DVD-RW, and DVD+RW stands for read/write. The -RW disks are often called backup media.
You can use a CD-RW, DVD-RW, or DVD+RW disk to back up important files.
You can erase the disk and start over if you like, and you can delete
individual files. In short, the -RW disks are much more like hard
disks, just not as fast!
1.4. Data CD versus audio CD
CDs come in two capacities, commonly referred to as data CDs and audio CDs.
A data CD has a capacity of about 650 MB, or enough space to store
about 74 minutes worth of music. Those are best to use when your goal
is to use the CD to store backup copies of files on your hard disk, or
to distribute copies of files to other people.
An audio CD has a capacity of about 700 MB, or
enough space to store about 80 minutes worth of music. Those are best
to use when you want to create your own custom music CDs to play in
your car stereo or in a CD player.
1.5. DVD- versus DVD+
There are two DVD standards to consider, although
the differences have little to do with DVDs as used in computers.
They're more subtle differences having to do with how DVDs store data
for watching movies on TV. So for the average computer user, choosing
between a + and — DVD is largely a matter of knowing what works with
your DVD player, DVD burner, and whatever other equipment you have.
NOTE
The only way to find out which types of disks
your DVD equipment can handle is from the documentation for that
specific equipment. As a rule, the DVD+ disks are compatible with more
DVD players than the DVD-R disks.
The only difference between a "disk" and a
"disc" is the spelling. Computer people usually spell it "disk." The
people who invented CDs and DVDs decided to spell it "disc." But no
matter how you spell it, it's a medium on which you can store
information. I'll use "disc" in places you're likely to see it spelled
that way.
2. What Kind of Drive Do I Have?
If you just purchased a new computer, you might not
be sure what type of drive you have. Getting information about your
CD/DVD drive isn't difficult. You can get some information right from
your Computer folder. First make sure there isn't a disk in the drive.
Then open your Computer folder and take a look at the icon for the
empty drive. The icon and description should provide some clues. To get
more information, you can right-click that icon, choose Properties, and
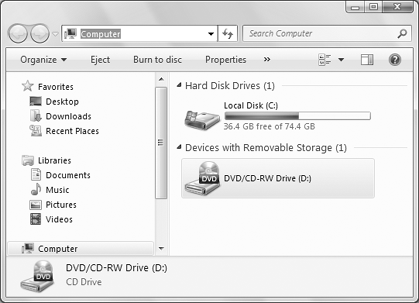
click the Hardware tab for more specific information. For example, in Figure 1, drive D: is a DVD/CD-RW drive.
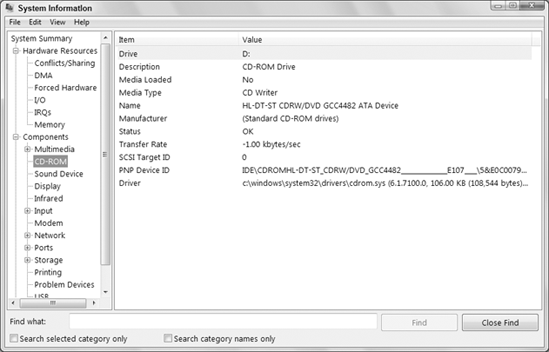
There's also a System Information window you can use to get specs on your system. Click the Start button, type sys,
and click System Information on the Start menu. In the window that
opens, click the + sign (if any) next to Components and click CD-ROM.
The pane to the right shows detailed information about the drive as in
the example shown in Figure 2.
Unfortunately, knowing the make and model of the
drive doesn't tell you all the different types of disks it can handle.
For instance, the Hitachi drive shown previously can read and write
virtually all CD and DVD disk types, but there's no indication of that
in either figure. After you know the make and model of the drive, you
can search the manufacturer's Web site for the model number for more
detailed specs. Or you can use a general search engine like Google or
Bing to search for both the make and model name (HL-DT-ST in my example).
Of course, there's always the old-fashioned
method of calling your computer manufacturer on the phone, or
contacting them by e-mail, and asking about the drive. At the very
least, you'll need to know the model of your computer. Then ask them
what kinds of disks the drive can handle.