3. List Column Indexing
SharePoint 2010 allows you to create unique
columns. Unique columns are indexed and help run queries faster. In any
list, you can add a column and choose to make it unique. When making it
unique, SharePoint will ask you if you would like to make the column
index simple as well. A unique column has to be made indexable, as
shown in Figure 1.
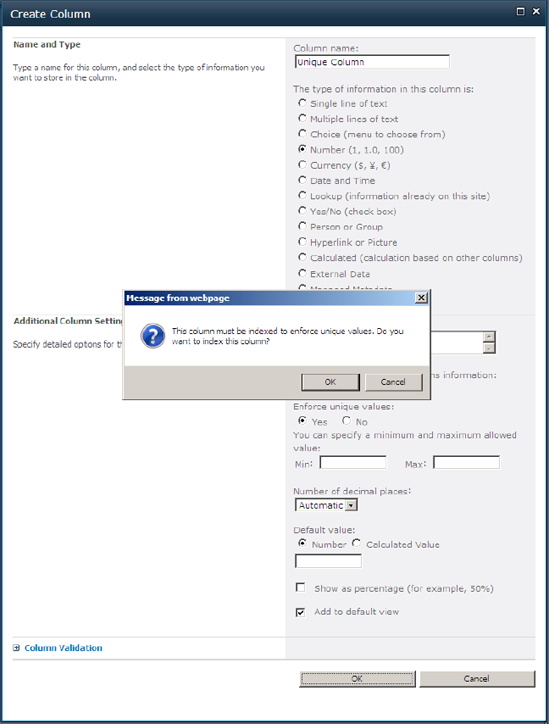
You can choose to make a column not indexed at a
later date, but before you remove a column from being indexed you have
to remove its uniqueness first. You also have the ability to create
indexes that use multiple columns. In order to do so, go to List
Settings and click the indexed columns link under the "Columns"
section. On this page, specifically at
_layouts/IndexedColumns.aspx?List=<<listGUID>>, you should
be able to see all the existing indices on the list. There is a maximum
of 20 indices you could create on any particular list. Also from here
you can click the Create a new index link, and choose to create an
index that uses a primary column and a secondary column. Do note that
not all sorts of columns can be used for indexing purposes.
Specifically, the following types of columns are allowed for indexing
purposes:
Single line of text
Choice field, but not multichoice
Number
Currency
Date/time
Look up, but not a multivalue look up
Person or group, but not multivalue
Title, except in a document library
Also it is important to note that uniqueness and
indexing are case insensitive. While indexing will make queries faster,
it will also increase the size of your database, and it does not help
the inserts and updates on any particular list. Also while indexing can
help speed up queries, they are still numerous facilities available in
SharePoint 2010 that allow the administrator to police what queries can
be run. This is commonly referred to as list throttling.
4. List Throttling
List throttling in SharePoint 2010 has been designed
to give IT administrators a tool to manage and police their servers.
Using the list throttling capabilities built inside of SharePoint 2010,
IT administrators can define some maximum limits at the web application
level. Using list throttling, you can configure and control the number
of items fetched as a result of a query. There are warning levels,
different levels for administrators, and the ability to configure time
windows for expensive queries or the ability to request throttle
overrides in the object model. Also, the administrators can choose to
block all possible throttle overrides on a per-web application limit.
Let's use a real example. Go ahead and write some code in a SharePoint console application, as shown in Listing 1. Do note that a SharePoint console app is slightly different from a regular console app .
Example 1. Sample Code for Checking Web Application Level List Throttling Settings
using (SPSite site = new SPSite(siteUrl))
{
Console.WriteLine("MaxItemsPerThrottledOperation:{0}",
site.WebApplication.MaxItemsPerThrottledOperation);
Console.WriteLine("MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationOverride:{0}",
site.WebApplication.MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationOverride);
Console.WriteLine("MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationWarningLevel:{0}",
site.WebApplication.MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationWarningLevel);
}
|
In Listing 1,
queries for various properties are available on the web application. If
you run the previous console application, you should see the following
output:
MaxItemsPerThrottledOperation:5000
MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationOverride:20000
MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationWarningLevel:3000
This output has three components. What
MaxItemsPerThrottledOperationWarningLevel is telling you is that you
will be given a warning on the list settings page if a list has more
than 3000 items in it, and the list is throttled. This warning can be
seen on the list settings page shown in Figure 2.

In order to enable throttling on any particular list, you have to set the SPList.EnableThrottling property to "true".
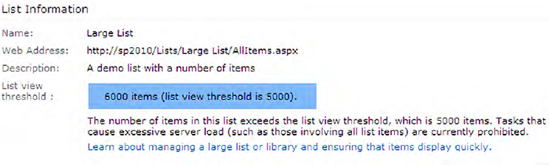
MaxItemsPerThrottledOperation tells you that if the
list contains 5,000 to 20,000 items, and if the administrator queries
the list, the administrator will be given all the lists items
requested. However the administrator will be shown a warning on the
list settings page, telling the administrator that even though his
query was successful, nonadministrative users will not be able to query
more than 5,000 items. This warning can be seen in Figure 3.
This is great, but in certain instances you want
throttling to be disabled. For instance, you may have a legitimate need
to query for all items in the list. Such querying can be done in off
hours, and that time window can be set by using the
SetDailyUnthrottledPrivilegedOperationWindow method on the
WebApplication Object. Also, such a time window can be disabled or
enabled by setting the UnthrottledPrivilegeOperationWindowEnabled
property on the WebApplication object.
What if you want to execute an expensive query
during business hours? You can do so in code by using the
SPQuery.RequestThrottleOverride and
SPSiteDataQuery.RequestThrottleOverride methods. Also, the IT
administrator can globally disable all such override requests at the
WebApplication level by using the
WebApplication.AllowOMCodeOverrideThrottleSettings property.
Yet another important property on the
SPWebApplication object is the MaxQueryLookupFields property. The total number
of joins in a single query cannot exceed the value of the
MaxQueryLookupFields defined on a web application. The default value of
MaxQueryLookupFields is 8.