Setting up proper file and folder security is one of
the most important tasks that an IT professional can perform. If
permissions and security are not properly configured, users will be able
to access resources that they shouldn't.
File and folder
security defines what access a user has to local resources. You can
limit access by applying security for files and folders. You should know
what NTFS security permissions are and how they are applied.
A powerful feature of
networking is the ability to allow network access to local folders. In
Windows 7, it is very easy to share folders. You can also apply security
to shared folders in a manner that is similar to applying NTFS
permissions. Once you share a folder, users with appropriate access
rights can access the folders through a variety of methods.
Before diving into the security section of folders, let's first take a look at some folder options.
1. Folder Options
The Windows 7 Folder Options
dialog box allows you to configure many properties associated with
files and folders, such as what you see when you access folders and how
Windows searches through files and folders. To open the Folder Options
dialog box, click Start =>
Computer, then select Folder And Search Options under the Organize
drop-down list. You can also access Folder Options through its icon by
choosing Control Panel => Large Icons View =>
Folder Options. The Folder Options dialog box has three tabs: General,
View, and Search. The options on each of these tabs are described in the
following sections.
1.1. Folder General Options
The General tab of the Folder Options dialog box, shown in Figure 1, includes the following options:
Whether folders are opened all in the same window when a user is browsing folders or each folder is opened in a separate window
Whether a user opens items with a single mouse click or a double-click
Whether to have the navigation pane show all folders and automatically expand to the current folder

1.2. Folder View Options
The options on the View tab of the Folder Options dialog box, shown in Figure 2,
are used to configure what users see when they open files and folders.
For example, you can change the default setting so that hidden files and
folders are displayed. Table 1 describes the View tab options.
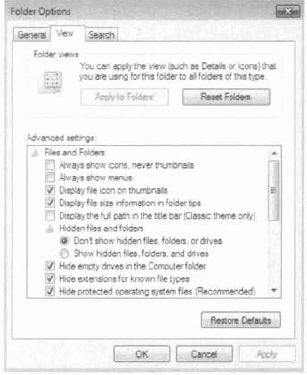
Table 1. Folder view options
| Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|
| Always Show Icons, Never Thumbnails | Shows icons for files instead of thumbnail previews. | Not selected |
| Always Show Menus | Shows the File, Edit, View, Tools, and Help menus when you're browsing for files. | Not selected |
| Display File Icon On Thumbnails | Displays the file icon on thumbnails. | Enabled |
| Display File Size Information In Folder Tips | Specifies whether the file size is automatically displayed when you hover your mouse over a folder. | Enabled |
| Display the Full Path In The Title Bar (Classic Theme Only) | Specifies
whether the title bar shows an abbreviated path of your location.
Enabling this option displays the full path, as opposedto showing an abbreviated path . | Not selected |
| Hidden Files And Folders | Specifies
whether files and folders with the Hidden attribute are listed.
Choosing Show Hidden Files, Folders, Or Drives displays these items. | Don't Show Hidden Files, Folders, And Drives |
| Hide Empty Drives In The Computer Folder | This option will prevent drives that are empty in the Computer folder from being displayed. | Enabled |
| Hide Extensions For Known File Types | By default, filename extensions, which identify known file types (such as .doc for Word files and .xls for Excel files) are not shown. Disabling this option displays all filename extensions. | Enabled |
| Hide Protected Operating System Files (Recommended) | By
default, operating system files are not shown, which protects operating
system files from being modified or deleted by a user. Disabling this
option displays the operating system files. | Enabled |
| Launch Folder Windows In A Separate Process | By
default, when you open a folder, it shares memory with the previous
folders that were opened. Enabling this option opens folders in separate
parts of memory, which increases the stability of Windows 7 but can
slightly decrease the performance of the computer. | Not selected |
| Show Drive Letters | Specifies
whether drive letters are shown in the Computer folder. When disabled,
only the name of the disk or device will be shown. | Enabled |
| Show Encrypted Or Compressed NTFS Files In Color | Displays encrypted or compressed files in an alternate color when they are displayed in a folder window. | Enabled |
| Show Pop-Up Description For Folder And Desktop Items | Displays whether a pop-up tooltip is displayed when you hover your mouse over files and folders. | Enabled |
| Show Preview Handlers In Preview Pane | Shows the contents of files in the preview pane. | Enabled |
| Use Check Boxes To Select Items | Adds
a check box next to each file and folder so that one or more of them
may be selected. Actions can then be performed on selected items. | Not selected |
| Use Sharing Wizard (Recommended) | This option allows you to share a folder using a simplified sharing method. | Enabled |
| When Typing Into List View | Selects whether text is automatically typed into the search box or whether the typed item is selected in the view. | Select The Typed Item In The View |
1.3. Search Options
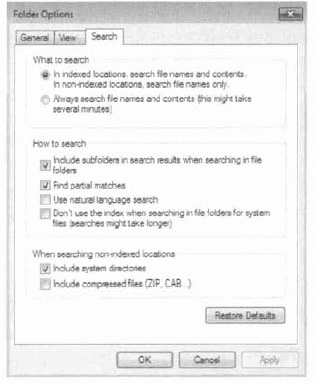
The Search tab of the Folder Options dialog box, shown in Figure 3,
is used to configure how Windows 7 searches for files. You can choose
for Windows 7 to search by filename only, by filenames and contents, or
by a combination of the two, depending on whether indexing is enabled.
You can also select from the following options:
Include subfolders
Find partial matches
Use natural language searches
Don't use the index when searching the file system
Include system directories in non-indexed locations
Include compressed files in non-indexed locations
To search for files and folders, click Start => Search and type your query in the search box. In the next section, we will look at how to secure these folders and files.
2. Securing Access to Files and Folders
On NTFS partitions, you can
specify the access each user has to specific folders or files on the
partition based on the user's logon name and group associations. Access
control consists of rights and permissions. A right (also referred to as
a privilege) is an authorization to perform a specific action.
Permissions are
authorizations to perform specific operations on specific objects. The
owner of an object or any user who has the necessary rights to modify
permissions can apply permissions to NTFS objects. If permissions are
not explicitly granted within NTFS, then they are implicitly denied.
Permissions can also be explicitly denied, which then overrides
explicitly granted permissions.
The following sections
describe design goals for access control as well as how to apply NTFS
permissions and some techniques for optimizing local access. Let's take a
look at design goals for setting up security.