In Windows 7, the command prompt is the place where you can execute command-line instructions. Most of the commands are the old standard MS-DOS
commands, some are enhancements of the MS-DOS commands, and others are
commands unique to Windows 7. When you need to work from the command
prompt, you can open a command-prompt
window and execute all your tasks there, including using the basic
commands, starting a program, and even starting a program in a new
window. Note that the command prompt is a powerful weapon that can
disrupt your system, delete files, and create general havoc. Don't
execute commands unless you know what they're designed for.
1. Run a Command
Open a command-prompt window by choosing Command Prompt from the Accessories folder of the Start menu.
At the prompt, type a command, including any switches and extra parameters, and press Enter.
Enter any additional commands you want to run.

1.1. The Top 10 Command-Prompt Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|
| cd | Switches to the specified folder (or directory). |
| cls | Clears the screen. |
| copy | Copies the specified files or folders. |
| dir | Shows the contents of the current directory. |
| exit | Ends the session. |
| ipconfig | Displays network connection information. |
| ping | Tests network connection using IP address. |
| path | Displays or sets the path the command searches. |
| prompt | Changes the information displayed at the prompt. |
| rename | Renames the specified file or files if the wildcard characters ? or * are used. |
Tip:
Many commands have switches that allow the use
of extra parameters, giving you greater control of the command. A switch
is the part of the command with the forward slash (/) followed by a
letter, a number, or some other instruction. A parameter is an
additional instruction you provide, such as the file name or the drive
letter.
2. Find a Command
At the command prompt, type help and press Enter.
Review the list of commands.
If the information scrolls off the screen, use the scroll bar or the scroll arrows so that you can see the entire list.
Tip:
To change some of the settings for the Command Prompt window—the
font, the cursor size, or the colors, for example—right-click the
window's title bar, and choose Properties from the shortcut menu.
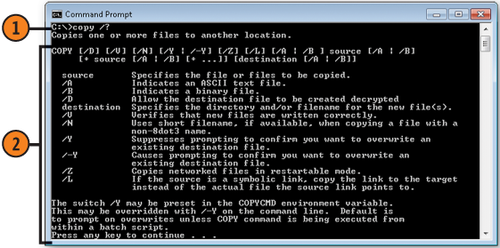
3. Get Information About a Command
Type a command followed by a space and /? and then press Enter to get information about the command.

Note:
Try This!
At the command prompt, type help > dosref.txt and press Enter. Use Notepad or WordPad to open the file dosref.txt
that's stored on your hard disk (it's the folder that was active when
you typed the command). The > symbol redirected the output from the
screen to the file. You now have a reference for the commands, which you can easily print out.