12. Changing Advanced Settings
The default settings for DFS Management are appropriate for
most installations, but if you need to change advanced namespace
settings such as the referral order, change how namespace servers
poll domain controllers for DFS metadata, or delegate DFS Management
permissions, use the information in the following sections.
12.1. Changing Namespace Referral Settings
To change the cache duration, the order in which domain
controllers or namespace servers refer clients to namespace
servers and folder targets, or the failback settings for an entire namespace,
right-click a namespace root or folder, choose Properties, and
click the Referrals tab. (See Figure 6.)
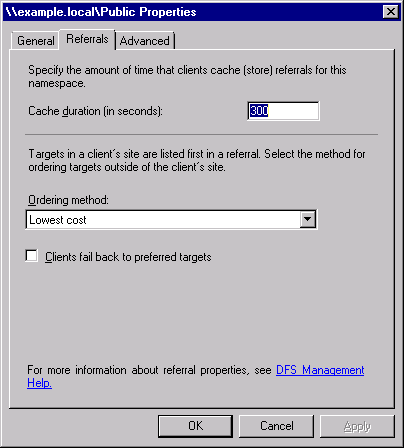
Use the following list to complete the process:
In the Cache Duration box, specify how long clients
should cache referrals before polling the domain controller or
namespace server for a new referral. In the Ordering Method drop-down box, choose how domain
controllers and namespace servers should refer clients to
folder targets and namespace servers. Select the Clients Fail Back To Preferred Targets option
to force a client to switch back to using its preferred server
when it comes back online.
The preferred server is based on site and any custom
referral ordering settings you specify on folder targets. This
setting is supported by clients running Windows XP with Service
Pack 2 (SP2) and the post-SP2 Windows XP client failback hotfix, Windows Server 2003 with Service
Pack 1 and the Windows Server 2003 client failback hotfix, and
Windows Server 2003 R2. See Knowledge Base article 898900 at
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/898900for
information on how to obtain this hotfix.
12.2. Overriding Referral Settings on Individual Folders
DFS folders inherit referral settings from the namespace
root unless you specifically override them. To override the
referral settings for a folder, right-click the appropriate
folder, choose Properties, click the Referrals tab, and then
specify the settings you want to override.
To explicitly set a single folder target as the preferred
target or set the folder target as a target of last resort,
right-click the folder target, choose Properties, click the
Advanced tab, select the Override Referral Ordering check box, and
then specify the priority for the target folder.
12.3. Delegating Management Permissions
DFS Management sets the permissions on the namespace object
in Active Directory or in the registry of the namespace server
(when using a stand-alone namespace). To change the ability of
users to perform common management tasks, use the following
list:
Create and manage
namespaces To view, add, or remove groups that can
manage namespaces, right-click the Namespaces node, choose
Delegate Management Permissions, and then use the Delegate
Management Permissions dialog box. Manage individual namespaces and
replication groups To view groups that can manage a
namespace or replication group, select the namespace or
replication group, and then click the Delegation tab. To
remove management permissions for a group, right-click the
group and choose Remove. To give management permissions for
the namespace to a group, right-click the namespace, choose
Delegate Management Permission, type the name of the group in
the Select Users Or Groups dialog box, and then click
OK. Create and manage replication
groups To view, add, or remove groups that can manage
replication, right-click the Replication node, choose Delegate
Management Permissions, and then use the Delegate
Management Permissions dialog box.
12.4. Changing Namespace Polling Settings
To change how namespace servers poll domain controllers for
the latest namespace metadata in a domain-based namespace,
right-click the appropriate namespace, choose Properties, click
the Advanced tab, and then choose one of the following polling
methods:
Optimize For Consistency
Polls the primary domain controller (PDC) emulator for new
namespace polls data every hour and after each change to the
namespace. Use this setting when the network contains 16 or
fewer namespace servers to minimize the time it takes to
propagate namespace changes to all namespace servers. This is
the default setting. Optimize For Scalability
Polls the nearest domain controller every hour for changes to
the namespace. Use this setting when the network contains more
than 16 namespace servers to reduce the load on the PDC
emulator. However, choosing this setting increases the amount
of time it takes to propagate namespace changes to all
namespace servers. Servers running Windows 2000 Server do not
support this setting and continue to use the Optimize For
Consistency polling method.
To enable the Optimize For Scalability polling method from a
command prompt, use the Dfsutil /Rootscalability command. For example, open the
Command Prompt window, change to the directory in which you placed
the Dfsutil.exe file, and then type Dfsutil
/Root:Example.local\Public /Rootscalability
/Enable.
13. Backing Up and Restoring the DFS Folder Targets
The DFS Namespaces database for domain-based DFS is stored in
Active Directory, and you can back it up and restore it using Active
Directory–aware backup methods. To back up the listing of folder targets for a stand-alone namespace root, type
the following text at a command prompt (replacing
ServerName and Namespace
with the name of the appropriate server name and namespace
root):
DFScmd /View \\ServerName\Namespace /Batch
>DFS_backup.bat
To restore this DFS structure, re-create the DFS namespace and
then run the batch file you created.
Note:
In addition to backing up the DFS topology, back up the
contents of the actual file shares routinely. Always test the
backup before relying on it. You can use the Dfsradmin
Replicationgroup command to export DFS Replication settings such
as replication group members and connections.
14. Using DFS Replication
An easy-to-use, fault-tolerant, and high-performance file
system is not worth much if the data you want to access is
unavailable or out of date. To ensure that files are available to
users even if a server goes down, create additional folder targets and use DFS Replication to keep the folder targets in sync. You
can also use DFS Replication to synchronize folders that are not
part of a DFS namespace—for example, to replicate data from a branch
office to a server in the main office that you back up regularly and
reliably.
14.1. Creating a Replication Group
A replication group is defined as two
or more servers that participate in replication. Replication groups define the replication topology
used by members for replication. To create a replication group,
follow these steps:
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then
click DFS Management. In the console tree, right-click the Replication node,
and then click New Replication Group. Follow the instructions in the New Replication Group
Wizard.
|
If other members of the replication group have data in the
replicated folders, Windows takes the following actions during
the initial replication:
If an identical file already exists on the target
server (any server other than the primary member), the
primary member does not replicate the file. If a file already exists on a target server but the
file is not identical to the version on the primary member,
Windows moves the file on the target server to the local
conflict folder and then replicates the primary member’s
version of the file, even if this file is older than the
version on the target server. If a file exists on a target server that is not
present on the primary member, Windows does not replicate it
during the initial replication but does replicate it during
subsequent replications to other members, including the
primary member.
After the initial replication, the primary member role
goes away and replication is multiple-master-based. Do not
delete, rename, or move files on the primary member or any
member that has already replicated until the first replication
is complete. (Look for Event 4104 in the DFS Replication log.)
Deleting, renaming, or moving files before the first replication
is complete can cause the files to reappear if they existed on a
target that had not yet replicated.
|
14.2. Replicating a DFS Folder
To create a replicated folder in a new replication group that replicates a DFS folder, use
the following steps:
Right-click the appropriate folder under the Namespaces
node of DFS Management, and choose Replicate Folder. The
Replicate Folder Wizard appears. On the Replication Group And Replicated Folder Name
page, confirm the name for the replication group and for the
replicated folder. (The name for the replication group must be
unique on the domain. To add to an existing replication group,
use the instructions in the following sections.) On the Replication Eligibility page, review the target
folders that will be replicated. Click
Next. On the Primary Member page, select the server that holds
the data that you want to use as the seed for the initial
replication. On the Topology Selection page, select one of the
following replication topologies: Hub And Spoke Spoke
servers replicate with one or two central hub servers. Hub
servers replicate with all other hub servers by using the
full-mesh topology, as well as with designated spoke
servers. Choose this topology in large network
environments and environments with multiple branch
offices. This topology requires a minimum of three
members. Full Mesh All servers
replicate with all other servers. Choose this topology
when there are fewer than 10 servers in the replication
group and all links have low enough costs (performance or
monetary) to allow each server to replicate with every
other server instead of a central hub server. No Topology This
option does not specify a topology and postpones
replication until you specify a replication topology
manually. To specify a replication topology after creating
the replication group, right-click the replication group
in the DFS Management snap-in and then choose New
Topology.
On the Hub Members page that appears if you chose the
Hub And Spoke topology, specify the hub servers. On the Hub And Spoke Connections page that appears if
you chose the Hub And Spoke topology, verify that the wizard
lists the proper spoke servers. To change the required hub
server with which a spoke member replicates preferentially, or
the optional hub member with which a spoke member replicates
if the required hub member is unavailable, select the spoke
server, click Edit, and then specify the required hub and the
optional hub. On the Replication Group Schedule And Bandwidth page,
choose when to replicate and the maximum amount of bandwidth
you want DFS Replication to use. To create a custom schedule, choose Replicate During The
Specified Days And Times and then click Edit Schedule. You can
create a custom schedule that uses Coordinated Universal Time
(UTC) or the local time of the receiving server. On the Review Settings And Create Replication Group page, review the settings and
then click Create. Review any errors and then click Close.
Windows then replicates topology and replication settings to all domain controllers.
A replication group member polls its nearest domain controller
regularly. (By default, replication group members perform a
lightweight poll every five minutes for Subscription objects
under the local computer container and a full poll every
hour.) It receives the settings after Windows updates the
domain controller. To change the replication polling interval,
use the Dfsrdiag command.
14.3. Creating a Branch Office Replication Group
To create a replication group that replicates a single
branch server with a single hub server, use the following
steps:
In the DFS Management snap-in, right-click Replication
and choose New Replication Group. The New Replication Group
Wizard appears.
Note:
Creating replicated folders within an existing
replication group is faster than creating a new replication
group for each replicated folder because the replication
group automatically applies its schedule, topology, and
bandwidth-throttling settings to the new replicated
folder.
On the Replication Group Type page, choose Replication
Group For Data Collection. On the Name And Domain page, type a name for the
replication group that is unique on the domain, specify in
which domain to host the replication group, and optionally
type a description of the replication group. On the Branch Server page, type the name of the branch
server that holds the data that you want to replicate with the
hub server. On the Replicated Folders page, click Add, and then use
the Add Folder To Replicate dialog box to specify the local
folder on the branch server to replicate with the hub server.
Click OK when you are finished. On the Hub Server page that appears if you chose
Replication Group For Data Collection on the Replication Group
Type page, type the name of the hub server that serves as a
replication target for the replicated folders. On the Target Folder On Hub Server page, specify the
local folder on the hub server in which you want to place
replicated data from the branch server. This folder is usually
located in a folder or volume that you back up
regularly. On the Replication Group Schedule And Bandwidth page,
choose when to replicate and the maximum amount of bandwidth
you want to allow DFS Replication to use. To create a custom schedule,
choose Replicate During The Specified Days And Times and then
click Edit Schedule. You can create a custom schedule that
uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) or the local time of the
receiving server. On the Review Settings And Create Replication Group
page, review the settings and then click Create. Review for
errors and then click Close.
Windows then replicates the topology and replication
settings to all domain controllers. A replication group member
polls its nearest domain controller regularly. (By default,
replication group members perform a lightweight poll every five
minutes for Subscription objects under the local computer
container and a full poll every hour.) It receives the settings
after Windows updates the domain controller. To change the
replication polling interval, use the Dfsrdiag command.
14.4. Creating a Multipurpose Replication Group
To create a replication group that replicates any number of
servers with any number of other servers, use the following
steps:
In the DFS Management snap-in, right-click Replication
and choose New Replication Group. The New Replication Group
Wizard starts. On the Replication Group Type page, choose Multipurpose
Replication Group. On the Name And Domain page, type a name for the
replication group that is unique on the domain, specify in
which domain to host the replication group, and optionally
type a description of the replication group. On the Replication Group Members page, add the servers
on which you want to replicate content. On the Topology Selection page, choose a replication
technology. On the Hub Members page that appears if you chose the
Hub And Spoke topology, specify the hub servers. On the Hub And Spoke Connections page that appears if
you chose the Hub And Spoke topology, verify that the wizard
lists the proper spoke servers. To change the required hub
server with which a spoke member replicates preferentially, or
the optional hub member with which a spoke member replicates
if the required hub member is unavailable, select the spoke
server, click Edit, and then specify the required hub and the
optional hub. On the Replication Group Schedule And Bandwidth page,
choose when to replicate and the maximum amount of bandwidth
you want to allow DFS Replication to use. To create a custom
schedule, choose Replicate During The Specified Days And Times
and then click Edit Schedule. You can create a custom schedule
that uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) or the local time
of the receiving server. On the Primary Member page, select the server that holds
the data that you want to use as the seed for the initial
replication. On the Folders To Replicate page, click Add, and then
use the Add Folder To Replicate dialog box to specify the
folder to replicate. Click OK when you are finished. On the Local Path Of Folder On
Other Members page, select a replication member that you want to participate
in the replication of the specified folder, click Edit, and
then use the Edit Local Path dialog box to enable replication
and specify the local folder on the target server in which to
place replicated data from the hub server. Repeat this step
for every replicated folder you specify in the Replicated
Folders page. On the Review Settings And Create Replication Group
page, review the settings and then click Create. Review any
errors and then click Close.
Windows then replicates the topology and replication
settings to all domain controllers. A replication group member polls its nearest domain
controller regularly. (By default, replication group members
perform a lightweight poll every five minutes for Subscription
objects under the local computer container and a full poll every
hour.) It receives the settings after Windows updates the domain
controller. To change the replication polling interval, use the
Dfsrdiag command.
14.5. Managing Replication Groups
Select a replication group, and then use the Memberships,
Connections, Replicated Folders, and Delegation tabs of the DFS
Management console to manage the replication group, as discussed
in the following list.
Note:
Click a column heading to change how Windows groups items
in the view. To add or remove columns, right-click the column
heading and choose Add/Remove Columns.
Use the following options on the Memberships tab to view and
manage the member servers for each replicated folder:
To disable a member of the replication group,
right-click the member and then choose Disable. Disable
members that do not need to replicate a specific replicated
folder. Do not disable members temporarily and then enable
them—doing so causes roughly one kilobyte of replication
traffic per file in the replicated folder and overwrites all
changes on the disabled member. To delete a member of the replication group, right-click
it and then choose Delete. To add a member server that participates in replication,
right-click the replication group in the DFS Management
console, choose New Member, and then use the New Member Wizard
to specify the local path of the replicated folders,
connections, and schedule. To change the size of the conflict or staging folders or
to disable the retention of deleted files, right-click the
member, choose Properties, click the Advanced tab, and then
use the Quota boxes. The conflict folder stores the “losing” files that
Windows deletes when it encounters two versions of the same
file during replication as well as the most recently deleted
files in the replicated folder, and the staging folder queues replication data.
Note:
The default size of the staging folder is 4096 MB, but by increasing
the size of the staging folder, you can increase the
performance of replication group members that replicate with
a large number of replication partners or that contain large
files that change often. Look for event ID 4208 in the
DFS Replication event log; if this event
appears multiple times in an hour, increase the staging
folder size 20 percent until the event no longer appears
frequently.
To create a report showing the replication health as well as RDC efficiency, right-click the replication group,
choose Create Diagnostic Report, and then use the Diagnostic
Report Wizard to create the report. To verify the replication topology, right-click the replication group and
then choose Verify Topology. On the Connections tab, view and manage all replication
connections. To add a new replication connection between two
members of a replication group, right-click the replication
group and choose New Connection. Then use the New Connection
dialog box to specify the sending member, the receiving
member, the schedule, and whether to create a one-way
replication connection or a two-way connection. Use the following options on the Replicated Folders tab
to view and manage all replicated folders: To add a new replicated folder to the replication
group, right-click the replication group in the DFS
Management console, choose New Replicated Folder, and then
use the New Replicated Folder Wizard to specify the
primary member and the local folders to replicate. To omit certain file types or subfolders from
replication, click the Replicated Folders tab, right-click
the replicated folder, choose Properties, and then use the
File Filter and Subfolder Filter boxes on the General
tab. To share a replicated folder on the network and
optionally add the folder to a DFS namespace, right-click
the replicated folder, choose Share And Publish In
Namespace, and then use the Share Or Publish Replicated
Folder Wizard.
Note:
RDC increases processor utilization on the server, so
you might want to disable it on servers with slow processors
or high-speed links, and in environments that replicate only
new content or files smaller than 64 KB. To disable RDC on a
connection, click the Connections tab, right-click the
member, choose Properties, and then clear the Use Remote
Differential Compression (RDC) check box. You can also
change the minimum file size that RDC engages from the 64 KB
default size by using the Dfsradmin ConnectionSet command.
Monitor RDC statistics and CPU utilization before and after
disabling RDC to verify that you reduce processor
utilization enough to warrant the increased network
traffic.
Note:
To change the replication polling interval, which controls how
often a server checks for updated files, use the Dfsrdiag
command.
|