Some Wi-Fi Limitations
When connecting to a Wi-Fi network, your Internet
connection speed can be affected by a variety of factors, including
where your computer is located, whether other wireless devices are in
the same area, and even what the slowest connection is beyond the
wireless router. Wireless networks operate on frequencies that are
similar to those used by other devices, such as microwave ovens or
cordless phones. Operating a 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) cordless phone next to
your 2.4GHz wireless laptop can cause interference or completely block
the wireless network connection. If you want to make phone calls while
surfing the Web, either use a wired telephone or a cordless phone that
operates at a different frequency than your wireless network.
One point that many people don’t realize is that
even if you have a high-speed wireless network connection (the 802.11g
protocol, for example, supports up to 54Mbit network connections), you
can still be limited by the speed of the connection from that router to
the Internet. So if your favorite coffee shop has 54Mbit wireless
connection, but uses a 1.5Mbit DSL router to connect out to the
Internet, your network connection (and that of everyone else in the
coffee shop sharing that connection with you) will be limited to the
1.5Mbit DSL connection.
How close you are to the wireless access point or
router, as well as physical obstructions, can affect the quality of your
Internet connection. To improve your connection speed, move closer to
the access point and make sure that there are no physical obstructions
between the access point and your computer.
Note
Worth
noting is that a “physical obstruction” can be many things. One
wireless access point we use in downtown San Jose, for example, has a
tree between where we work and the actual antenna. During dry weather,
the tree isn’t much of an obstacle. When it rains, however, the water
collecting on the leaves of the tree is enough of a physical obstacle to
the radio waves that it causes substantial problems.
Choosing a Network Location
The first time that you connect to a network, you
must choose a network location. This automatically sets the appropriate
firewall and security settings for the type of network that you connect
to. If you connect to networks in different locations (for example, a
network at your home, at a local coffee shop, or at work), choosing a
network location can help ensure that your computer is always set to an
appropriate security level.
There are four network locations:
Home Network—
Choose Home Network for home networks or when you know and trust the
people and devices on the network. Computers on a home network can
belong to a HomeGroup. Network discovery is turned on for home networks,
which allows you to see other computers and devices on the network and
allows other network users to see your computer.
Work Network—
Choose Work Network for small office or other workplace networks.
Network discovery, which allows you to see other computers and devices
on a network and allows other network users to see your computer, is on
by default, but you can’t create or join a HomeGroup.
Public Network—
Choose Public Network for networks in public places (such as coffee
shops or airports). This location is designed to keep your computer from
being visible to other computers around you and to help protect your
computer from any malicious software from the Internet. HomeGroups are
not available on public networks, and network discovery is turned off.
You should also choose this option if you’re connected directly to the
Internet without using a router or if you have a mobile broadband
connection.
Domain Network—
The Domain Network location is used for domain networks such as those
at enterprise workplaces. This type of network location is controlled by
your network administrator and can’t
be selected or changed. One advantage of Domain Networks is that they
allow you to centrally manage resources and permissions for all of your
users. If you are using domains, you should refer to your network
documentation and check with Microsoft about configuring your Windows 7
systems to properly run on your domain.
Note
If you know you won’t need to share files or printers, the safest choice is Public Network.
To Change a Network Location
Here’s how to change a network location:
1. | Open the Network and Sharing Center by clicking the Start button, Control Panel, Network and Sharing Center.
|
2. | Click Work Network, Home Network, or Public Network, and then click the network location you want.
|
3. | Select a network and click Connect or Disconnect (see Figure 1).
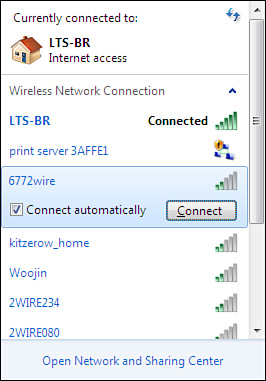
|
Tip
If you want Windows to automatically connect to a
network without any intervention from you, select Connect Automatically
as shown in Figure 10.5.
Caution
Choosing
Home Network or Work Network changes the firewall configuration to
allow communication to and from your computer, which can be a security
risk.
Connecting to the Internet
The Connect to the Internet Wizard will guide you through the steps of setting up an Internet connection:
1. | Open the Connect to the Internet Wizard by clicking the Start button and then clicking Control Panel.
|
2. | Then click Network and Sharing Center.
|
3. | Click Set up a New Connection or Network and then double-click Connect to the Internet.
|
Note
If you’re connected to a
local area network, you might already be connected to the Internet. To
find out, open your web browser and try accessing a website.