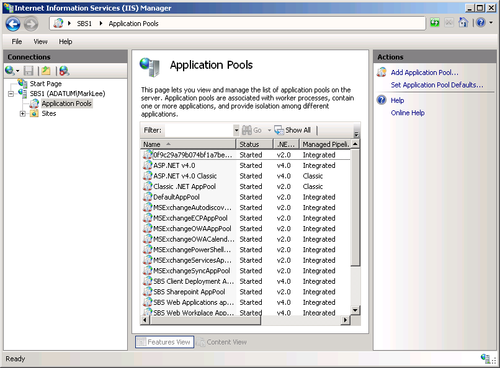
2. Understanding the IIS Architecture
IIS takes the form of a role in
the Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system. The Windows SBS 2011 setup
program installs and configures eight different roles on your server
during the installation process, among them the Web Server (IIS) role. The Web Server (IIS) role is a modular service that has 46 role services, as shown in Figure 1, which provide IIS with various security, management, logging, and application capabilities. By default,
Windows SBS 2011 installs all the IIS role services except for those
which compose the FTP Server, although it does not necessarily require
all the role services it installs.
In a Windows Server 2008 R2 installation, IIS has one default
website with a placeholder splash screen, which uses the standard port
for HTTP communications, port 80. This site and the splash screen are
still accessible on a Windows SBS 2011 server if you use a Uniform
Resource Locator (URL) containing only the server’s name or Internet
Protocol (IP) address, as shown in Figure 2.
However, the default IIS installation in Windows SBS 2011 also includes
several other sites, which are accessible using various other URLs.
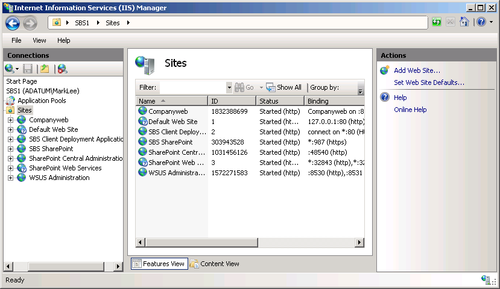
In IIS, a site
is an individual set of web pages that is separate from the other sites
running on the computer. In Windows SBS 2011, the default IIS sites are
all intended for use by a single organization, but it is also possible
to use IIS to create completely separate sites for different companies,
each with its own content and configuration settings. With IIS, you can
create as many additional sites as your server hardware can support. You
create and manage sites using the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager application, as shown in Figure 3.
Each site points to a
location on a local drive that holds the files containing the site’s
content, such as HTML, image, and application files. Working with the
content is a matter of creating and editing the files at this location.
IIS also supports the use of virtual directories,
which are pointers to other locations on the same computer or on the
local network. For example, if you have a site with its home directory
on the local drive, but you want to publish some files located on
another computer, you can either copy those files to the home directory
(which can cause version synchronization problems) or just create a
virtual directory on the site that points to the folder on the other
computer. The files appear on the site, yet remain in their original
location.
3. Running Multiple Sites
Hosting multiple websites on a single server presents a problem for IIS. When web browsers connect to a site, they do so by sending an HTTP request message to the web server’s IP address using the well-known HTTP port number 80. When requests for different sites arrive at the server, how is IIS supposed to differentiate them and forward each request to the correct site?
The answer is by configuring each site with a different set of bindings. Bindings
are rules that tell IIS how to associate incoming requests with
specific sites. IIS supports three types of bindings, as follows:
IP address
It is possible to assign more than one IP address to a single computer.
By doing this, you can configure IIS to use a different address for
each site. However, you must also register a different name in a Domain
Name System (DNS) domain for each address.
Port number
Web browsers send all their HTTP requests to port 80 on the destination
server unless the user specifies a different port number in the URL.
You can create bindings that assign a different port number to each site
on an IIS server, enabling the server to distinguish among the incoming
requests. However, to access a site that uses a nonstandard port
number, users must specify that number in their URLs, following the
server name and a colon, as in the example www.adatum.com:1024.
In Windows SBS 2011, the WSUS site uses port number bindings because
the URL that Windows Update clients use to access the web server, which
contains the port number 8530, is hidden from users in a Group Policy
object (GPO). In a situation like this, in which users do not have to
remember the port number and type it in a URL, port number bindings are a
viable option. Another reason to use port number bindings is to keep a
site hidden from the average user. The SharePoint Central Administration
site on your server uses a nonstandard port number, which is unknown to
the network users, but which administrators can access through the
Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard Console.
Host header Communications between browsers and web servers are based on IP addresses, not server names, but HTTP messages have a Host field that contains the server name that the user specified in the browser. A host header binding associates a particular Host field value with one of the sites on the IIS
server, even if all the host names resolve into the same IP address. In
Windows SBS 2011, the client deployment and SharePoint sites all use
host header bindings.
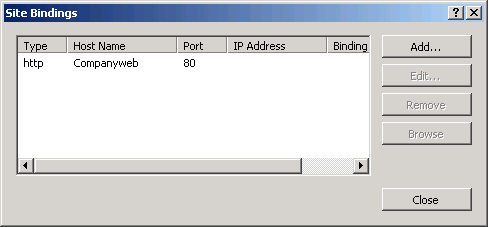
To configure or modify the bindings for a site, you select a site in IIS Manager and open its Site Bindings dialog box, as shown in Figure 4.
4. Running Web Applications
When software
developers create standalone client/server applications, they have to
design both the server and the client components from scratch, including
the client user interface. Web applications for Windows SBS 2011
simplify the software design and deployment process by using the
existing mechanisms of IIS on the server and Internet
Explorer on the browser. Internet Explorer provides the basic functions
that simplify the design of the user interface, and IIS includes role
services that provide support for a number of application development
environments, including Active Server Pages (ASP), ASP.NET, and Internet Server Application Programming Interface (ISAPI).
Originally, the Web consisted
of static pages written in HTML, and the only function of the web server
was to transmit those pages to browsers on request. Today, however, web
applications enable sites to do much more than simply display static
information. Application-enabled websites can generate pages on demand,
using information provided by the user or extracted from a database.
The Companyweb site included with
Windows SBS 2011 is a perfect example of this arrangement. Clients
connect to the SharePoint site, and IIS runs the SharePoint web
application that generates pages using content stored in a Microsoft SQL
Server database. Windows SBS uses a single computer for the web server
and the database server, but with Windows Server 2008 R2, it is also
possible to deploy the components on separate computers.
IIS is capable of running
multiple applications, each associated with a different site, and it
can do so without one application jeopardizing the stability of the
others or of the entire computer. IIS does this by using individual
address spaces called application pools.
Each application pool runs in its own protected space, so that if an
application crashes, it cannot have any effect outside the pool. This is
called worker process application mode. The Windows SBS 2011 setup program creates 20 separate application pools for the various sites in IIS, as shown in Figure 5.