6. List options
CSS gives you greater control over bulleted points.
With Cascading Style Sheets, you can now display a specific bulleted
point based on a graphic image, or you can choose from the standard
built-in bullets, including disc, circle, and square. The CSS List
category also enables you to specify the type of ordered list, including
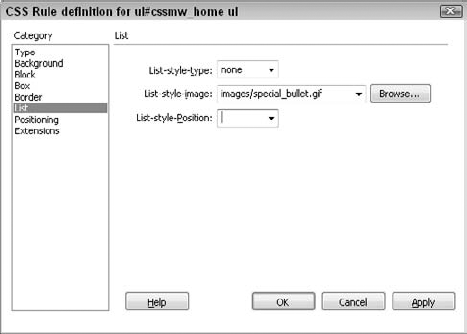
decimal, Roman numerals, or A-B-C order. Figure 7 shows, and Table 6-6 describes, the settings for lists.
Table 6. List Category for Styles| List Setting | Description |
|---|
| Type | Selects
a built-in bullet type. The options include disc, circle, square,
decimal, lowercase Roman, uppercase Roman, lowercase alpha, and
uppercase alpha. | | Bullet Image | Sets an image to be used as a custom bullet. Enter the path to the image in the text box. | | Position | Determines whether the list item wraps to an indent (the default) or to the margin. |
7. Positioning options
For many designers, positioning has increased
creativity in page layout design. With positioning, you have exact
control over where an element is placed on a page. The positioning
attributes are often applied to div tags to create page layouts without resorting to tables. Figure 8 shows the various attributes that provide this pinpoint control of your page elements. The options are described in Table 7.
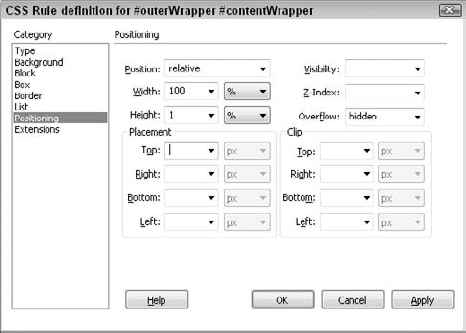
Table 7. CSS Positioning Attributes| Positioning Setting | Description |
|---|
| Type | Determines
whether an element can be positioned absolutely or relatively on a
page. The third option, static, does not enable positioning and renders
elements as they would be positioned with regular HTML. | | Width | Sets the width of the element. | | Height | Sets the height of the element. | | Visibility | Determines whether the element is visible or hidden, or inherits the property from its parent. | | Z-Index | Sets the apparent depth of a positioned element. Higher values are closer to the top. | | Overflow | Specifies
how the element is displayed when it's larger than the dimensions of
the element. Options include the following: Clip, where the element is
partially hidden; None, where the element is displayed and the
dimensions are disregarded; and Scroll, which inserts scroll bars to
display the overflowing portion of the element. | | Placement | Sets
the styled element's placement and dimensions with the left and top
attributes and the width and height attributes, respectively. | | Clip | Sets the visible portion of the element through the top, right, bottom, and left attributes. |
8. Extensions options
The specifications for Cascading Style Sheets are
rapidly evolving, and Dreamweaver has grouped some cutting-edge features
in the Extensions category. As of this writing, most of the Extensions
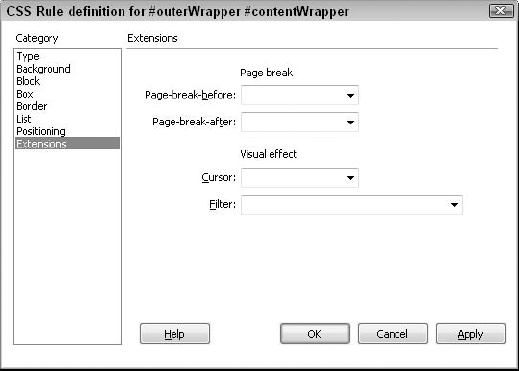
attributes (see Table 8) are supported by Internet Explorer 4.0 and above, whereas only the Cursor extension is supported in Netscape Navigator 6.x. The Extensions settings shown in Figure 9 affect three different areas: page breaks for printing, the user's cursor, and special effects called filters.
Table 8. CSS Extensions Attributes| Extensions Setting | Description |
|---|
| Pagebreak | Inserts
a point on a page where a printer sees a page break. Currently
supported only by Internet Explorer, versions 5.0 and higher. | | Cursor | Defines
the type of cursor that appears when the user moves the cursor over an
element. Currently supported by Internet Explorer, versions 4.0 and
higher as well as Netscape 6. | | Filter | Filters
enable you to customize the look and transition of an element without
having to use graphic or animation files. Currently supported only by
Internet Explorer 4.0 and above. |
NOTE
One of the problems with the Web's never-ending evolution of page design is evident when you begin to print the page. The Pagebreak
attribute alleviates this problem by enabling the designer to designate
a style that forces a page break when printing; the break can occur
either before or after the element is attached to the style. This
attribute is especially important for print media styles.
The Filter attribute offers 16 different
special effects that can be applied to an element. Many of these
effects, such as Wave and Xray, are quite stunning. Several effects
involve transitions, as well. Table 9 details these effects.
Table 9. CSS Filters| Filter | Syntax | Description |
|---|
| Alpha | Alpha (Opacity=opacity, FinishOpacity=finishopacity, Style=style, StartX=startX, StartY=startY, FinishX=finishX FinishY=finishY)
opacity is a value from 0 to 100, where 0 is transparent and 100 is fully opaque.
startX, startY, finishX, and finishY are pixel values indicating where the effect should start and end.
style can be 0 (uniform), 1 (linear), 2 (radial), or 3 (rectangular). | Sets the opacity of a specified gradient region. This can have the effect of creating a burst of light in an image. | | BlendTrans* | blendTrans (Duration=duration)
duration is a time value for the length of the transition, in the format of seconds.milliseconds. | Causes an image to fade in or out over a specified time. | | Blur | blur (Add=add, Direction=direction, Strength=strength)
add is any integer other than 0.
direction is any value from 0 to 315 in increments of 45.
strength is any positive integer representing the number of pixels affected. | Emulates motion blur for images. | | Chroma | chroma (Color= color)
color must be given in hexadecimal form — for example, #rrggbb. | Makes a specific color in an image transparent. | | DropShadow | Dropshadow (Color=color, OffX=offX, OffY=offY, Positive=positive)
color is a hexadecimal triplet.
offX and offY are pixel offsets for the shadow.
positive is a Boolean switch; use 1 to create shadow for nontransparent pixels and 0 to create shadow for transparent pixels. | Creates a drop shadow of the applied element, either image or text, in the specified color. | | FlipH | FlipH | Flips an image or text horizontally. | | FlipV | FlipV | Flips an image or text vertically. | | Glow | Glow (Color=color, Strength=strength)
positive is a Boolean switch; use 1 to create shadow for nontransparent pixels and 0 to create shadow for transparent pixels.
color is a hexadecimal triplet.
strength is a value from 0 to 100. | Adds radiance to an image in the specified color. | | Gray | Gray | Converts an image in grayscale. | | Invert | Invert | Reverses the hue, saturation, and luminance of an image. | | Light | Light | Creates the illusion that an object is illuminated by one or more light sources. | | Mask | Mask (Color=color)
color is a hexadecimal triplet. | Sets all the transparent pixels to the specified color and converts the nontransparent pixels to the background color. | | RevealTrans | RevealTrans (Duration=duration, Transition=style)
duration is a time value that the transition takes, in the format of seconds.milliseconds.
style is one of 23 different transitions. | Reveals an image using a specified type of transition over a set period of time. | | Shadow | Shadow (Color=color, Direction=direction)
color is a hexadecimal triplet.
direction is any value from 0 to 315 in increments of 45. | Creates a gradient shadow in the specified color and direction for images or text. | | Wave | Wave (Add=add, Freq=freq, LightStrength=lightstrength, Phase=phase, Strength=strength)
add is a Boolean value, where 1 adds the original object to the filtered object and 0 does not.
freq is an integer specifying the number of waves.
lightstrength is a percentage value.
phase specifies the angular offset of the wave, in percentage (for example, 0% or 100% = 360 degrees, 25% = 90 degrees).
strength is an integer value specifying the intensity of the wave effect. | Adds sine wave distortion to the selected image or text. | | Xray | Xray | Converts an image to inverse grayscale for an X-rayed appearance. |
|