After you've selected a type and name for a
new style or chosen to edit an existing style, the CSS Rule Definition
dialog box opens. A Category list from which you select a style category
(just as you select a category of preferences in Dreamweaver's
Preferences dialog box) is located on the left side of this dialog box.
Dreamweaver offers you eight categories of CSS styles to help you define your style sheet:
Type
Background
Block
Box
Border
List
Positioning
Extensions
You can define styles from one or all categories. The
following sections describe each style category and its available
settings.
NOTE
Although CSS rendering has been vastly improved
in Dreamweaver CS5, particularly in Live view, not all possible CSS
attributes are viewable in the Design view, most notably those in the
Extensions category.
1. Type options
The Type category specifies the appearance and layout
of the typeface for the page in the browser window. The Type category,
shown in Figure 1,
is one of the most widely used and supported categories — it can be
rendered in all current browser versions as well as way back to Internet
Explorer 3.0 and Navigator 4.0.
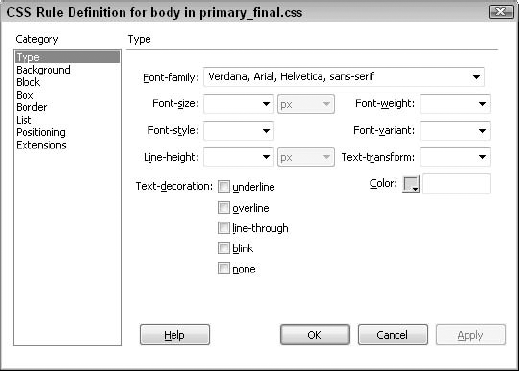
Table 1 explains the settings available in this category.
Table 1. CSS Type Attributes
| Type Setting | Description |
|---|
| Font | Specifies the font or a collection of fonts, known as a font family.
You can edit the font list by selecting Edit Font List from the
drop-down list.
|
| Size | Selects
a size for the selected font. If you enter a value, you can then select
the measurement system in the adjacent text box (the default is
pixels). The relative sizes, such as small, medium, and large, are set
relative to the parent element. Values can be selected from the
drop-down list or entered by hand. |
| Style | Specifies
a normal, oblique, or italic attribute for the font. An oblique font
may have been generated in the browser by electronically slanting a
normal font. |
| Line Height | Sets the line height of the line (known as leading
in traditional layout). Typically, line height is a point or two more
than the font size, although you can set the line height to be the same
as or smaller than the font size for an overlapping effect. |
| Decoration | Changes
the decoration for text. Options include underline, overline,
line-through, blink, and none. The blink decoration is displayed only in
Netscape 4.x and earlier browsers. |
| Weight | Sets
the boldness of the text. You can use the relative settings (light,
bold, bolder, and boldest) or apply a numeric value. Normal is around
400; bold is 700. |
| Variant | Switches
between normal and small caps. Small caps is a font style that displays
text as uppercase, but the capital letters are a slightly larger size. |
| Case | Forces a browser to render the text as uppercase, lowercase, or capitalized. |
| Color | Sets
a color for the selected font. Enter a color name or select the color
swatch to choose a browser-safe color from the color picker. |
2. Background options
Since Netscape Navigator 2.0, Web designers have been
able to use background images and color. Thanks to CSS Background
attributes, designers can now use background images and color with
increased control. Whereas traditional HTML background images are
restricted to a single image for the entire browser window, CSS
backgrounds can be specified for a single paragraph or any other CSS
selector. (To set a background for the entire page, apply the style to
the <body> tag.) Moreover, instead of an image
automatically tiling to fill the browser window, CSS backgrounds can be
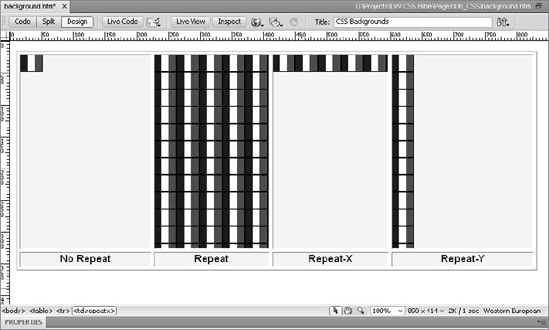
made to tile horizontally, vertically, or not at all (see Figure 2). You can even position the image relative to the selected element.
The current versions of browsers support the CSS Background attributes shown in Figure 3 and described in Table 2.
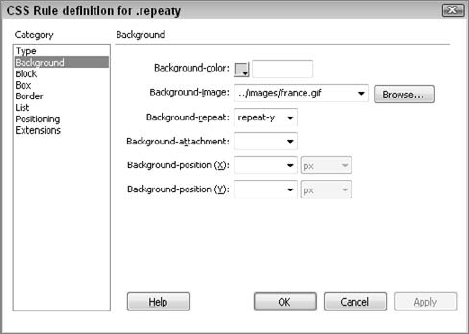
Table 2. CSS Background Attributes
| Background Setting | Description |
|---|
| Background Color | Sets
the background color for a particular style. Note that this setting
enables you to set background colors for individual paragraphs or other
elements. |
| Background Image | Specifies a background image. |
| Repeat | Determines the tiling options for a graphic:
no repeat displays the image in the upper-left corner of the applied style. repeat tiles the background image horizontally and vertically across the applied style. repeat-x tiles the background image horizontally across the applied style. repeat-y tiles the background image vertically down the applied style.
|
| Attachment | Determines
whether the background image remains fixed in its original position or
scrolls with the page. This setting is useful for positioned elements.
If you use the overflow attribute, you often want the background image
to scroll in order to maintain layout control. |
| Horizontal Position | Controls
the positioning of the background image in relation to the style sheet
elements (text or graphics) along the horizontal axis. |
| Vertical Position | Controls
the positioning of the background image in relation to the style sheet
elements (text or graphics) along the vertical axis. |