An outline is a
list of a document’s major and minor sections, presented as headings.
Each heading is the title of a section, and each one is assigned a
level that shows its priority in the overall scheme of things. The
document’s most important sections take the highest heading level
(level 1), the next-most important are level 2, and so on, from most
important to least important. You can create outlines with as many as
nine heading levels.
You can divide any section into subsections, and
divide those into subsubsections, right on down the line. Because the
title of each section and subsection is formatted with one of Word’s
heading styles (Heading 1, Heading 2, and so on), it’s easy to keep
track of them all. Figure 1 shows an example of an outline from one of my old term papers about the great American poet, William Carlos Williams.
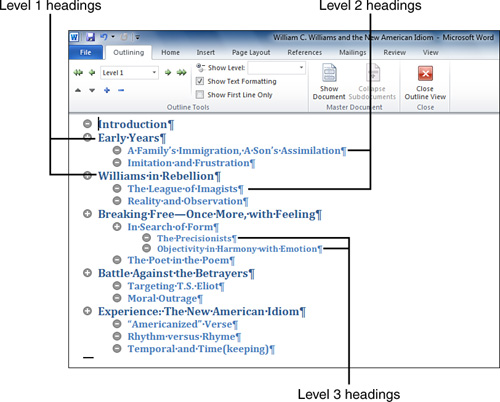
In the figure, notice that the outline includes
three heading levels; each level is distinguished by its formatting and
its indentation. Level 1 headings have the largest font and are not
indented. Subordinate headings are progressively smaller and indented
farther from the left margin.
|
Always make sure that your outline’s headings are
formatted with styles that Word recognizes as heading styles. When you
use heading styles, Word can automatically do a few things for you,
such as adding the headings to a table of contents and building a
document map. The safest approach is to use Word’s built-in heading
styles for this purpose. If you create your own heading styles, be sure
to base them on Word’s heading styles.
|
Working in Outline View
The easiest way to create an outline is by working in Outline view. This special view provides all the tools you need to create and modify an outline.
Switching to Outline View
Here’s how to switch in and out of Outline view:
1. | On
the View tab, click Outline. (Alternatively, click the Outline View
button near the right end of the status bar.) Word switches to Outline
view, as shown in Figure 2, and the Outlining tab appears on the ribbon.
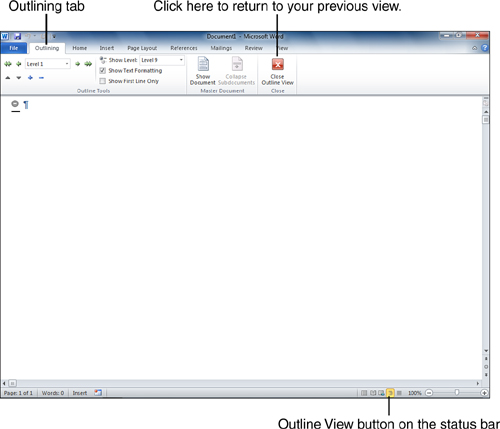
|
2. | To switch from Outline view to another view, do one of the following:
- On the Outlining tab, click Close Outline View to return to your previous view.
- Click the View tab; then click the button for your preferred view.
- On the status bar, click the button for your preferred view.
|
If the Outlining tab doesn’t appear when you switch
to Outline view, you can turn it on. Go to the File tab and click
Options. In the Word Options dialog box, click Customize Ribbon. In the
Customize the Ribbon list (on the right side of the dialog box), check
the Outlining check box, and then click OK. From now on, the Outlining
tab will open and close when you switch to and from Outline view.
The Outlining tab provides a few tools that let you control your view of the outline:
- Show Level:
This drop-down list enables you to decide how many heading levels you
want to see. For example, if you select Level 2 from the list, Word
hides level 3 or lower headings.
- Show Text Formatting:
Select this check box if you want to see how your headings will look in
the document. Deselect the check box to display the headings as
unformatted (normal) body text.
- Show First Line Only:
When this check box is selected, Word displays the first line of normal
text (if there is any) underneath each heading. Uncheck this box to
hide the normal text and view only headings.