alternate text
Text that appears in the position where a graphic will be while the graphic loads. Normally, it identifies the graphic, such as Picture of Kennedy.
Because some Web graphics can be very large, providing alternate text
enables a user to decide whether to wait for the image to load.
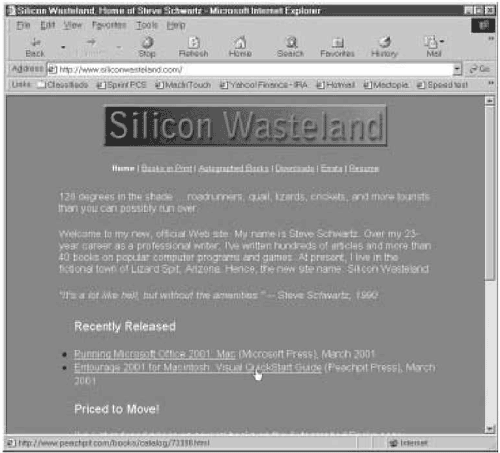
browser
A program that decodes
the information for the Web pages you see on your monitor. The dominant
browsers are Microsoft Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator (Figure 1).
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
The language in which Web pages are created.
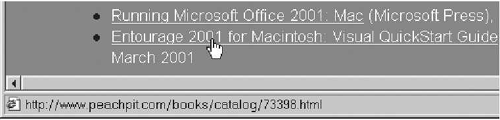
link (hyperlink)
Words or graphics on a Web
page that—when clicked—transport you to another Web site, another page
in the current Web site, or to another spot on the same page (Figure 2).
map
A URL assigned to a graphic or text string, creating a link to another site or page.
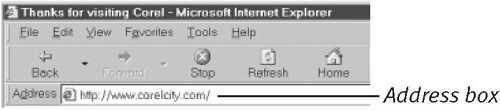
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
An address for a Web page. An example of a URL is http://www.bearhome.com. To view a Web page, you can type its URL in your browser's Address box (Figure 3).
Web server
A computer connected to the Web that serves
Web pages to the computer users who wish to view the pages. When you
click a link for a Web page that's available on a particular server, the
data is transmitted from the server over the Internet to your computer.
World Wide Web
An international system for linking text, graphics, and multimedia documents on the Internet.