WORD’S FIND AND REPLACE
features are real time savers. For example, you can quickly find out if
you covered a particular topic in a lengthy report, or you can changes
names, dates, and prices throughout documents with just a few
keystrokes.
Using Find
Word’s Find command is useful when you want to seek
out text that you may have trouble visually locating in a document. The
Find command doesn’t change any text; it simply locates and highlights
the specified text for you. Follow these steps:
Choose Home > Editing > Find, or press the Ctrl+F keys. The Navigation pane appears on the left side of the screen (see Figure 1).
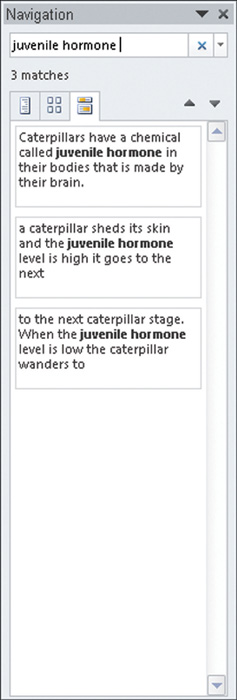
In
the text box, type the word or phrase that you want to search for. As
you type, Word automatically highlights and displays each occurrence of
the word or phrase you’re looking for. |
The Find command begins its search at the location of the insertion point.
|
The
Navigation pane also lists the other occurrences of the searched text.
Click any occurrence to instantly jump to the text. If you want to
discontinue the search, simply close the Navigation pane. Tip
Unless you specify whole words (see the next
section), Word locates any instance containing the letters you specify.
For example, if you enter read in the Find box, Word also locates words like bread or reading.
Extending Search Options
If you need to be a little more specific about what
you’re searching for, Word provides a number of extended options to
assist you.
Open the Navigation pane by choosing Home >
Editing > Find (or press the Ctrl+F keys), and in the search text
box, type the word or phrase for which you want to search. Click the
More Options arrow next to the text box, which displays a menu like the
one you see in Figure 2. Choose Options, which displays the Find Options dialog box (also shown in Figure 2),
and then select the options you want. Click OK when you are finished,
and Word continues the search using the options you selected.
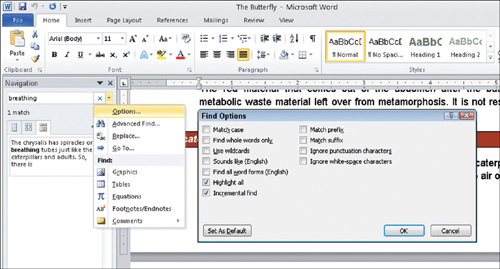
Take a brief look at the most commonly used options:
Match Case:
Check this to locate instances that match the upper- and lowercase
letters as you entered them in the Find box. For example, if you typed Go, Word will not locate go or GO. Find Whole Words Only: Check this to locate instances of the entire word only. For example, if you enter read in the Find box, Word will ignore words like bread or reading. Use Wildcards:
Check this to use the question mark (?) or asterisk (*) wildcards in
your search. The ? character matches any single character, and the *
character matches any number of characters. For example, if you enter b?d in the Find box, Word finds bad, bed, or bidding, but not bread. If you enter b*d, Word locates words like bad, bed, abide, bidding, bread, bored, and so forth. Tip
Word also recognizes wildcard characters like the at
sign (@) or angle bracket (<). See the Word Help system for a
complete description.
Sounds Like: Check this to locate instances that are phonetically the same as the text in the Find box. For example, if you entered foul, Word also locates fowl. Find All Word Forms: Check this to locate all grammatical forms of the search word. For example, if you enter they, Word also locates their, theirs, them, and themselves. Highlight All: Checked by default, this option tells Word to highlight all occurrences of the found text. Incremental Find:
Also checked by default, the Incremental Find option allows Word to
start searching as soon as you start typing in the Find box. Match Prefix: Check this to locate words that only begin, not contain or end, with the search word. For example, if you enter mini, Word also locates minimum or miniature, but not administration. Match Suffix: Check this to locate words that only end, not contain or begin, with the search word. For example, if you enter ration, Word also locates demonstration but not rational. Ignore Punctuation Characters: Check this to ignore punctuation marks, such as ‘ ? - “ ! ; : , . and /. For example, if you entered 1478, Word also locates 1,478 and 14.78. Ignore White-Space Characters: Check this to ignore spaces and tabs. For example, if you enter lonestar, Word also locates lone star.
|