One of the most useful features within
a typical SSMS dialog box is the ability to script the actions of a
dialog box instead of actually executing the action against the server.
For example, launch the New Database dialog box from the Databases node
in Object Explorer. This will launch the dialog box shown in Figure 1. As an example, enter SmartCommunityBank in the “Database name” text box.
Figure 1. New Database dialog box in SQL Server Management Studio
If you click the OK
button, the database will be created, and the dialog box will close.
However, if you want to know exactly what T-SQL statements will be
executed as a result of what you input in this dialog box, click the
downward-facing arrow on the Script button at the top of the dialog
box. This will pop up a list of destinations for the script, as shown
in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Script options
If you select Script Action to New Query Window, this will open a new Query Editor window and populate it with the CREATE DATABASE script shown here:
CREATE DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank]
CONTAINMENT = NONE
ON PRIMARY
( NAME = N'SmartCommunityBank', FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\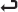
MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\SmartCommunityBank.mdf' , SIZE = 4096KB , FILEGROWTH 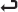
= 1024KB )
LOG ON
( NAME = N'SmartCommunityBank_log', FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\
MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\SmartCommunityBank_log.ldf' , SIZE = 1024KB , FILEGROWTH 
= 10%)
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 110
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET ANSI_NULL_DEFAULT OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET ANSI_WARNINGS OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET ARITHABORT OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET AUTO_CLOSE OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET AUTO_CREATE_STATISTICS ON
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET AUTO_SHRINK OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS ON
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET CURSOR_CLOSE_ON_COMMIT OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET CURSOR_DEFAULT GLOBAL
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET CONCAT_NULL_YIELDS_NULL OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET NUMERIC_ROUNDABORT OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET RECURSIVE_TRIGGERS OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET DISABLE_BROKER
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET DATE_CORRELATION_OPTIMIZATION OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET PARAMETERIZATION SIMPLE
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT OFF
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET READ_WRITE
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET RECOVERY FULL
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET MULTI_USER
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET PAGE_VERIFY CHECKSUM
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] SET TARGET_RECOVERY_TIME = 0 SECONDS
GO
USE [SmartCommunityBank]
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.filegroups WHERE is_default=1 AND name = N'PRIMARY')
ALTER DATABASE [SmartCommunityBank] MODIFY FILEGROUP [PRIMARY] DEFAULT
GO
Note Choosing to script the action of a dialog box is a great way to learn which T-SQL statements perform which actions.
In this case, you can see that the CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a database.
To create the database, click the Execute button the toolbar.