The basic syntax is
netsh interface ipv4 set address name = ""
static IP-address subnet-mask default-gateway
For example, you can use the following command to
configure the NIC named “Local Area Connection” with an IP address of
192.168.1.15, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and a default gateway of
192.168.1.1.
netsh interface ipv4 set address name = "local area connection"
static 192.168.1.15 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Note
The default name of the first NIC is Local Area Connection on Windows systems. Because the NIC’s name (Local Area Connection) has spaces within it, it must be enclosed in quotes.
Some other commands you can use to configure the NIC are shown in the following table.
| Command | Description |
|---|
Get TCP/IP information from DHCP.
netsh interface ipv4
set address [name=]
"NIC-name" [source=]
dhcp
C:\>netsh interface
ipv4 set address name =
"local area connection"
source = dhcp
| Changes the NIC so that it gets TCP/IP configuration automatically from DHCP. |
Get DNS from DHCP.
netsh interface ipv4
set dnsserver [name=]
"NIC-name " [source=]
dhcp
C:\> netsh interface
ipv4 set dnsserver
"local area connection"
dhcp
| Changes the NIC to get the DNS address automatically from DHCP. |
Set IP address of preferred DNS server with set.
netsh interface ipv4 set
dnsserver [name=]"NIC-
name" [source=]static
[address=] Preferred-
DNS-IP-Address
C:\>netsh interface
ipv4 set dnsserver
name="local area
connection"
source=static
192.168.1.5
| Sets the IP address of the preferred DNS server.
Note
This command removes all other DNS Server IP addresses, if any are configured.
|
Set IP address of preferred DNS server with add.
netsh interface
ipv4 add dnsserver [name=]"NIC-name
"
[address=] Preferred-
DNS-IP-Address index=1
C:\>netsh interface
ipv4 add dnsserver
name="local area
connection" 192.168.1.6
index=1
| Note
The add command has slightly different syntax than the set command. For example, you cannot use the indexset command.
clause with the
This command adds the address of a DNS server and sets it as the
preferred DNS server (with an index of 1). If other DNS servers are in
the list, they are moved down the list.
Note You
cannot use this command to modify the order of existing DNS server
addresses. If you use an IP address of a DNS server already in the
list, the command fails. However, you can use the set command to set one DNS server address, and then use the add command to add additional DNS server addresses with the index clause to specify the order.
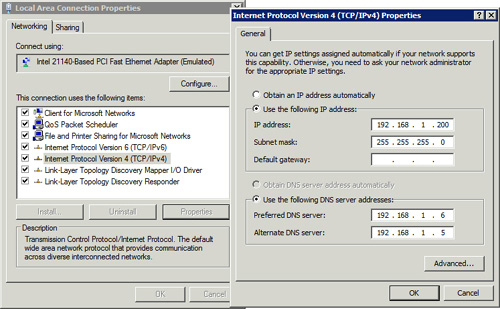
Figure1 shows the result of this command in combination with the previous add command. The setadd command with an index of 1 is set 192.168.1.6 as the preferred DNS server, and bumped 19.168.1.6 to the alternate. |
Set alternate DNS server.
netsh interface
ipv4 add dnsserver [name=]"NIC-name"
[address=] Preferred-
DNS-IP-Address index=2
C:\>netsh interface
ipv4 add dnsserver
name="local area
connection" 192.168.1.7
index=2
| This
command adds 192.168.1.7 as the alternate. If another server was
designated as the alternate, it will be moved down one in the list.
Tip
You can add DNS servers with different indexes.
|
Tip
If you want to identify the names of the IPv4 interfaces on the system, you can use the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces