3. Troubleshooting Step by Step
A functioning Internet connection
depends on an entire chain of hardware and software components that
reaches all the way from your keyboard to a computer that might be
halfway around the world. Troubleshooting is a real detective’s art, and
it’s based more on methodical tracking down of potential suspect
problems than intuition. If something goes wrong, you have to go through
each component, asking “Is this the one that’s causing the problem?”
Windows 7 comes with network-troubleshooting capabilities that, in some
cases, can identify and repair problems automatically. If you encounter
Internet connection problems—especially problems using high-speed
broadband Internet service—try these steps:
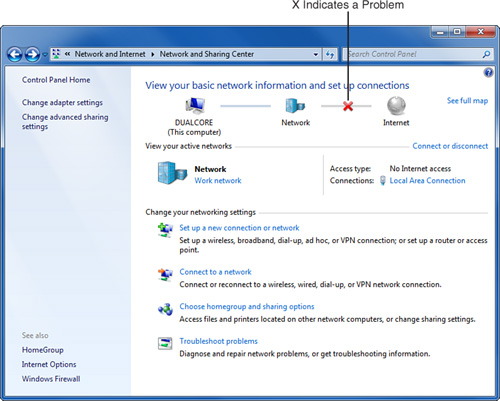
1. | Click
Start, Control Panel, View Network Status and Tasks (under Network and
Internet). This displays the Network and Sharing Center. If there is a
problem with your Internet connection, Windows displays a red X, as
shown in Figure 1.
|
2. | Double-click the red X.
|
3. | If Windows displays a message indicating that it might be able to repair the problem, click Repair.
|
4. | If
that does not solve the problem, go back to the Network and Sharing
Center. At the bottom of the page, click Troubleshoot Problems, and then
click Internet Connections. Click Advanced, Run As Administrator, and
then click Next. Follow the troubleshooting wizard’s prompts from there.
If the wizard’s diagnosis is “The DNS server isn’t responding,”
and if you connect to the Internet through a shared connection using a
router, this most likely means that your connection sharing router can’t
connect to the Internet. The problem is either with the router, your
cable or DSL modem, or its connection to the Internet. If you can bring up the router’s setup web page, the router is working,
so your best bet is to contact your ISP for further assistance.
|
5. | If
this does not fix the problem, and if your computer connects to the
Internet through a wireless or wired Ethernet connection, go back to the
Network and Sharing Center. Click Troubleshoot Problems, and select
Network Adapter. Again, click Advanced, Run As Administrator, and then
click Next.
|
If the problem occurred because your computer
failed to obtain its network settings from a router, this procedure will
often work. In many cases, though, you’ll need to locate the problem
yourself, using good, old-fashioned Sherlock Holmes–style deductive
reasoning. Here’s how it goes. Let’s assume that you are having trouble
using a certain website. It could be that
You can view some of its pages but not others, or you see text displayed but not the streaming video or sound.
In
this case, you know that your Internet connection itself is fine
because something does appear. The problem, then, is that the video or
sound application isn’t working. You might want to check the index to
see whether we discuss the application in this book. You might also
check the application’s built-in help pages. If the application was one
that you downloaded or purchased, check the manufacturer’s website for
support information or an updated software version.
Nothing on this particular site is responding. In this case, see if you can view any other website. Try www.google.com, www.quepublishing.com, your ISP’s website, or your local newspaper’s website.
If
you get a response from even one other website, again, your Internet
connection is fine. The problem is most likely with the site you’re
trying to use or with your ISP. Check to be sure that Internet Explorer
isn’t set up to block access to the site you’re interested in.
You
can’t view any web pages on any site. If this is the case, you know
that your Internet connection itself is at fault. This chapter can help
you find out what’s wrong.
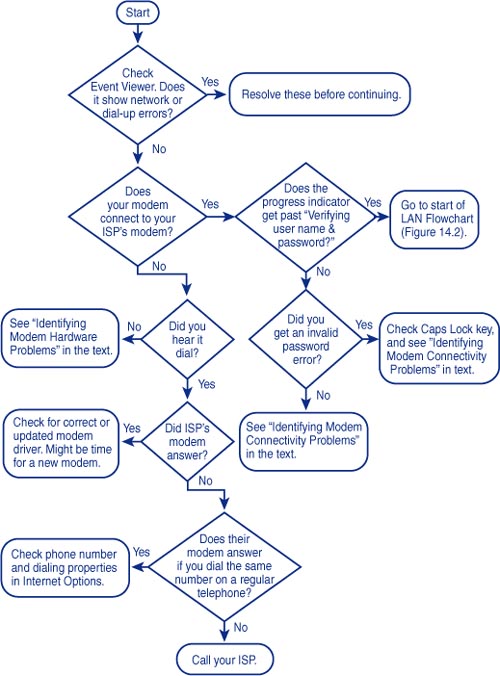
To that end, Figures 2 and 3
show flowcharts to help direct you to the source of the problem. The
first chart is for dial-up connections to an ISP; the second is for
broadband or LAN connections. If you’re having Internet connection
trouble, follow the appropriate flowchart for your type of connection.
The endpoints in each flowchart suggest places to look for trouble. I
discuss these in the sections that follow.