2. Adjusting Dial-Up Connection Properties
As
configured by the wizard, your dial-up connection is properly set up
for most ISPs. However, the wizard doesn’t do a good job of setting up
the area code and call-waiting settings, so you might want to manually
adjust these. You won’t likely need to change any of the other
settings, but just in case (and because I know you’re curious), I walk
you through the various settings and properties that are part of a
dial-up connection.
Tip
You
can instantly view your list of dial-up connections by clicking the
Network icon in the notification area of the taskbar, as described in
the next section. |
To adjust a connection’s properties, click the Network icon in the taskbar, as shown in Figure 2. This displays all dial-up connections you’ve configured (see Figure 3).
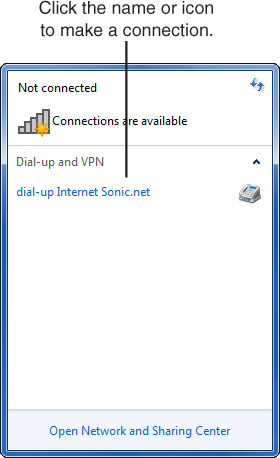
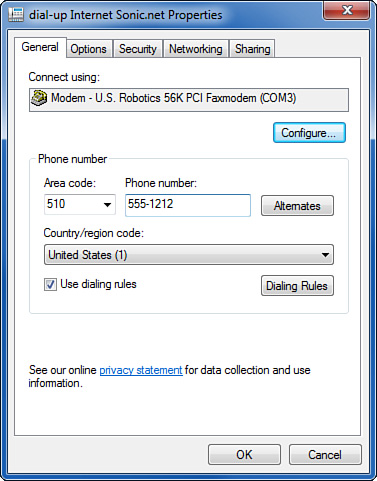
Right-click the icon for your dial-up connection and select Properties. You’ll see five tabs, shown in Figure 4, which I will run through in the order in which they appear. Only a few settings ever need to be changed for an ISP connection:
The
General tab lists modem properties and the ISP telephone number. The
following two settings are the most important ones to examine and if
necessary, change:
If you travel with
your computer, check Use Dialing Rules, and be sure that the ISP’s area
code is set correctly in its own box, and is not entered in the same
box as the phone number. Figure 4 shows how it should look.
If your telephone line has call waiting service, you must tell Windows to disable call waiting when it dials your ISP.
To
do this, click the Dialing Rules button. Select your current location
and click Edit. If the location name is “My Location,” change it to the
name of your city. Then, at the bottom, check To Disable Call Waiting,
Dial: and select the code used by your telephone company.
If
you have multiple modems, you can choose at the top of this tab which
one to use for this particular connection. (If you select more than one
modem, Windows will attempt to use them simultaneously. Don’t do this
unless your ISP offers “modem binding” service.)
Using the Configure button for the modem, you can set the maximum speed used to communicate from the computer to the modem. For external
modems connected via a COM port, if you don’t have a special-purpose
high-speed serial port, you might want to reduce this speed from the
default 115200 to 57600.
Using the
Alternates button for the telephone number, you can add multiple
telephone numbers for your ISP, which will be automatically tried, in
turn, if the first doesn’t answer.
On the Options tab, you can configure dialing and redialing options.
Select the Display Progress While Connecting option to have progress information displayed during the connection process.
Select
the Prompt for Name and Password, Certificate, etc. option to have
Windows 7 prompt you for your dial-up username and password each time
you connect. You can also use dial-up networking to log on to your
Windows domain. Don’t check this option if you use a commercial ISP;
that’s only for connections to corporate networks.
You can select to have Windows 7 prompt you for the phone number of your ISP each time you connect.
You
can select a time to wait before hanging up the line when no activity
occurs. By doing so, if you pay an hourly rate to your ISP, you can
help cut costs by having your computer disconnect itself from the
Internet if it detects that you’ve not been using your connection for a
set amount of time.
To maintain a permanent, or nailed-up,
dial-up connection, check Redial If Line Is Dropped and set the
disconnect time to Never. (Do this only with the consent of your ISP.)
The Security tab controls whether your password can be sent in unencrypted form. It’s okay to send your ISP password unsecured.
The
Networking tab determines which network components are accessible to
the Internet connection. If you’re dialing in to a standard ISP, leave
File and Printer Sharing unchecked.
Tip
If
you want to rename a dial-up connection, you have to go about it an odd
way: Open the Network and Sharing Center and select Manage Adapter
Settings. An icon for your dial-up connection will appear here.
Right-click it and select Rename. |
The
Sharing tab allows other network users to connect through your
computer’s Internet connection.
Click OK to save your changes.