If you use a dial-up connection with an
analog modem, after you’ve set up an icon for your ISP, making the
connection is a snap. You use this same procedure if you use a
broadband connection with Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
that requires you to log on:
1. | Click the Network icon in your taskbar .
|
2. | Select the appropriate connection from the list and click Dial.
|
3. | When Windows displays a connection dialog box (see Figure 1). If you previously let Windows remember the password, you can simply skip ahead to step 4.
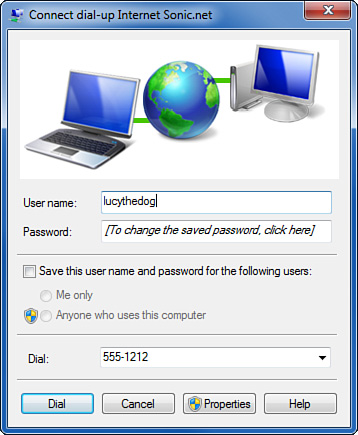
Otherwise, enter the password assigned by your ISP. At this point, you
can check Save This User Name and Password for the Following Users.
Select “Me Only” or, if you want to allow others to connect with your
account (or you don’t care who uses your account), select Anyone Who
Uses This Computer. Then, click Dial.
|
4. | For
a dial-up connection only, check that the phone number is correct,
including area code and any required prefix numbers. You might need to
click Properties to correct your current location (Dialing From) and/or
the Dialing Rules if the prefix or area code isn’t correct.
|
5. | Click Dial to make the connection.
|
Windows then dials your ISP and establishes the connection.
If
you attempt to connect to your ISP, but the modem doesn’t make an
audible attempt to connect, there are several possible solutions: Your
phone line might not be correctly plugged into the modem. Be sure the
phone cable is plugged into the correct jack on the modem. The phone line might not be working. Try an extension phone in the same wall jack to see if there’s a dial tone. The
modem might be working, but its speaker volume might be turned down.
(This has fooled me more than once!) Some external modems have volume
knobs. You can set the volume on an internal modem by opening Control
Panel, Hardware and Sound, Device Manager. Expand the Modems option in
the tree to view all your modems, right-click the modem in the tree,
and select Properties. Select the Modem tab and adjust the volume
control. The modem might have a hardware
problem. Open the modem properties, as described in the previous
paragraph. View the Diagnostics tab and click Query Modem. After 5–15
seconds, you should see some entries in the Command/Response list. If
an error message appears instead, your modem is not working properly.
If it’s an external modem, be sure it’s powered up.
|
|
If
the connection fails, Windows displays a (usually) sensible message
explaining why: There was no dial tone because your modem is unplugged,
there was no answer at the ISP or the line is busy, or your user ID and
password failed. In the last case, you get three tries to enter the
correct information before Windows hangs up the phone.
If
you attempt to connect to your ISP, and the modem makes the call, but
the Internet connection still fails, Windows should indicate what sort
of problem was encountered. You might have typed your account name and
password incorrectly. Try one or two more times. If it still doesn’t
work, a call to your ISP is the best next step. Your ISP might require
you to enter the account name information in an unintuitive way.
(Earthlink, for example, at one time required you to put ELN\ before your account name.) Your ISP’s customer support people can help you straighten this out. |
|
When your connection is made, you should be able to browse websites, check your email, and so on.
Hanging Up a Dial-Up Connection
When you finish using your Internet connection, click the Network icon in the taskbar. Click the name of your Internet connection, then click Disconnect. Windows will hang up the connection.