2. Controlling Device Installation
When
you are formulating a plan to control the installation of devices
(typically, USB devices) in your enterprise, you can use Group Policy to
specify whether devices can be installed and, if so, which criteria
should be applied. Depending upon company policy, your plan could have
one of the following outcomes:
Prevent users (except for administrators) from installing any device.
Allow users to install only devices that are on an approved list. If a device is not on the list, the user cannot install it.
Prevent users from installing devices that are on a prohibited list. If a device is not on the list, the user can install it.
Deny
read or write access to users for devices that are removable or that
use removable media such as CD and DVD burners, external hard drives,
and portable devices such as media players, smart phones, or Pocket PC
devices.
You need to be familiar with the device
installation process and the identification strings that match a device
with the device driver packages available on a computer. Obtaining
device identities (IDs) and global unique identifiers (GUIDs) is
discussed later in this section.
By restricting the devices that users can
install, you can reduce the risk of data theft. Users will find it more
difficult to make unauthorized copies of company data if they cannot
install unapproved devices that support removable media on their
computers. You can plan to use Group Policy to deny write access to
users for devices that are removable or that use removable media.
Restricting device installation can also reduce support costs. You can
ensure that users install only those devices that your help desk is
trained and equipped to support. This reduces both support costs and
user confusion.
In an enterprise environment in which you manage a
large number of client computers, you can apply Group Policy settings
to manage device installation on computers that are members of a domain
or of an OU in a domain. You can choose from one of the following
strategies:
Prevent installation of all devices
You plan to prevent standard users from installing any device but to
allow administrators to install or update devices. In this scenario, you
configure two computer Group Policy settings. The first prevents all
users from installing devices, and the second exempts administrators
from the restrictions.
Allow users to install authorized devices only
You plan to allow users to install only the devices included on a list
of authorized devices. In this scenario, you initially prevent standard
users from installing any device. You then create a list of authorized
devices and configure Group Policy so that standard users can install
only specified devices.
Prevent installation of prohibited devices only
You plan to allow standard users to install most devices but prevent
them from installing devices included on a list of prohibited devices.
In this scenario, you do not use Group Policy to prohibit installation
of all devices; instead,
you create a list of prohibited devices and configure Group Policy so
that standard users can install any device except those on the list.
Control the use of removable media storage devices
You plan to prevent standard users from writing data to removable
storage devices or to devices with removable media such as USB memory
drives or a CD or DVD burner. In this scenario, you configure a computer
Group Policy to allow read access but deny write access to USB memory
devices and to any CD or DVD burner device on users’ computers. You can
then configure a setting that prevents this policy from affecting users
who are members of the Administrators group.
Note: System installation
These plans and policies do not restrict the use
of devices by the system, for example, the Windows ReadyBoost feature
on Windows Vista clients.
Group Policy Settings That Control Device Installation
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 introduce
new policy settings that enable you to control device installation. You
can configure these policy settings individually on a single computer,
but in the enterprise environment, you are more likely to apply them to a
large number of computers through Group Policy in an Active Directory
domain. These are computer policies and affect any user logged on to a
computer, except for the Allow Administrators To Override Device
Installation Policies setting, which exempts members of the built-in
local Administrators group from any of the device installation
restrictions. The following policy settings allow you or members of your
administrative team to implement your device installation plan:
Prevent Installation Of Devices Not Described By Other Policy Settings
If this policy setting is enabled, users cannot install or update the
drivers for devices unless they are described by either the Allow
Installation Of Devices That Match Any Of These Device IDs policy
setting or the Allow Installation Of Devices Using Drivers That Match
These Device Setup Classes policy setting. If your plan involves
disabling or not configuring this policy setting, users can install and
update the driver for any device that is not described by the Prevent
Installation Of Devices That Match Any Of These Device IDs policy
setting, the Prevent Installation Of Devices Using Drivers That Match
These Device Setup Classes policy setting, or the Prevent Installation
Of Removable Devices policy setting.
Allow Administrators To Override Device Installation Restriction Policies
If this policy setting is enabled, it allows members of the local
Administrators group to install and update the drivers for any device,
regardless of other policy settings. Administrators can use the Add
Hardware Wizard or the Update Driver Wizard to install and update the
drivers for any device. If your plan disables or does not configure this
policy setting, administrators are subject to all policy settings that
restrict device installation.
Prevent Installation Of Devices That Match Any Of These Device IDs
This policy setting enables you to specify a list of Plug and Play
hardware IDs and compatible IDs for devices that users cannot install.
Enabling this policy setting prevents users from installing or updating
the driver for a device if any of its hardware IDs or compatible IDs is
included in the list. If your plan disables or does not configure this
policy setting, users can install devices and update their drivers as
permitted by other policy settings for device installation. This policy
setting takes precedence over any other policy settings that allow users
to install a device and prevents users from installing a device even if
its ID matches another policy setting that would allow installation.
Prevent Installation Of Devices Using Drivers That Match These Device Setup Classes
This policy setting enables you to specify a list of Plug and Play
device setup class GUIDs that define devices users cannot install. If
you enable this policy setting, users cannot install or update drivers
for a device that belongs to any of the listed device setup classes. If
your plan disables or does not configure this policy setting, users can
install and update drivers for devices as permitted by other policy
settings for device installation. This policy setting takes precedence
over any other policy settings that allow users to install a device and
prevents users from installing a device with a GUID on the list even if
its ID matches another policy setting that would allow installation.
Allow Installation Of Devices That Match Any Of These Device IDs
If you enable this policy setting, you can specify a list of Plug and
Play hardware IDs and compatible IDs that describe devices users can
install. Plan to use this setting only when the Prevent Installation Of
Devices Not Described By Other Policy Settings policy setting is enabled
and does not take precedence over any policy setting that would prevent
users from installing a device. If you enable this policy setting,
users can install and update any device with a hardware ID or compatible
ID that matches an ID in this list if that installation has not been
specifically prevented by the Prevent Installation Of Devices That Match
These Device IDs policy setting, the Prevent Installation Of Devices
Using Drivers That Match These Device Setup Classes policy setting, or
the Prevent Installation Of Removable Devices policy setting. If another
policy setting prevents users from installing a device, users cannot
install it even if the device is also described by a value in this
policy setting. If your plan involves disabling or not configuring this
policy setting and no other policy describes the device, the Prevent
Installation Of Devices Not Described By Other Policy Settings policy
setting determines whether users can install the device.
Allow Installation Of Devices Using Drivers That Match These Device Setup Classes
If you enable this policy setting, you can specify a list of device
setup class GUIDs that describe devices users can install. Plan to use
this setting only when the Prevent Installation Of Devices Not Described
By Other Policy Settings policy setting is enabled and does not take
precedence over any policy setting that would prevent users from
installing a device. If you enable this setting, users can install and
update any device with a device setup class that matches one of the
device setup class GUIDs in this list unless that installation has not
been specifically prevented by the Prevent Installation Of Devices That
Match Any Of These Device IDs policy setting, the Prevent Installation
Of Devices Using Drivers For These Device Setup Classes policy setting,
or the Prevent Installation Of Removable Devices policy setting. If
another policy setting prevents users from installing a device, users
cannot install it even if the device is also described by a value in
this policy setting. If your plan involves disabling or not configuring
this policy setting and no other policy setting describes the device,
the Prevent Installation Of Devices Not Described By Other Policy
Settings policy setting determines whether users can install the device.
Note: Planning device installation
The way the device installation computer
policies interact with each other is fairly intuitive and not as complex
as it seems when described on paper. If you are formulating plans in
this area, practice using these policies until you are familiar with
what they do and how they interact.
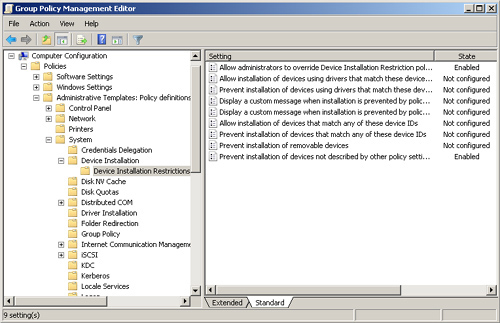
Figure 4 shows the Device Installation Restriction policies in Group Policy Management Editor. Figure 5
shows one of the simplest and most used sets of policy settings that
prevents standard users from installing devices but permits
administrators to do so.
Obtaining Hardware IDs, Compatible IDs, and GUIDs
You can allow or prevent
the installation of specific devices by enabling the appropriate Group
Policy setting and adding a list of hardware IDs, compatible IDs, or
both. You can also specify device setup class GUIDs that describe
devices users can install.
Hardware IDs
Hardware IDs provide the most exact match
between a device and a driver package. The first string in the list of
hardware IDs is referred to as the device ID because it matches the
exact make, model, and version of the device. The other hardware IDs in
the list match the details of the device less exactly. For example, a
hardware ID might identify the make and model of the device but not the
specific version. This scheme allows Windows to use a driver for a
different version of the device if the driver for the correct revision
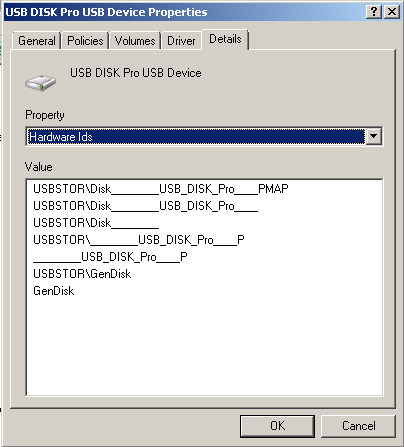
is not available. Figure 6
shows the list of hardware IDs for a USB flash memory device. You can
access this from the device’s Properties dialog box in Device Manager.
Compatible IDs
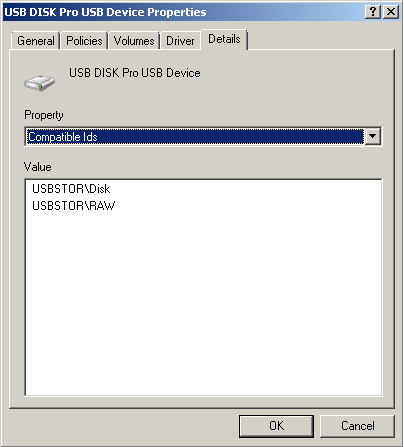
Windows Server 2008
uses compatible IDs to select a device driver if the operating system
cannot find a match with the device ID or any of the other hardware IDs.
Compatible IDs are listed in the order of decreasing suitability. These
strings are optional and, when provided, they are generic, such as
Disk. When a match is made using a compatible ID, you can typically use
only the most basic functions of the device. Figure 7 shows the list of hardware IDs for a USB flash memory device.
GUIDs
A
GUID defines a device setup class, which the device manufacturer
assigns to a device in the device driver package. The device setup class
groups devices that are installed and configured in the same way. For
example, all CD drives belong to the CDROM device setup class and use
the same co-installer. When Windows Server 2008 starts, it builds a tree
structure in memory with the GUIDs for all the detected devices.
In addition to the GUID for the device setup
class of the device itself, Windows Server 2008 might need to insert the
GUID for the device setup class of the bus to which the device is
attached (for example, USB). When you use device setup classes to
control users’ installation of device drivers, you must specify the
GUIDs for all the device’s device setup classes, or you might not
achieve the results you want. In addition, GUIDs are held in the HKLM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\ClassGUID registry key and are not as easily obtained as hardware IDs.
For these reasons, hardware IDs rather than GUIDs are typically used to specify the devices than can or cannot be installed. Figure 8 shows a hardware ID list specified for the Allow Installation Of Devices That Match Any Of These Device IDs setting.
