When you modify an object in your project file, such
as the Standard Task Calendar, or create a new custom view or report,
they are only available and saved within the currently opened project
file. Project 2010 provides the Organizer feature, which enables you
to manage and reuse custom or modified objects. The Organizer is used
to copy modified or custom objects from one project file to another or
to GLOBAL.MPT.
To access the Organizer, select the File tab, Organizer (see Figure 1).

You can also access the Organizer by using one of the following options:
Accessing the More Views dialog box by selecting the View tab, Task Views or Resource Views, Other Views, More Views, Organizer
Accessing the More Tables dialog box by selecting the View tab, Data, Tables, More Tables, Organizer
Accessing the More Filters dialog box by selecting the View tab, Data, Filter, More Filters, Organizer
Accessing the More Groups dialog box by selecting the View tab, Data, Group by, More Groups, Organizer
Table 18.2 lists objects contained within the Organizer.
Table 1. Organizer Objects
| Type | Description |
|---|
| Views | Views
are tables and charts that are used to organize, categorize, and
display project data. Views are used to view two main categories of data
within project: tasks and resources. Project provides three different
types of views: charts or graphs, sheets, and forms. You can customize
views to create new views to fit your needs.
|
| Reports | Reports
are predefined, printable representations of project information. You
can customize reports so that they best fit your needs.
|
| Modules | Modules represent macros that you create within Microsoft Project. Microsoft Project uses Visual Basic to create macros. |
| Tables | Tables
are collections of fields, organized by rows and columns, reminiscent
of a spreadsheet. Tables are used in many views, either by themselves or
in conjunction with charts or graphs. You can customize tables to best
fit your needs.
|
| Filters | Filters
are used to highlight or isolate specific information in the view based
on the specified criteria. Microsoft Project supports two types of
filters: task and resource. You can customize filters to best fit your
needs. |
| Calendars | Calendars
are used for specifying date exceptions and details to be used within
the project schedule. Microsoft Project contains three types of
calendars: project, task, and resource. You can customize calendars to
best fit your needs. |
| Maps | Maps
are used to track data exported to other programs. They are also used
in the Export Wizard when saving project data to Excel or other export
formats.
|
| Fields | Fields
are columns or boxes that contain a specific type of information about a
task, resource, or assignment. You can create custom fields to best fit
your needs.
|
| Groups | Groups
are tools to organize and summarize the display of project information.
Project supports two types of groups: task and resource. You can
customize groups to best fit your needs. |
The GLOBAL.MPT File
GLOBAL.MPT
is a special type of file in Microsoft Project that is a part of every
new or existing project file. All projects inherit all the features of
the GLOBAL.MPT. The first time you launch Microsoft Project, a copy of
the GLOBAL.MPT file is created and becomes the active GLOBAL.MPT file. A
backup of the GLOBAL.MPT is also created, called GLOBALbackup.MPT. The
global contains all the default objects that Project comes with, such as
the Gantt Chart view or the standard calendar (see the list of objects
in Table 1).
It also contains the default selections in the Tools, Options dialog
box. For instance, if you change the Default task type from Fixed Units
to Fixed Duration in the Schedule tab of Tools, Options, and click the
Set as Default on the screen, you have changed the GLOBAL.MPT. Whenever
you make changes to the GLOBAL.MPT file, you affect all new project
files created from that point forward. GLOBAL.MPT is stored in the
default location on every computer under C:\Program Files\Microsoft
Office\OFFICE12\1033 directory.
When
you open GLOBAL.MPT, you will see the Organizer but it will not act as a
normal project file. There are two ways you could share the objects of
the GLOBAL.MPT from your desktop with others: Send your GLOBAL.MPT to
them to copy and use, or send a project with the custom objects you have
built. They can open the file on their desktop and move the custom
objects into their own GLOBAL.MPT using the Organizer.
Manipulating Objects Using the Organizer
You can use the Organizer
to copy, rename, and delete objects in Project. Rather than opening the
GLOBAL.MPT file directly, you can move custom fields or changes to
default objects within any project file to the GLOBAL.MPT using the
Organizer. The following sections explore the details of each one of
these actions.
Using the Organizer to Copy Objects
To open an object by using the Organizer, open the file that contains the custom object and follow these steps:
1. | To
display the Organizer, select the File tab, Organizer. Note that if you
are copying an object to a file other than GLOBAL.MPT, make sure that
both the source and the target files are open.
|
2. | Select the tab that contains the object you would like to copy. Figure 2
shows the Fields tab selected. The fields that have been used,
modified, or newly created are listed on the right. The fields that
would currently be included in the GLOBAL.MPT file are listed on the
left.
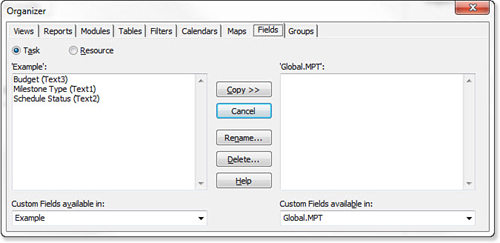
|
3. | Use the Custom Fields Available In drop-down box on the left to specify the target file to have the selected object copied into.
|
4. | Use the Custom Fields Available In drop-down on the right to specify the source file to copy the selected object from.
|
5. | Use the Task or Resource radio button to specify the type of field you would like to copy.
|
6. | Select the field you would like to copy from your source file (on the right).
Tip You
can copy multiple objects at once by selecting the first one and
holding down the Shift key to select a range of objects. You can also
select objects that are contained in the list out of order by holding
down the Ctrl key and selecting each one. |
|
7. | Click
the Copy button to copy the field. If a field with the same name
already exists in the target file, Project will display a confirmation
to replace the former field with a new one (see Figure 3).
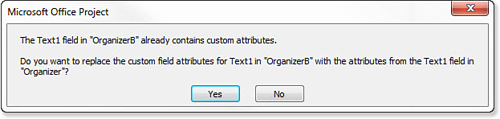
|
8. | Click
the Yes button to replace the field in the target file with the one
from the source file. You can also click Cancel from the warning dialog
box and then click the Rename button in the Organizer to provide another
name that is currently not being used for the field being copied to the
target file.
Tip If
you accidentally overwrite an object, you can restore it by copying it
from the GLOBAL.MPT file, as long as the object in the GLOBAL.MPT file
has not previously been customized. You might want to make a backup copy
of the GLOBAL.MPT before making major changes so that you can copy the
original object to replace the edited one. |
|
9. | Click the Close button to close the Organizer dialog box and save your changes.
|
Using the Organizer to Rename Objects
In addition to copying objects, you can also use the Organizer to rename existing ones.
Note
If
the item you are copying is currently visible in Microsoft Project and
you are copying the item from a file into the currently active project,
you will get a message saying you cannot perform the copy. |
To rename an object using the Organizer, follow these steps:
1. | Open the Organizer by selecting the File tab, Organizer.
|
2. | Select the tab for the object you would like to rename.
|
3. | In the GLOBAL.MPT file that you want to reflect the change, select the object to rename.
|
4. | Click the Rename button.
|
5. | Provide the new name and click the OK button to save your changes.
|
6. | Click Close to exit the Organizer window.
|
Note
Objects
in the GLOBAL.MPT file are not automatically updated. So, in order for
your changes to be reflected in the new project files, the custom object
must be copied in the GLOBAL.MPT. Any existing projects that contain
the object must be manually updated as well. |
Using the Organizer to Delete Objects
You can use the Organizer
to permanently delete objects. Note that you cannot delete objects
currently in use. To do so, follow these steps:
1. | Open the Organizer by selecting the File tab, Organizer.
|
2. | Select the tab that contains the object you would like to delete.
|
3. | In the GLOBAL.MPT file that contains the object, select the object to delete.
|
4. | Click the Delete button. A confirmation box appears. Click Yes to confirm object deletion.
|
5. | Click the Close button to exit the Organizer window. |