3. Block options
One of the most common formatting effects in
traditional publishing, long absent from Web publishing, is justified
text — text that appears as a solid block. Justified text is possible
with the Text Align attribute, one of the seven options available in the CSS Block category, as shown in Figure 4. Indented paragraphs are also a possibility.
Dreamweaver includes an option for setting the Display attribute. As the name implies, the Display attribute determines how an element should be presented. Display
accepts a wide range of values — 18 in all — but only a few are
currently supported by even the latest browsers. That said, the
supported values — block, inline and, curiously enough, none — are very important indeed. Setting a Display attribute to None effectively hides the element to which the CSS attribute is applied; setting the same attribute to Block or Inline reveals the element. Many collapsible/expandable lists depend on the Display attribute to achieve their effects.
Table 3 lists the CSS Block options.
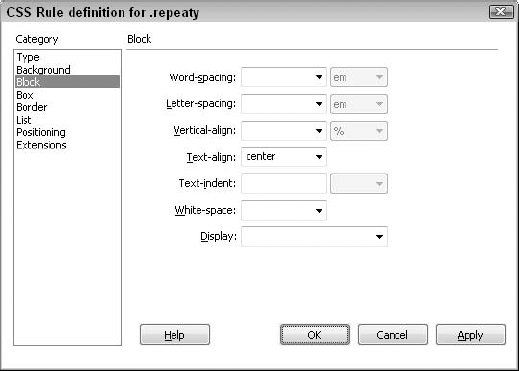
Table 3. CSS Block Attributes| Block Setting | Description |
|---|
| Word Spacing | Defines
the spacing between words. You can increase or decrease the spacing
with positive and negative values, set in ems by default. (In CSS, 1 em
is equal to the height of a given font.) If you have a 12 pt. font, to
increase the spacing between words to 24 pts., set the Word Spacing
value to 2 ems. | | Letter Spacing | Defines
the spacing between the letters of a word. You can increase or decrease
the spacing with positive and negative values, set in ems by default. | | Vertical Alignment | Sets
the vertical alignment of the style. Choose from baseline, sub, super,
top, text-top, middle, bottom, or text-bottom, or add your own value. | | Text Align | Sets text alignment (left, right, center, and justified). | | Text Indent | Indents the first line of text on a style by the amount specified. | | Whitespace | Controls
display of spaces and tabs. The normal option causes all whitespace to
collapse. The Pre option behaves similarly to the <pre> tag; all whitespace is preserved. The Nowrap option enables text to wrap if a <br> tag is detected. | | Display | Determines
how a tag is represented. Possible values include none, inline, block,
list-item, run-in, compact, marker, table, inline-table,
table-row-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row,
table-column-group, table-column, table-cell, and table-caption. |
4. Box options
The Box attribute defines the placement and settings for elements (primarily images) on a page. Many of the controls (shown in Figure 5) emulate spacing behavior similar to that found in <table>
attributes. If you are already comfortable using HTML tables with cell
padding, border colors, and width/height controls, you'll quickly learn
how to use these Box features, which are described in Table 4.
|
To have the same padding or margins all around a box
area, check the Same For All option. This option allows you to set one
value — Top — to use for all four sides.
|
|
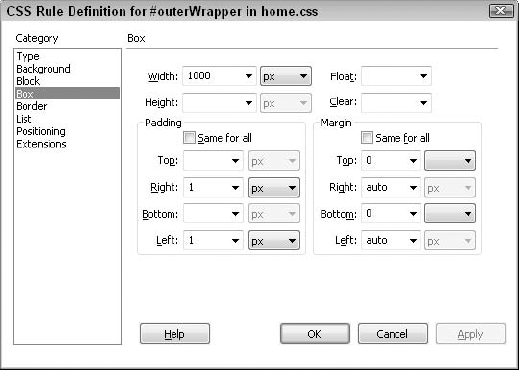
Table 4. CSS Box Attributes| Box Setting | Description |
|---|
| Width | Sets the width of the element. | | Height | Defines the height of the element. | | Float | Places the element at the left or right page margin. Any text that encounters the element wraps around it. | | Clear | Sets
the side on which AP elements cannot be displayed next to the element.
If an AP element is encountered, the element with the Clear attribute places itself beneath the AP element. | | Margin | Defines the amount of space between the borders of the element and other elements in the page. | | Padding | Sets
the amount of space between the element and the border or margin, if no
border is specified. You can control the padding for the left, right,
top, and bottom independently. |
5. Border options
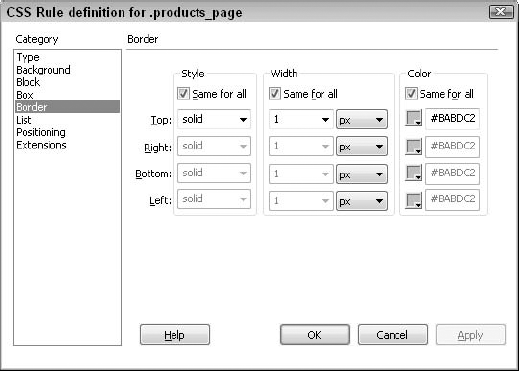
With Cascading Style Sheets, you can specify many
parameters for borders surrounding text, images, and other elements such
as Java applets. In addition to specifying separate colors for any of
the four box sides, you can also choose the width of each side's border,
as shown in the CSS Border category (see Figure 6). You can use eight different types of border lines, including solid, dashed, inset, and ridge. As with the Padding and Margin attributes in the Box category, Dreamweaver includes a Same For All option under the Style, Width, and Color attributes to save you the work of having to enter the same value for all four sides. Table 5 lists the Border options.
Table 5. CSS Border Attributes| Border Setting | Description |
|---|
| Style | Sets
the style of the border. You can use any of the following border
styles: dotted, dashed, solid, double, groove, ridge, inset, and outset. | | Width | Determines the width of the border on each side. Choose thin, medium, or thick, or enter a number to set a width. | | Color | Sets the color of the border on each side. |
|
CSS Border attributes are especially useful for highlighting paragraphs of text with a surrounding box. Use the Box category's Padding attributes to inset the text from the border. |
|