Unsolicited email messages are often
referred to as spam. These usually unwanted and often offensive
messages are utilized as cheap advertising for unscrupulous
organizations. In the past several years, the increase in spam traffic
has surpassed even the most liberal estimates, and many studies have
found that spam traffic accounts for up to 85%–90% of the messaging
traffic on the Internet today.
Spam does
not just affect your patience and productivity; it affects companies,
Internet service providers, and anyone else who is hosting messaging
services. The battle against spam is just beginning, and legal battles
are well under way against both known spammers and companies that host
the messaging services. In some cases, employees are suing employers on
grounds that the employer has not taken adequate steps to protect them
from offensive materials.
Exchange Server 2007 Antispam Features
Spammers
are becoming increasingly more creative and cunning, frequently
changing their email addresses, domain names, content, and more to get
past a company’s protective measures.
Microsoft
has provided at least some basic form of antispam technologies in
Exchange since version 5.5 and Outlook 98. For example, junk mail
filters were provided to help identify messages that had either
offensive material or other keywords indicating the message was spam.
This form of spam prevention placed most, if not all, of the
responsibility on the end user to block unwanted email messages.
Exchange Server 2007, when combined with Outlook 2007, provides several methods of reducing unwanted spam messages:
Increase protection through integrated security technologies
Improved email legitimacy assurance
Distribution lists restricted to authenticated users
Connection filtering
Content filtering
Frequent antispam updates
Spam quarantine
Recipient filtering
SenderID
Sender reputation
IP reputation service
Outlook junk email filter lists aggregation
Protecting Against Web Beaconing
A
common and very popular format for email messages is Hypertext Markup
Language, or HTML. This format is so popular because of the rich
content that can be presented, including graphics, images, font
formatting, and more. However, HTML-based messages can also present
security problems and annoyances because of the ability to hide various
codes and images within the message.
One such security problem is called web beaconing. Web beaconing
is a term used to describe the method of retrieving valid email
addresses and information on whether a recipient has opened a message.
Advertisers, spammers, and the like utilize web beaconing to help them
become more profitable and improve audience targeting. For instance,
when an unsuspecting user opens an email message that contains a web
beacon, the user’s email address and possibly other information is sent
to the solicitor, notifying them that they a) have reached a valid
recipient and b) have reached a recipient who is willing to open their
message before deleting it. The user is oblivious that their personal
information has been given.
Outlook 2003
and 2007 can be used to block web beacons and, consequently, prevent
the user’s email address from ending up in the wrong hands. By default,
if Outlook suspects that the content of a message could be used as a
web beacon, it presents a pop-up window warning users that links to
images, multimedia, or other external content have been blocked to help
protect their privacy. The text content of the email message is
viewable by the user, and the user is then presented with an option to
unblock the content. This enables the user to make a conscious decision
of whether to display all the contents of the message.
This
default setting is recommended because it is an excellent way to
protect end users from unsolicited emails; however, it is possible to
disable this option. To change the default settings in Outlook 2003, do
the following:
1. | In Outlook 2003, select Tools, Options.
|
2. | Click the Security tab and then click Change Automatic Download Settings.
|
3. | In
the Automatic Picture Download Settings window, choose whether to
download pictures or other content automatically. Outlook 2003 can also
be customized to automatically download content from safe lists or from
websites listed in the trusted Microsoft Internet Explorer security
zones.
|
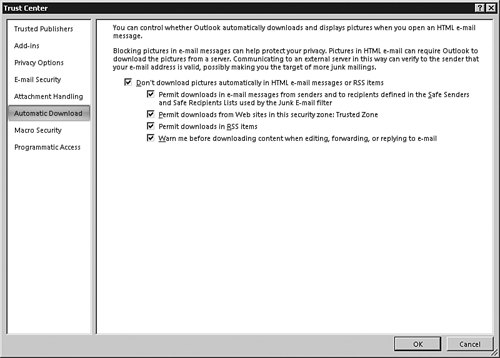
To change the default settings for automatic downloading of content in Outlook 2007, do the following:
1. | Select Tools, Trust Center.
|
2. | Click the Automatic Download tab, as shown in Figure 1. Select the desired settings from the available options. By default, all options are selected.
|
Note
If
Automatic Picture Download is turned off, messages from or to email
addresses or domain names on the Safe Senders and Safe Recipients lists
are treated as exceptions and the blocked content is downloaded. Safe
Senders and Safe Recipients lists are discussed in more depth later in
this chapter.