Status System
ConfigMgr
maintains status on many of its technologies. Package status provides a
summary of the version and time packages were copied to various
distribution points. Advertisement status details when clients have
received advertisements and started advertisements. It also shows the
succeeded or failed status in the overall execution of the
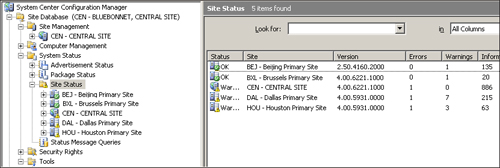
advertisement. Site status gives administrators a bird’s-eye view of the
health of the entire ConfigMgr site’s infrastructure. ConfigMgr’s
component status details the health of each individual component in the
site, such as discovery method’s running state, sender health, DPs, MPs,
and so on. Figure 6 shows the site status system from the ConfigMgr console.
Desired Configuration Management
DCM is a component built
in to ConfigMgr that was previously provided in an SMS 2003 feature
pack. DCM allows you to assess the compliance of computers with regard
to a number of configurations, such as whether the correct Microsoft
Windows operating system versions are installed and configured
appropriately, whether all required applications are installed and
configured correctly, whether optional applications are configured
appropriately, and whether prohibited applications are installed. You
can also check for compliance with software updates and security
settings.
DCM is a
framework where the ConfigMgr client has an agent, enabled at the site
level, tracking baselines defined by the ConfigMgr administrator. You
can also track deviations from the baseline. Each item, known as a configuration item,
is tracked against a baseline; the item can be reported against or be
corrected when the deviation occurs. System Center Configuration Packs,
available from the Microsoft System Center Pack Catalog at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?Linkid=71124, define Microsoft best practices for various product configurations.
You can evaluate
both published and manually created baselines for compliance in your
organization. Published configuration data from Microsoft and other
vendors is available at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=71837. You can assign these configuration baselines to a collection, just like an advertisement, and evaluate them on a schedule independent
of inventory and other agent schedules. Similar to inventory
information, you can evaluate configuration baseline compliance when
clients are offline; ConfigMgr sends the compliance data upon
reconnection to the site hierarchy. Figure 7 displays the DCM home page in the Configuration Manager 2007 console.
Network Access Protection
NAP, new in
ConfigMgr 2007, works with the Microsoft Windows Network Policy Server
(NPS) on Windows Server 2008. NAP helps enforce compliance with selected
software updates on clients capable of supporting NAP (NAP-capable
clients). These clients include Windows XP SP 3 and Windows Vista. Using
NAP, a client has restricted network access until it becomes compliant.
Configuration
Manager by itself does not enforce compliance with Network Access
Protection; it provides the means by which Configuration Manager clients
produce a statement of health with a noncompliant status if they do not
have the required software updates in the Configuration Manager NAP
policies you configure. A Configuration Manager System Health Validator
(SHV) point confirms the health state of the computer as compliant or
noncompliant and passes this information to the Network Policy Server. Policies
on the NPS then determine whether noncompliant computers will be
remediated and, additionally, whether they will have restricted network
access until they are compliant.
Remediation is the
mechanism of making a noncompliant computer compliant to ensure that
clients conform to compliance policies. Configuration Manager
remediation uses the software update packages you have already created,
with the Software Updates feature.
Reporting
Reporting in ConfigMgr is
functionally very similar to that in SMS 2003. Dozens of reports,
utilizing Transact-SQL (T-SQL), expose detailed hardware and software
inventory data about the clients in the hierarchy. ConfigMgr 2007 adds a
number of troubleshooting reports.
You can launch reports
directly through the ConfigMgr console or through the reporting point
site system website, and you can easily create custom reports utilizing
the existing SQL views exposing the ConfigMgr site’s data.
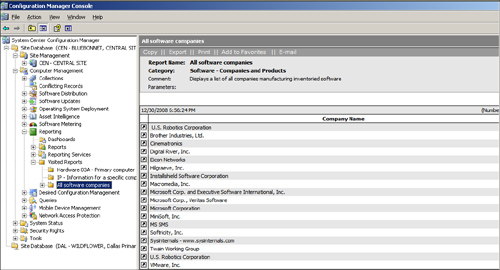
Figure 8
illustrates ConfigMgr reports; this particular report lists all
software companies collected during software inventory. With
Configuration Manager 2007 R2, you can choose to use Microsoft SQL
Reporting Services for reporting.
Reports only query data
from the local site server, some of which will be from child sites in
the hierarchy if they exist. Because inventory and other types of data
flow up the hierarchy, child sites data will show up in ConfigMgr
reports run on a parent site. ConfigMgr groups reports into categories
to facilitate organization, and reports may link to one another
to provide an experience similar to drill-down reporting. You can
configure reports to prompt the user for data, to provide lists of
available options for prompts, or to be fully automated.
Security
Security in ConfigMgr is
based completely on WMI, Microsoft’s implementation of Web-Based
Enterprise Management. WBEM allows access to providers such as Win32,
WMI, SNMP, and Desktop Management Interface (DMI). In addition to
collecting data, WBEM provides a method to secure the data by utilizing a
class and instance model. As an example, the Packages node is a class
containing a package for Microsoft Office, which would be an instance
within the Packages class.
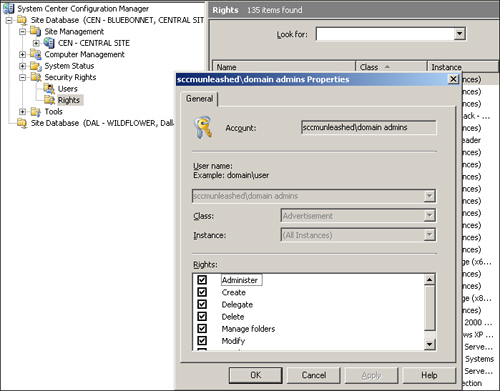
As shown in Figure 9,
you need to permit granular rights specific to the class to individuals
or groups, and then to specific instances of that class. Although a
ConfigMgr administrator may have administrative rights on the ConfigMgr
server and the SQL database for ConfigMgr, if not granted class and
instance rights through the ConfigMgr console, the administrator cannot
access any of the ConfigMgr objects within the ConfigMgr console.
By
default, only the account used to install ConfigMgr has rights to all
ConfigMgr classes and instances. As a best practice, the account used to
install ConfigMgr should be a service or application account.