After creating packages/programs and the
collection you intend to advertise them to, it is important to
understand how ConfigMgr distributes programs. Here are the three major
types of distribution points in ConfigMgr:
Standard distribution points
BITS-enabled standard distribution points
Branch distribution points
In
addition, each type of distribution may be “protected.” The next
sections discuss each of these distribution points and their usage in
the ConfigMgr 2007 software deployment process.
Tip: Client Roaming and Distribution Points
Client
roaming allows clients to move between sites in the ConfigMgr hierarchy
and still be managed while making the best use of available network
resources. Roaming allows a client currently not in the boundaries of
its site to find the closest distribution point to download source
files for functions such as software distribution. Roaming clients can
access advertisement content as long as the content is available from
the distribution point if the setting “When a client is connected
within a slow or unreliable network boundary:
Do not run program” is unchecked on the advertisement (configured on
the Advertisement Properties, Distribution Points tab). If a client is
roaming to a subnet boundary outside the boundaries of a ConfigMgr
site, it will be unable to access ConfigMgr resources.
1. Standard Distribution Points
ConfigMgr deploys software using distribution points. A distribution point
(DP) is a server role in ConfigMgr that receives packages for
distribution throughout the site. DPs provide local network access to
software distributed by ConfigMgr. As an example, if Microsoft Office
is being deployed to an environment with locations in Dallas, Houston,
Beijing, and Brussels, it is preferable for each of these locations to
install from the local area network (LAN), versus copying the data
across the link multiple times to install the software on the client
workstations in that location.
Distribution points are server roles defined in ConfigMgr console -> Site Database -> Site Management -> <Site Code> <Site Name> Site Settings -> Site Systems. ConfigMgr adds new servers as either a new server or a new server share.
Note: Comparing Server and Server Share Distribution Points
A
distribution point is the only site system you can create as a server
share; all other roles are created as servers. Server shares allow you
to choose a specific drive and create a Windows share that ConfigMgr
uses for the distribution point role—but the disadvantage is you have
to monitor that share to ensure the drive does not fill up. When the
distribution point is a server, ConfigMgr will manage the space for you
by creating new SMSPKGx$ shares when
more space is required. The downside with server-based distribution
points is you cannot control growth; ConfigMgr can potentially take
over all available NTFS drive space on the designated server.
Distribution points on servers can also be configured as branch
distribution points and support Internet-based clients; these DPs are
not supported with server shares.
After
defining a server as a site server, you can assign the various server
roles available, including the distribution point server role. To add
the distribution point server role to the Wildflower site server in the
DAL ConfigMgr site, perform the following steps:
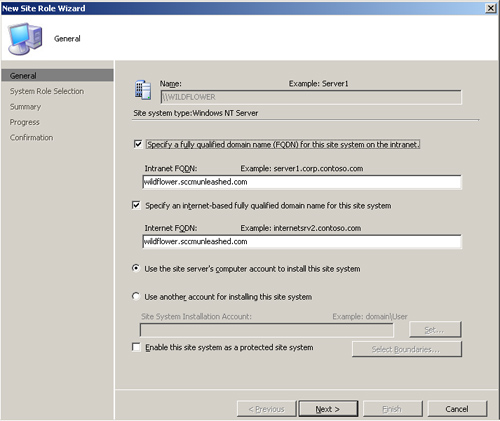
1. | Start by highlighting the Wildflower server under Site Database -> Site Management -> <Site Code> <Site Name> Site Settings -> Site Systems. Right-click and choose New Roles to initiate the New Site Role Wizard. On the first page, specify the settings shown in Figure 1:
- Intranet FQDN—
Specify the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for this site system on
the intranet. This setting determines the name intranet-based systems
will use to connect to the server, and is required for native mode and
publishing in DNS. Enter the default FQDN, which is wildflower.sccmunleashed.com.
- Internet FQDN—
Specify the Internet-based Fully Qualified Domain Name for this site
system. This setting determines what name Internet-based systems will
use when connecting to the server. Enter the default FQDN, wildflower.sccmunleashed.com.
- Account—
You can select Use the site server’s computer account to install this
site system or Use another account for installing this site system.
Choose the default setting, which is using the site server’s computer
account.
- Protected Site System— Set this site server to be configured as a protected site system.
|
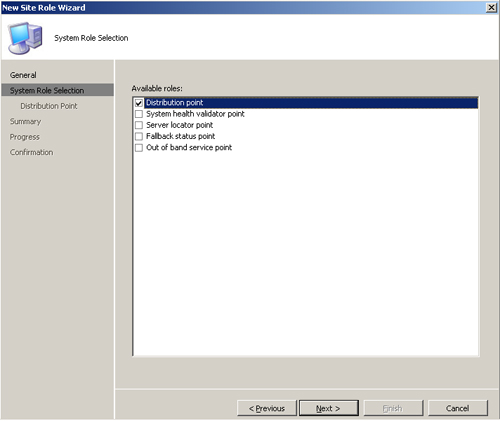
2. | On
the System Role Selection screen, specify the available roles to
activate on this site system. Only those site system roles not
previously assigned to the site system are displayed. For this example,
add the distribution point role, as shown in Figure 2.
|
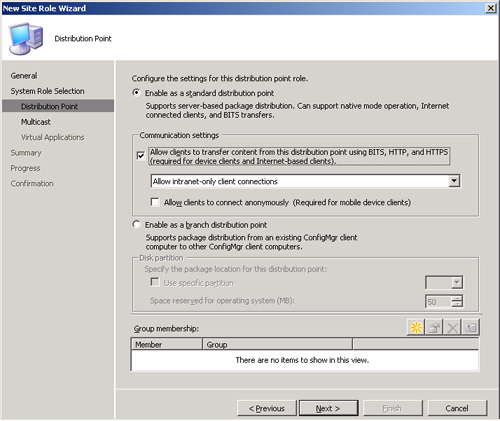
3. | Specify
the details for the configuration of the distribution point role you
are creating on Wildflower. This includes several settings, displayed
in Figure 3:
- Enable as a standard distribution point—
This is the default configuration, which allows configuring the
Communication Settings section of the screen. Because you are creating
a standard distribution point, select this option.
Note: Binary Differential Replication and Delta Replication in ConfigMgr
One
of the benefits of Configuration Manager 2007 is its ability to update
source files for a previously deployed package by only sending changes
that occurred after deploying the package. As an example, the OpsMgr
packages were pushed out to the various distribution points, but the
agent now needs updating to include a newly released version
of the software. When the new version of the package is sent to the
distribution points, ConfigMgr only sends those parts of the package
that changed after it was last sent to those distribution points. This
approach helps minimize the network impact of updating packages in a
ConfigMgr environment.
Binary
delta replication and delta replication are not the same. Delta
replication is performed at the file level, whereas binary delta
replication is performed at the byte level. Delta replication can work
while binary delta replication is disabled. If you enable binary delta
replication, standard delta replication is disabled as a result.
- Communication settings—
Allow clients to transfer content from this distribution point using
BITS, HTTP, and HTTPS (required for device clients and Internet-based
clients). Options available for this setting include the following:
Allow intranet-only client connections Allow Internet-only client connections Allow both intranet and Internet client connections
Tip: Why Does Only the Intranet Option Appear?
If
your ConfigMgr environment is in native mode, three communications
settings options appear on the Distribution Point page of the New Site
Role Wizard:
Allow intranet-only client connections Allow Internet-only client connections Allow both intranet and Internet client connections
If your ConfigMgr environment is in mixed mode (the case with the site shown in Figure 3), the only option available is Allow intranet-only client connections.
Also
in native mode, the box for Allow clients to connect anonymously is
checked and grayed out, whereas in mixed mode this option can be
checked or unchecked.
This
setting indicates whether BITS will be used for the DP, and is required
for connections from mobile device clients and Internet-based clients.
For Windows 2008 server systems, you will need to download, install,
and configure WebDAV manually if your DP will be using this setting.
BITS is used on the distribution point, so check this option, as shown
in Figure 3. - Enable as a branch distribution point— This sets the distribution point to be a branch distribution point.
For
this option to be available, the site system you are configuring must
be listed as a client in the collection. This is because the branch
distribution is a client component (rather than a server component) and
will require a healthy ConfigMgr client for activation. - Group membership—
Provides a way to group distribution points together into logical
groupings. As an example, you could create a grouping for all
distribution points in a site. Take the default configuration, which is
not to identify any group memberships for this distribution point.
|
4. | Finish
the New Site Role Wizard process through the Summary, Progress, and
Confirmation pages to complete creating the new distribution point.
|
|
When
a distribution point site role is assigned to a system, ConfigMgr
chooses the drive with the largest amount of free space to store the
ConfigMgr data. However, there will be situations when you need to
choose where the distribution point data is stored. For these types of
situations, it is best to create a new server share. This allows you to
define the share on the server, which enables you to choose where you
want to store the data.
As
an example, if you create a new distribution point on the Wildflower
server as a server type, ConfigMgr automatically chooses the
NTFS-formatted drive with the largest amount of free space (G: in this
case) and creates a SMSPKGG$ share on the G: drive. However, if you
configure this new distribution point on the Wildflower server as a new
server share, you can create a share called “share” (or SMSPKGF$ to be
consistent with the ConfigMgr naming standard) and store data on the F:
drive instead of the G: drive.
Another available option is to create a file at the root of the drive (i.e. C:\) named NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.sms that you want to prevent ConfigMgr from installing any components on.
|
In
summary, distribution points are most useful in environments where the
systems will receive software deployments and a local server (part of
the LAN) can provide the software distribution point role. Using
regular or standard distribution points is suggested for those
environments without a requirement to restrict which systems can
communicate with the DP.