1. Testing Network Cables
If
your computer can’t communicate with any other computer on your LAN,
and the Device Manager doesn’t indicate a faulty network card, you might
have a wiring problem. Wiring problems can be the most difficult to
solve because it’s difficult to prove that data is leaving one computer
but not arriving at another.
If
your computer is not properly wired into the LAN or is connected
through a wireless network, in many cases, Windows displays an offline
icon right on the system tray and indicates that your network card is
disconnected. It might not, though, so you shouldn’t take a lack of
this kind of message to mean that no wiring problems exist.
If
your network uses UTP cabling plugged in to a hub, there’s usually a
green LED indicator on each network card and at each port on the hub.
Be sure that the lights are on at each end of your network cable and
those for the other computers on your LAN.
Note
If
you really want to get into the guts of your network cabling or are
planning a major installation and want to learn more details so that
you can oversee a professional installation, I recommend that you read Networking with Microsoft Windows Vista by Paul McFedries, published by Que. |
You
also can use inexpensive (about $75) cable test devices that check for
continuity and correct pin-to-pin wiring order for UTP wiring. They
come as a set of two boxes. One gets plugged in to each end of a given
cable run, and a set of blinking lights tells you whether all four wire
pairs are connected and in the correct order. (If you install your own
network cabling and/or make your own patch cables,.)
2. Checking Network Configuration
If
hardware isn’t at fault, you might have a fundamental network
configuration problem. Often the Event Log or Device Manager gives
these problems away, but if they don’t, you can use another batch of
tools to check the computer’s network configuration.
ipconfig
If your computer can’t communicate with others on your LAN, after you check the Event Log and Device Manager, use the ipconfig
command-line utility to see whether your computer has a valid IP
address. Check other computers on the LAN, too, to ensure that they do
as well.
In the Command Prompt window
(which you open by choosing Start, All Programs, Accessories, Command
Prompt), type the following command:
The results should look something like this:
Windows IP Configuration
Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . : myvpc-hb
Primary Dns Suffix . . . . . . . : mycompany.com
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . : Yes
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : Intel 21140-Based PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-03-FF-DD-CA-5F
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::ed10:dff9:693c:803d%8(Preferred)
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.15.108(Preferred)
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . : Friday, October 20, 2006 5:55:11 PM
Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . : Friday, October 27, 2006 5:55:23 PM
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.15.1
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.15.1
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 201327615
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.15.1
NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . : Enabled
(Unless you’re troubleshooting IPv6 Teredo connections, ignore the parts that mention Tunnel Adapters.)
The most important items to look for are the following:
Host Name—
This should be set to the desired name for each computer. If you can
correspond with some computers but not others, be sure that the ones
that don’t work are turned on and correctly named. Make sure you don’t
have two computers with the same name, and that none of the computer
names is the same as the workgroup name.
IP Address—
This should be set appropriately for your network. If your LAN uses
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS), the address will be a number in the
range 192.168.0.1 through 192.168.0.254. If your LAN uses DHCP for
automatic configuration, your network manager can tell you whether the
IP address is correct. Networks with cable/DSL sharing routers usually use numbers starting with 192.168.x where x is a number from 0 to 15.
If
your IP address starts with the numbers 169.254, your computer is set
for automatic configuration but no DHCP server was found, so Windows
has chosen an IP address by itself. This is fine if your LAN uses this
automatic configuration system; perhaps you’ve just connected a few
computers so you can share files and printers. However, if you expected
to get Internet access through your network—that is, if you use ICS or
a hardware Internet connection router, or you have a more complex
network with a DHCP server—this is a serious problem. Restart the
connecting sharing computer or the router, and then restart your
computer and try again.
Network Mask— This is usually 255.255.255.0, but other settings are possible. All computers on the same LAN should have the same network mask.
Each
computer on the same LAN should have a similar valid IP address and the
same network mask. If they don’t, check your network configuration. The
built-in Windows Repair function may also be used to help fix problems
with DHCP-based (automatic) IP address assignment.
Computer
You
can check computer’s identification and workgroup or domain membership
setup from the Computer window. To do so, click Start, Computer. Look
at the bottom of the screen for the computer name and domain or
workgroup name, as shown in Figure 1.
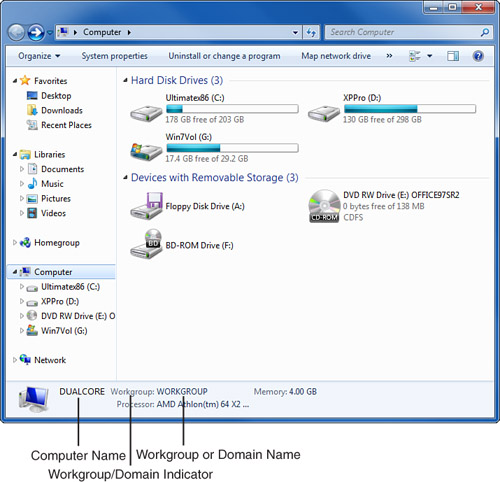
On
a Windows Workgroup network, the workgroup name should be the same on
all computers on your workgroup LAN. All of the computer names must be different from each other.
Note
None
of your computers can use the workgroup or domain name as its computer
name. For example, if your workgroup is MSHOME, you can’t also name a
computer MSHOME. If you find this on one of your computers, change that
computer’s name. |
On
a Windows domain network, you should see your computer’s name displayed
as part of a Windows domain name (for example, my computer named myvpc-hbmyvpc-hb.mycompany.com on a domain network) and the domain name. Your domain name might not include .com. It might say .local
instead or use a different ending. In any case, be sure that your
computer is actually a domain member. If the word “Workgroup” appears
instead, your computer is not a domain member and will not be able to
use domain logins or some domain resources. would be called
Network Connections
You
can manually check all installed network protocols and services and
their configuration by viewing Network Connections and viewing the
properties for Local Area Connection. To view this screen, click Start,
Control Panel, View Network Status and Tasks (under Network and
Internet), Change Adapter Settings. Then, right-click your Local Area
Connection icon (or the appropriate wireless connection icon) and
select Properties.
Confirm that
each required protocol is installed and correctly configured. In
general, the settings on each computer on your LAN should match, except
that the IP address differs (usually only in the last of its four
dot-separated numbers). If your LAN uses automatic IP address
configuration, use the ipconfig command, described earlier, to check the settings.