1. Monitoring User Activity
Sorting tasks, under the owner, the
Users tab enables you to disconnect a user or handle a specific task
listed under a given user (end task, create a dump file, open file
location, search online, or see the properties of a task). Each user,
and each of that user’s child tasks, is individually listed with CPU
and memory utilization. There is also a right-click option on any given
user that takes you directly to Manage User Accounts.
2. Monitoring Details
From the Details tab, shown in Figure 1,
you can handle many of the requests available in earlier versions of
Task Manager, including ending a task, ending a process tree, setting
priority, setting affinity, creating a dump file, opening the file
location, or going to the services.
• Set Affinity—Configuring
threads to run on specific processors allows unused cores to be
activated and clock speeds to be increased. Configuring threads to run
on different processors may increase performance.
• Search Online—The Search Online option is again only a right-click away for a Bing search on the selected topic.
• Analyze Wait Chain—A
feature previously available by opening Resource Monitor now finds
itself present right within Task Manager. This tree view shows which
processes are using or waiting to use a required resource that is being
used by another process.
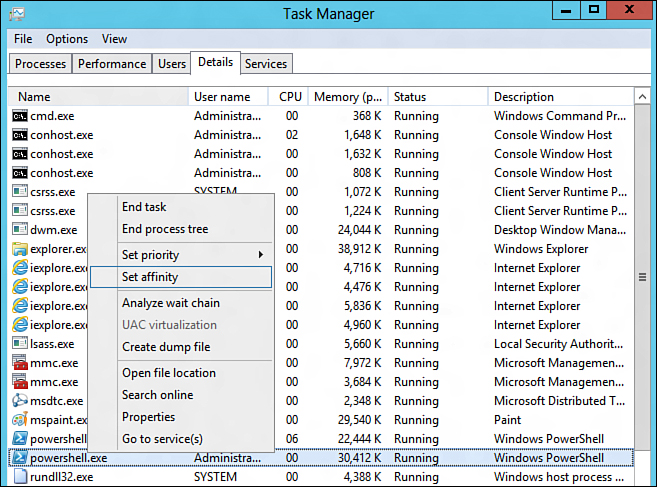
Figure 1. The Details tab.
3. Monitoring Services
For the most part unchanged from its
predecessor, the Services tab continues to show the name, process ID
(PID), description, status, and group of all services. This makes
starting, stopping, or restarting an offending service feasible within
one tool. You also have a link that takes you directly to the Services
Microsoft Management Console (MMC), should you need to change startup
type, change the service account, set recovery options, or study
dependencies.
4. Related PowerShell Functionality
As discussed, Task Manager enables you to
quickly see information about and interact with processes and tasks.
Here are some ways to go about similar tasks with Windows PowerShell.
Get-Process
The Get-Process cmdlet returns running processes on the target computer (local or remote).
Description
The Get-Process cmdlet returns running processes on a local or remote computer.
A basic execution (without any parameters) of
the command returns all the running processes on the local computer.
You can also specify process using the name or PID. As with any
PowerShell commands, you can pass a process object through the pipeline
to Get-Process using the identity value.
By default,
Get-Process returns a process object that has detailed information
about the process and supports methods that let you start and stop the
process. You can also use the parameters of Get-Process to get file
version information for the program that runs in the process and to get
the modules that the process loaded.
5. Examples
Get-Process *
What it does: This lists all running
processes on a local computer. This is a quick snapshot of running
processes that can easily be used on a remote computer as well.
Get-Process explorer.exe | get-member
What it does: This lists all the properties
of the explorer.exe process. Listing the properties of an object
provides detailed information about the component as well as
identifying further operations that can be performed.
Get-Process * | ft name, workingset, basepriority, starttime, threads, cpu,
processoraffinity –auto
What it does: This returns a set of useful
properties for all running processes on the local computer. Formatting
the output using commands such as Format-Table, or ft, makes comparing
relevant data and identifying patterns much easier.
Tip
The processor affinity value is calculated by
adding the representative values for each core. In our sample system
with eight CPUs, we have the following values: 1 for (Core0), 2 for
(Core1), 4 for (Core2), 8 for (Core3), 16 for (Core4), 32 for (Core5),
64 for (Core6) and 128 for (Core7). For example, if cores 0 through 3
were selected, the representative values of 1, 2, 4 and 8 would be
added to get the processor affinity value of 15.
Get-Service
The Get-Service cmdlet gets the services on a local or remote computer.
Description
The Get-Service cmdlet returns information
about services on the local computer or on a remote computer. Services
in various states including running and stopped services are returned.
You can direct Get-Service to get only
particular services by specifying the service name or display name of
the services, or you can pipe service objects to Get-Service.
Examples
Get-Service w32time –DependentServices
What it does: This
lists services dependent on the windows Time service. An understanding
of service boot order and dependencies can help troubleshoot boot
issues.
Get-Service | Where {$_.Status –eq "Running"}
What it does: This lists the current running
services on the local computer. A very useful way to quickly determine
running services on the local or remote computer.
Start-Process and Stop-Process
Starts and stops one or more processes on the local computer.
Description
Starts or stops one or more processes on the
local computer. To specify the process, enter a filename (executable or
script file). You can use the parameters of the command to specify
options, such as loading a user profile, starting the process in a new
window, or using alternate credentials.
Examples
Start-Process temp.txt -Verb print
What it does: Starts Notepad (or other
associated program) to open C:\Temp.txt and print it. A handy way to
include simple application actions within a script.
Stop-Process –processname netlogon -force
Start-Process –processname netlogon
What it does: Restarts the Netlogon process without confirmation, a common maintenance task.