2. Enterprise Edition Example
The other topology Microsoft tested is an expanded Enterprise
Edition deployment designed for very large organizations. This topology
is scaled to support 40,000 users and used seven different virtual hosts. The logical layout of the Enterprise Edition topology is displayed in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Enterprise Edition Virtual Topology
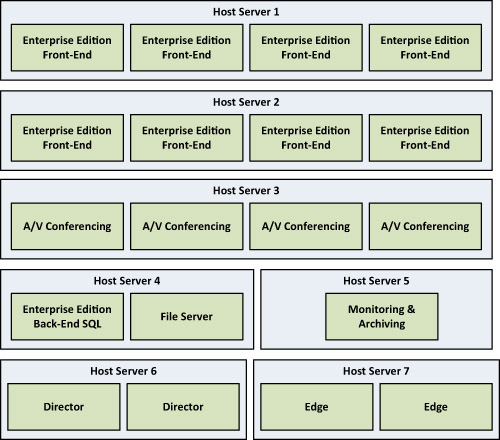
Front-End Hosts and VMs
Two hosts were dedicated to run eight Enterprise Edition Front-End
Servers with a machine running Windows Server 2008 R2 and the following
hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with 16 processor cores
• 64 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 0)
• Four or more network adapters
Each virtual machine running the Enterprise Edition Front-End Server role used the following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• One network adapter
A/V Conferencing Host and VM
The third virtual host server ran four different A/V Conferencing
Server virtual machines. This offloaded A/V conferencing from the
Front-End Servers to provide greater scalability. As with a physical
deployment, for every 10,000 users, a dedicated A/V Conferencing Server
should be deployed. The host had the following hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with 16 processor cores
• 64 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 0)
• Four or more network adapters
Each A/V conferencing server virtual machine used the following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• One network adapter
Back-End Host and VMs
The fourth host server was dedicated to the Back-End SQL Server and
Back-End File Server. It had the following hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with 8 processor cores
• 32 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 1+0)
• Two or more network adapters
Each virtual machine running the Back-End SQL Server or File Server role used the following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• One network adapter
Monitoring and Archiving Host and VM
The fifth host server was dedicated to running a single virtual
machine providing the Monitoring and Archiving roles with a collocated
SQL Server database. The host had the following hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with four processor cores
• 16 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 1+0)
• Two or more network adapters
The single virtual machine running the
Monitoring and Archiving roles with a collocated SQL instance used the
following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• One network adapter
Director Host and VMs
The sixth virtual host server was dedicated to running two virtual
machines with the Director role installed. The host had the following
hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with eight processor cores
• 32 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 0)
• Two or more network adapters
Each virtual machine serving as a Director used the following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• One network adapter
Edge Server Host and VMs
The final virtual host server was dedicated to running two
virtualized Lync Edge Servers. These were intentionally placed on a
separate host for security reasons because the Edge Servers communicate
with external hosts. The host had the following hardware configuration:
• 2.26 GHz or higher CPU with eight processor cores
• 32 GB RAM
• 500 GB SAS disk (RAID 0)
• More than four network adapters
Each virtual machine serving as a Director used the following configuration:
• Four virtual CPUs
• 15 GB RAM
• Two network adapters