Software configuration problems can easily
be the cause of Internet connection problems, and it’s fairly simple to
determine that this is the problem—you can’t make any Internet
connection whatsoever, although the Device Manager says your network
card or modem seems to be working correctly. The potential problems
depend on the type of Internet connection you use.
Troubleshooting a Dial-Up Connection
If your modem appears to connect to your ISP but
you still can’t access any web pages or Internet services, here are
some steps you can take:
1. | In
Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options. Select the
Connections tab. Be sure you have selected the correct dial-up
connection. Select the dial-up connection entry and click Settings. Be
sure that Use a Proxy Server for This Connection is not checked. (The
exception to this rule is if you are using a third-party connection
speed-enhancement program; in this case, the software manufacturer might
specify proxy settings.) Close all the Settings dialog boxes.
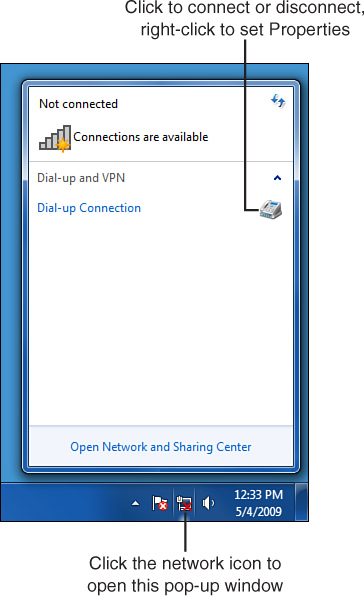
| 2. | Click the network icon at the bottom-right corner of your screen to display the connection list, as shown in Figure 4.
Right-click the entry for your dial-up connection and select
Properties. Alternatively, click Start, Control Panel, View Network
Status and Tasks (under Network and Internet), click Change Adapter
Settings, and then right-click the entry for your dial-up connection and
select Properties.
View the Networking tab. Under Components Used by This
Connection, only the Internet Protocol Version 4 and Version 6 entries,
and possibly QoS Packet Scheduler, should be checked.
| 3. | On
the Security tab, look at the Authentication settings. This should be
set to Allow These Protocols, with at least the Unencrypted Password and
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) boxes checked if
you’re connecting to an ISP, and the Microsoft CHAP box checked as well
if you’re connecting to your office LAN.
|
If none of these steps identifies a problem,
it’s time to call your ISP for assistance. You might have to spend a
half hour on hold listening to really bad music, but at this point, it’s
their job to help you get online, and they should help you cheerfully
and expertly. (Otherwise, you should get a new ISP.)
Troubleshooting a Cable or DSL Modem Connection
If
your computer connects directly to a cable or DSL modem, you might have
one or two network cards installed in your computer, depending on
whether you’re sharing the high-speed connection on your LAN.
To check for the proper settings, follow these steps:
1. | In a Command Prompt window (click Start, All Programs, Accessories, Command Prompt), type ipconfig /all
and press Enter. Be sure that the IP address and DNS information for
the network card that connects to your high-speed modem is accurate.
Your ISP’s tech support people can help you confirm this.
Note If you have DSL or cable service but your computer connects to a connection sharing router and the router connects to the DSL or cable modem, don’t follow these instructions. Instead. |
| 2. | If
your DSL provider requires you to “sign on” before using the Internet,
you’ll be using a sort of “dial-up” connection, except that the
connection is made digitally over the DSL network. (This is called
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet, or PPPoE.) You set up this
connection using the Broadband (PPPoE) option.
If
this is the case, and if you use a LAN adapter to connect to your DSL
modem, the IP address displayed for the LAN adapter itself will have an
IP address that is used only to communicate with your DSL modem. Be sure
to check with your ISP to be certain that this computer-to-modem
connection is configured correctly; if it’s not, you won’t be able to
make the connection to your ISP.
Use the Connection icon to connect to your ISP. You can get to it
quickly by clicking the network icon in the taskbar (as shown in Figure 16.4). Select the name of the connection for your Internet service, and click Connect.
When the logon process has completed, ipconfig /all
should show a dial-up connection with a different IP address. This is
your real, public Internet address for the duration of the connection.
| 3. | If
you’re sharing your computer’s high-speed connection with your home or
office LAN using two network cards in your computer, be sure you’ve
enabled sharing on the correct connection. The connection to check as
“shared” is the one that connects to your high-speed DSL or cable modem.
The LAN-side connection is not the shared connection and should have an
IP address of 192.168.0.1.
|
Troubleshooting a LAN Connection
If you connect to the Internet via a wired or
wireless connection on your LAN, the first question is, can you
communicate with other computers on your LAN? To test this, you should
use the ping command.
Open a Command Prompt window (click Start, All Programs, Accessories, Command Prompt) and type the command ipconfig. The output of ipconfig lists a number called a gateway address. To test the connection to your gateway, type ping followed by the gateway address, and then press Enter. For example:
Tip Windows has a diagnostic
and repair function that resets all the software components of a LAN
connection, including the DHCP address assignment. This often solves LAN
problems. To use it, open the Network Connections page, find your LAN
or wireless connection, right-click it, and select Diagnose. If a
problem is identified, follow the instructions or select the Reset
option. A quicker path to the Diagnose function is through the network icon on your taskbar (see Figure 16.4). Click the network icon, right-click your connection name, select Status, then click Diagnose. |
This tests the connection to the computer or router that is sharing its Internet connection. If ping
says “Request timed out” or “Transmit failed” instead of listing four
successful replies, you have a LAN problem that you need to fix first.
If you can communicate with other computers on the LAN but not the Internet, can anyone else on your LAN access the Internet?
If no one can, the problem is in your LAN’s connection to the Internet.
If your LAN uses Windows’ built-in Internet Connection Sharing (ICS),
go to the sharing computer and start diagnosing the problem there.
Otherwise, follow these steps:
1. | Open a Command Prompt window and type ipconfig /all to view your TCP/IP settings. The output appears similar to that shown in Listing 1. (The Tunnel Adapter entries are not important here and are not shown.)
Listing 1. Output from the ipconfig /all Command
Windows IP Configuration
Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . .: MyComputer
Primary Dns Suffix . . . . . . . .:
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . .: Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . .: No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . .: No
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . .:
Description . . . . . . . . . . . .: Intel PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . .: 00-03-FF-D0-CA-5F
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . .: Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . .: Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . .: fe80::8014:cfc7:9a98:cdfe%10(Preferred)
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . .: 192.168.1.106(Preferred)
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . .: 255.255.255.0
Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . .: Sunday, July 5, 20097:22:23 PM
Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . .: Sunday, July 5, 2009 7:22:22 PM
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . .: 192.168.1.1
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . .: 192.168.1.1
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . .: 167773183
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . .: 192.168.1.1
NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . .: Enabled
|
Within the output, check the following:
The DNS suffix search list and the
connection-specific DNS suffix should be set correctly for your ISP’s
domain name or your company’s domain name. (This is helpful but not
crucial.) It can also be left blank. The IP address should be appropriate for your LAN. If you’re using ICS, the number will be 192.168.0.xxx. If you’re using a hardware connection-sharing device, the number might be different. If your IP address appears to be 169.254.xxx.yyy,
the sharing computer or router was not running when you booted up your
computer, or it is no longer set up to share its connection. Get the
sharing computer or router restarted and then skip to step 2. The
default gateway address should be the IP address of your router or
sharing computer, usually something similar to 192.168.0.1 or
192.168.1.1. The
default gateway address and your IP address should be identical for the
first few sets of numbers, corresponding to those parts of the subnet
mask that are set to 255. That is, both might start with 192.168.0 or
192.168.1. If your computer gets its IP
address information automatically, DHCP Enabled should be set to Yes. If
your computer has its IP address information entered manually, no DHCP
server should be listed. If you’re using
connection sharing, the DNS server address will be 192.168.0.1.
Otherwise, the DNS server numbers should be those provided by your ISP
or network administrator. If your computer gets its settings automatically or uses a shared connection, continue with the next two steps.
| 2. | Be
sure the master router or sharing computer is running. Then, in the
Network Connections window, right-click your Local Area Connection icon
and select Diagnose. This might lead you through solving the problem.
Alternatively, view the Network and Sharing Center, and select
Troubleshoot Problems from the task list. Select Internet Connections,
then repeat the process selecting Network Adapter.
| 3. | Repeat the ipconfig
command and see whether the correct information appears now. If it
does, you’re all set. If not, the master computer or the router is not
supplying the information described previously and needs to be set
correctly before you can proceed.
|
These steps should take care of any
software configuration problems. If none of these steps indicates or
solves the problem, check that your network or modem hardware is
functioning correctly.
|