Most people never need to edit the Registry
by hand because most Registry keys are set by the software that uses
them. However, you might need to edit the Registry by hand if you’re
directed by a technical support person who’s helping you fix a problem,
or when you’re following a published procedure to make an adjustment for
which there is no Control Panel setting.
In the latter case, before going any further, I
need to say this one last time, to make it absolutely clear: Unless
you’re quite certain that you can’t make a mistake, back up the Registry
(or at least the section you want to change) before making any changes.
The next few sections cover the basics of the Registry Editor.
Viewing the Registry
The Registry Editor doesn’t have a Start menu item. The easiest way to run it is to type regedit into the Search field on the Start menu. When regedit appears in the results pane under Programs, take one of the following actions, depending on your needs:
If you are logged on as an Administrator, press Enter or click regedit. When the User Account Control dialog box appears, click Continue. The Registry Editor will run with full elevated privileges.
If you are not logged on as an Administrator but need to change settings in only the HKEY_CURRENT_USER section of the Registry, press Enter or click regedit. The Registry Editor will run with reduced privileges, and you will not be able to change systemwide settings.
If you are not logged on as an Administrator but need to change systemwide settings in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, right-click regedit
and select Run as Administrator. Enter an Administrator account’s
username and password. The Registry Editor will then run with full
elevated privileges.
Note
The reason for these
complicated variations is that malicious programs and email attachments
can easily abuse the Registry Editor, so it’s subject to UAC
restrictions. The Registry Editor must be running in elevated mode to
modify Registry keys that are secured to be changeable only by the
Administrator. By the way, there is no indication in the Registry
Editor’s title bar to tell whether it’s running with elevated
privileges—you just have to remember. |
Regedit displays a two-pane display much like Windows Explorer, as shown in Figure 1.
The top-level keys, which are listed below Computer, can be expanded
just like drives and folders in Explorer. In the pane on the right are
the values for each key. The name of the currently selected key appears
in the status bar.
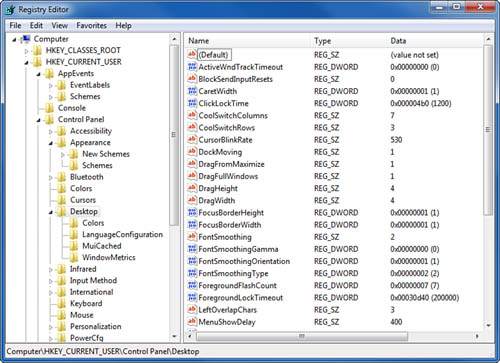
Values have names, just as the files in a folder
do, and it’s in the values that configuration information is finally
stored. Each key has a (Default) value, which is the value of the key
itself, and any number of named values. For example, Figure 28.1 shows the key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop. The value of HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop itself is undefined (blank), and the value HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop\DragFullWindows is 1.
Registry values have a data type, which is usually one of the types shown in Table 1. The Registry Editor display lists values by their technical names.
Table 1. Data Types Supported by Regedit
| Technical Name | “Friendly” Name | Description |
|---|
| REG_SZ | String value | Textual information, a simple string of letters. |
| REG_BINARY | Binary value | Binary data, displayed as an arbitrary number of hexadecimal digits. |
| REG_DWORD | DWORD (32-bit) value | A single number displayed in hexadecimal or decimal. |
| REG_QWORD | QWORD (64-bit) value | A single number displayed in hexadecimal or decimal. QWORD values are used primarily by 64-bit Windows applications. |
| REG_MULTI_SZ | Multistring value | A string that can contain more than one line of text. |
| REG_EXPAND_SZ | Expandable string value | Text that can contain environment variables (such as %TEMP%). |
Other data types, such as REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN and REG_RESOURCE_LIST, exist, but they are obscure and rare and can’t be edited with Regedit.
Note
When I search the Registry, most of the time, I check all the Look At boxes but not Match Whole String Only. |
Searching in the Registry
You can search for a Registry entry by key name,
value name, or the contents of a value string. First, select a starting
point for the search in the left pane. You can select Computer to
select the entire Registry, or you can limit your search to one of the
top-level keys or any subordinate key. Next, select Edit, Find from the
menu and enter a search string in the Find dialog box. The Find feature
is not case sensitive, so it doesn’t matter whether you use upper- or
lowercase letters. You can check any of the Look At boxes to designate
where in the Registry you expect to find the desired text: in the name
of a key, in the name of a value, or in the data, the value itself.
Tip
The search function has two limitations: You can’t enter a backslash (\) in the search string when looking for a key or value name; Regedit won’t complain, but it won’t find anything, either. You can’t search for the initial HKEY_xxx part of a key name. That’s not actually part of the name; it’s just the section of the Registry in which the key resides.
For example, to find a key named HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\MIDFile\shell\Play\Command,
you can’t type all that in and have Find jump right to the key. If you
already know the full pathname of a key, use the left pane of Regedit to
browse for the key directly. |
Check Match Whole String Only to search only for items whose whole name or value is the desired string.
Click Find Next to start the search. The Regedit
display indicates the first match to your string; by pressing F3, you
can repeat the search to look for other instances.