The ADOX library is used to work with the schema of
the data source objects, such as tables, views (queries), indexes, and
so on. ADOX is quite simple to use and can be incredibly useful for
working with and creating new objects, as well as setting security
options. This last section describes the more common features of ADOX.
1. Adding References to ADOX
To implement ADOX, a
reference to the ADOX library needs to be added to the code project.
Select the "Microsoft ADO Ext. 2.8 for DDL and Security" option in the
References dialog box. Once this reference has been added to the code
project, you should be able to begin using the ADOX library.
2. The ADOX Object Model
The ADOX model contains one top-level object, Catalog, which contains five collections: Tables, Groups, Users, Procedures, and Views.
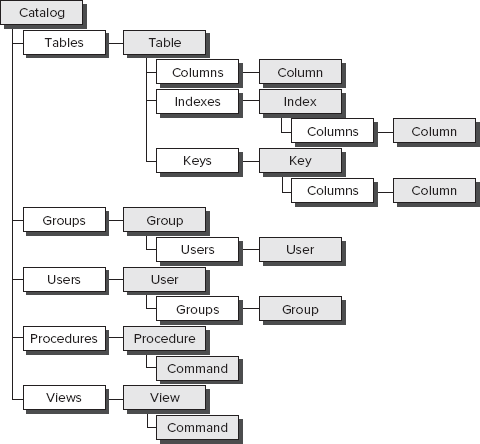
In addition to this model, each of the Table, Index, and Column objects also contains a standard ADO Properties collection.
3. Working with Tables
ADOX provides a number of
methods for working tables in the data source. Specifically, ADOX
provides the capability to create, modify, and delete Table objects. This functionality is contained in the Catalog.Tables object. This section outlines several examples of working with the Tables object to accomplish these tasks.
3.1. Creating a Table
It is very easy to create a new Table object in the data source. Simply create a new Table object, append the desired columns, and then append the new table to the Catalog. The following code provides an example of creating a new Table object.
Public Sub CreateTable()
' Define Variables
Dim cat As New ADOX.Catalog
Dim tbl As New ADOX.Table
' Set the Connection to the Current Database
cat.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
' Set the table name and create the columns with common Access types
tbl.Name = "TempTable"
tbl.Columns.Append "ID", adInteger ' Long type
tbl.Columns.Append "Title", adVarWChar, 100 ' Text type
tbl.Columns.Append "Cost", adCurrency ' Currency type
tbl.Columns.Append "Notes", adLongVarWChar ' Memo type
tbl.Columns.Append "Size", adDouble ' Double type
tbl.Columns.Append "IsValid", adBoolean ' Boolean type
tbl.Columns.Append "Created", adDate ' DateTime type
' Set some Access Field Properties
tbl.Columns("ID").ParentCatalog = cat
tbl.Columns("ID").Properties("AutoIncrement") = True ' Set Autonumber
' Append the new table to the Tables collection
cat.Tables.Append tbl
cat.Tables.Refresh
End Sub
The preceding code also sets the AutoIncrement field property to make the ID field an AutoNumber field. Many of the Access-specific field properties can be set using the Properties object on the Columns collection. However, there are several field types and properties that cannot be set through ADOX, such as Hyperlink, Multi Value, and Attachment field types.
3.2. Deleting a Table
Deleting a table can be completed by calling the Delete method from the Catalog.Tables collection and supplying the name of the table, as shown in the following code.
Public Sub DeleteTable()
' Define Variables
Dim cat As New ADOX.Catalog
' Set the Connection to the Current Database
cat.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
' Delete the table from the Tables collection
cat.Tables.Delete "TempTable"
cat.Tables.Refresh
End Sub
4. Working with Views (Queries)
ADOX provides a number of
methods for working views in the data source. Specifically, ADOX
provides the capability to create, modify, and delete these objects.
This functionality is contained in the Catalog.Views object. This section outlines several examples of working with the Views object to accomplish these tasks.
4.1. Creating a Query
To create a new query, simply supply a Command object and a name, and it will be created by appending it to the Catalog.Views object. The following code is an example of creating a new view from a simple SQL command in the current database.
Public Sub CreateQuery()
' Define Variables
Dim cat As New ADOX.Catalog
Dim cmd As New ADODB.Command
' Open the Catalog
cat.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
' Create the Command object that represents the View
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT [Contacts].* FROM [Contacts]"
' Provide the Name and Create the View
cat.Views.Append "AllContacts", cmd
End Sub
4.2. Modifying a Query
To modify an existing query, simply provide a new Command object with the desired values. The following code provides an example.
Public Sub ModifyQuery()
' Define Variables
Dim cat As New ADOX.Catalog
Dim cmd As New ADODB.Command
' Open the Catalog
cat.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
' Create the Command object that represents the View
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT [Contacts].[First Name] FROM [Contacts]"
' Set the View Command
cat.Views("AllContacts").Command = cmd
End Sub
4.3. Deleting a Query
Deleting a query can be completed by calling the Delete method on the Catalog.View object, as shown in the following code.
Public Sub DeleteQuery()
' Define Variables
Dim cat As New ADOX.Catalog
Dim cmd As New ADODB.Command
' Open the Catalog
cat.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
' Delete the Query
cat.Views.Delete "AllContacts"
End Sub
5. Managing Security with ADOX
Finally, one very
powerful feature ADOX provides is the capability to manage database
security. ADOX can set a database password and manage user and group
permissions (when supported).