2.4. Unified Messaging Server
The Unified Messaging server role was introduced in
Exchange Server 2007 and is reasonably similar in Exchange Server 2010.
There are a few useful new features such as voicemail preview,
protected voicemail, and the personal auto-attendant. One notable
change is that the inbound faxing function is no longer supported. This
server role integrates voicemail with Exchange mailboxes and provides
voice auto-attendant functions and phone access to email and calendar.
The Unified Messaging server requires an IP-based telephone switch or a
traditional public branch exchange (PBX)-to-IP gateway.
The Unified Messaging server role integrates into your environment, as shown in Figure 6.
This server must be in the same Active Directory site as a Hub
Transport server and preferably the same site as the Mailbox servers
that hold the mailboxes it is supporting. Further, the Unified
Messaging server roles should sit on the same subnet as the IP-based
PBX or PBX-to-IP gateway.

The following functions are handled by the Unified Messaging server role:
Accepts inbound VOIP phone calls for users
if they do not answer their voice line in the same way that a
traditional voicemail system accepts calls. The VOIP system or
PBX-to-IP gateway passes along identifying information to Unified
Messaging, indicating which phone extension had been called.
Identifies which user mailbox a phone call is intended for and retrieves the user's outgoing message from their mailbox.
Provides
voicemail for users of the IP-based phone system or through the
PBX-to-IP gateway; includes voicemail greetings and options. Inbound
voicemail is recorded as a Windows Media Audio (WMA) file and stored as
a message in a user's Inbox.
Allows
users to dial into the Unified Messaging server to retrieve voicemail,
listen to email messages, review their calendar, or change appointments
Provides voice menus and prompting call menus acting as an auto-attendant system.
|
Many administrators are concerned about the size of
a user's mailbox once their voicemail starts to be directed to the
user's Inbox. Visions of 30-second messages being stored as 1 MB
attachments flash through people's heads.
In reality, it is not that bad, though. Granted,
your mail storage requirements will rise just a bit because there will
be additional content stored in the user's mailbox. However, voicemail
messages are not as large as you might think. Unified Message supports
three codecs (coder/decoders) when recording a voice mail message.
These are the MP3 code (the default for Exchange Server 2010), Windows
Media Audio (WMA), Group System Mobile (GSM), and G.711 Pulse Code
Modulation (PCM). You can pick these on a systemwide basis or override
them on a user-by-user basis. Each of these has advantages and
disadvantages, of course.
The MP3 codec requires about 2 KB per second so a
30-second message would be about 60 KB. The WMA codec requires about 7
KB per message plus 1 KB for each second. So a 30-second message would
be about 37 KB. The GSM codec requires about 1.6 KB per second. The PCM
codec records a much higher quality voice message but at a cost of
approximately about 16 KB per second of voice. The MP3 codec is
probably your best bet for most users as it is almost universally
compatible with most mobile devices, including the iPhone.
|
If you look in the service console on a server with the Unified Messaging role installed, you will see the services shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Exchange Server 2010 Unified Messaging Server Services
| Service Display Name, Short Name, and Executable | Function |
|---|
| Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology/MSExchangeADTopology/ADTopologyService.exe | Locates
Active Directory domain controllers and global catalog servers, and
provides Active Directory topology information to Exchange services.
Most Exchange services depend on this service; if it does not start,
the Exchange server will probably not function. |
| Microsoft Exchange File Distribution/MSExchangeFDS/MSExchangeFDS.exe | Replicates the offline address book files to other Client Access servers. |
| Microsoft Exchange Monitoring/MSExchangeMonitoring/Microsoft.Exchange.Monitoring.exe | Handles
the interaction between management and troubleshooting tools and the
Exchange server. Used by tools such as the Exchange Management Shell
diagnostic cmdlets. |
| Microsoft Exchange Service Host/MSExchangeServiceHost/Microsoft.Exchange.ServiceHost.exe | Provides
a service host for Exchange components that do not have their own
service. These include components such as configuring Registry and
virtual directory information. |
| Microsoft Exchange Speech Engine Service/MSSpeechService/SpeechService.exe | Handles text-to-speech processing for Unified Messaging. |
| Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging/MSExchangeUM/umservice.exe | Handles
processing of inbound voice calls, records voicemail messages,
implements auto-attendant functions, and provides end users with access
to their voicemail, email, and calendar via the phone. |
2.5. Edge Transport Server
The Edge Transport functionality is another new
feature that was included with Exchange Server 2007. The Edge Transport
server provides a slimmed-down version of the Exchange message
transport functionality that requires neither Active Directory nor
components such as the information store.
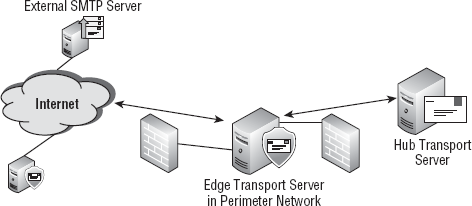
The Edge Transport server is usually placed in an
organization's perimeter network rather than the internal network, as
shown in Figure 7.
|
One common misconception about the Edge Transport
server role is that it is required; it is not. An Exchange 2010 Hub
Transport server can send and receive email directly with the Internet
or it can use any third-party SMTP relay or message hygiene system.
|
There are a number of reasons that the Edge
Transport role has advantages over using an Exchange 2003 server in
your perimeter network:
To process delivery reports, nondelivery
reports, and address rewrites, the information store service must be
running and the default mailbox database must be mounted.
Placing
an Exchange 2000/2003 server in the perimeter network requires many
ports to be opened on the firewall from the perimeter network to the
internal network.
Allowing inbound email directly to an Exchange server could jeopardize both Exchange and Active Directory.
For these reasons, a server role was developed that
has many of the advantages of an Exchange 2010 server. However, it can
be made much more secure because it can run in the perimeter network as
a stand-alone computer and does not require Active Directory
membership. Here are some of the characteristics of the Edge Transport
server role:
It should be deployed in the perimeter network.
It
can be managed with Exchange Management Shell scripts and the Exchange
Management Console in much the same way a regular Exchange server is
managed.
The Edge Transport server
receives LDAP updates from an internal Hub Transport that updates
information such as valid SMTP domains, recipients, and safe sender and
blocked sender lists for each user.
The
only components required to run the Edge Transport role are the message
transport system and an instance of the Active Directory Lightweight
Directory Services database.
Features
such as transport rules can be implemented in the perimeter network and
provide message policy enforcement for messages entering or leaving the
organization that is separate from that provided on the internal
network.
Connectivity between internal Hub Transport servers and Edge Transport servers is authenticated and the data stream encrypted.
The
content filter functionality and other antispam and message security
tools are built in, as is the ability to add third-party content
filtering/message hygiene tools.
Microsoft
Forefront Security for Exchange Server can be employed on the Edge
Transport server role for virus detection and quarantine.
For medium and large organizations, higher
availability comes in the form of installing multiple Edge Transport
servers and providing load balancing using multiple DNS Mail Exchanger
(MX) records, network load balancing, DNS round-robin, or failover
using multiple Internet connections.
If you look at the service console on an Exchange Server 2010 Edge Transport server, you will find the services in Table 5.
Table 5. Exchange Server 2010 Edge Transport Server Services
| Service Display Name, Short Name, and Executable | Function |
|---|
| Microsoft Exchange ADAM/ADAM_MSExchange/dsamain.exe | Runs
the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (ADLDS) database
also known as the ADAM service. This service stores the Edge Transport
configuration and recipient information. |
| Microsoft Exchange Anti-spam Update/MSExchangeAntispamUpdate/Microsoft.Exchange.AntispamUpdateSvc.exe | Handles the antispam automated signature and configuration updates. |
| Microsoft Exchange Credential Service/MSExchangeEdgeCredential/Microsoft.Exchange.EdgeCredentialSvc.exe | Handles the Edge Transport credential service. |
| Microsoft Exchange Monitoring/MSExchangeMonitoring/Microsoft.Exchange.Monitoring.exe | Handles
the interaction between management and troubleshooting tools and the
Exchange server. Used by tools such as the Exchange Management Shell
diagnostic cmdlets. |
| Microsoft Exchange Service Host/MSExchangeServiceHost/Microsoft.Exchange.ServiceHost.exe | Provides
a service host for Exchange components that do not have their own
service. These include components such as configuring Registry and
virtual directory information. |
| Microsoft Exchange Transport/MSExchangeTransport/MSExchangeTransport.exe | Handles message transport between Hub Transport servers, Edge Transport servers, and external SMTP servers. |
| Microsoft Exchange Transport Log Search/MSExchangeTransportLogSearch/MSExchangeTransportLogSearch.exe | Handles the remote search capabilities for the Exchange server transport log files. |