The websites hosted by IIS on
your Windows SBS 2011 server are accessible like any other website—by
typing a URL in a browser window. However, Windows SBS provides a number
of tools that make the sites more readily accessible to users and
administrators.
1. Accessing the Client Deployment Site
The first site that each workstation accesses on the Windows SBS server is the client
deployment site, which joins the computer to the domain and configures
it to access the network’s resources. To connect to this site, a user or
administrator simply has to type the word connect in the browser’s address box. This works for two reasons:
The Windows SBS
2011 setup program creates an Alias (CNAME) resource record in the
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain that equates the name connect with the name of the server. When the workstation performs a DNS name resolution on the name connect, it receives the IP address of the server in return.
The client deployment website has a host header binding that associates the name connect with the site. As a result, IIS forwards HTTP requests containing connect in the Host field to the client deployment site.
2. Using Shortcuts and Links
In addition to joining the
workstation to the network, the Connect Computer Wizard configures the
workstation so that users have various ways to access the websites on
the Windows SBS 2011 server, including the following:
On the Start
menu, the wizard creates a Windows SBS program group that contains an
Internal Web Site shortcut pointing to the SharePoint site: companyweb.
In the Internet Explorer Favorites list, the wizard creates links to the Internal Web Site and to the RWA site.
3. Using Remote Web Access
As mentioned earlier, RWA is a
portal site that contains no content of its own, but provides users
with access to the other Windows SBS 2011 websites, as well as other
internal network resources. RWA is unique among the default Windows SBS
websites in that it is available both to internal network users and to
Internet users at remote locations. For internal users, RWA provides a
convenient central access point for the Windows SBS network resources.
For users at remote locations, however, RWA also provides the unique
ability to log on to the AD DS domain from outside the physical network.
Once connected to the RWA site, a user with the correct permissions can perform several tasks:
Connect to the OWA site
Connect to the Internal companyweb website
Establish a Remote Desktop Services connection to a workstation on the internal network
Access shared folders on the network
Change the user’s password
View the Windows Small Business Server 2008 Client Computer Help pages
Users with administrative credentials can perform these additional tasks:
To provide this remote
access, your Windows SBS 2011 server, your Internet access router, and
your Internet domain must be configured properly. This configuration
consists of the following elements:
The Windows SBS 2011 setup program creates the RWA site in IIS and configures it with a host header binding that associates the site with the host name remote.
The Internet Address Management Wizard creates a DNS resource record in your Internet domain, pointing the host name remote to your router’s external (Internet) address.
The
Internet Address Management Wizard configures your router to admit
Internet traffic through ports 25, 80, 443, 987, and 3389 and forward
the traffic to your server.
The
Windows SBS 2011 setup program creates a certificate installation
package that enables you to distribute your server’s self-signed
certificate to remote computers.
3.1. Connecting to the RWA Site
The RWA website is accessible to users, both on the internal Windows SBS network and on the Internet, through the URL http://remote.domain_name.com, where domain_name.com
is the name of the Internet domain name you registered using the
Internet Address Management Wizard. The server name in this URL resolves
to the external address of your router, and the router forwards the
traffic to your Windows SBS server. Internal users on the Windows SBS
network can connect to the RWA site more easily by using the Favorite
that the Connect Computer Wizard creates in Internet Explorer.
Tip:
If computers on the
Internet are unable to connect to your server using RWA, the most likely
causes of the problem are a missing or incorrect DNS resource record
for the host name remote in your domain, or an improperly configured
router that is not forwarding all the required port traffic to the
server.
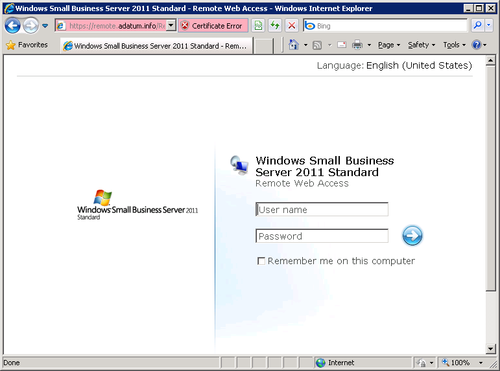
When a user on the internal network connects to the RWA site, a sign-in page appears, as shown in Figure 1. The user must log on using his or her AD DS domain account to enter the site.
For Internet users, the process might be slightly more complicated in some cases. The RWA site uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, which uses digital certificates
to confirm the identity of the server. If, during your initial Windows
SBS 2011 server configuration, you used the Add A Trusted Certificate
Wizard to purchase a certificate from a third-party provider and install
it on your server, clients on the Internet trust the server’s certificate and allow the browser to access the RWA site.
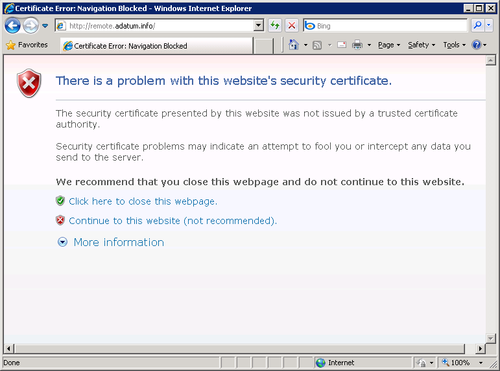
If you did not purchase a certificate from a trusted third-party provider, your server is using a self-signed certificate. Computers on the local network trust the server’s self-signed
certificate because they are members of the same AD DS domain. However,
computers on the Internet are not members of the domain and have no
reason to trust the server’s certificate. As a result, when Internet
computers attempt to connect to the RWA site, a Certificate Error page appears, as shown in Figure 2.
3.2. Installing a Server Certificate
The appearance of the Certificate Error page does not prevent the computer from accessing the site. Users can click the Continue to this website link to proceed to the RWA
logon page, but unless they are aware of the reason for the error, they
might be reluctant to do so. To prevent the Error page from appearing,
you can either obtain a certificate from a commercial provider or
install your server’s self-signed certificate on each Internet computer
that will access the RWA site.
Windows SBS 2011 provides a
certificate installation package that simplifies the process of
deploying the server certificate to remote clients. To deploy the server
certificate, use the following procedure:
On your Windows SBS 2011 server, open Windows Explorer and browse to the Public\Public Downloads folder.
Copy the Install certificate package archive file to a removable medium, such as a flash drive or a writable CD or DVD.
On the computer where you want to deploy the certificate, insert the drive or disk.
Open Windows Explorer and copy the Install certificate package file to a local folder.
Browse to the Install certificate package file, right-click it and, from the context menu, select Extract all. The Extract Compressed (Zipped) Folders Wizard appears.
Click Extract. The wizard extracts the files from the archive and displays them in Windows Explorer.
Double-click the InstallCertificate program. An Open File – Security Warning dialog box appears.
Click Run. The Certificate Installation dialog box appears.
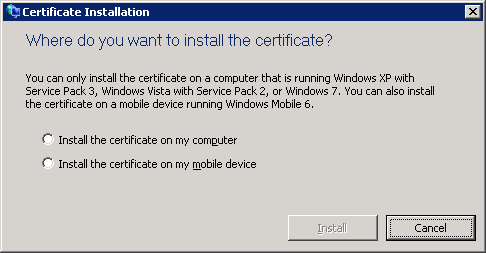
Select the Install the certificate on my computer option and click Install.
If a User Account Control dialog box appears, click Continue. A Certificate Installation message box appears, indicating that the certificate is installed.
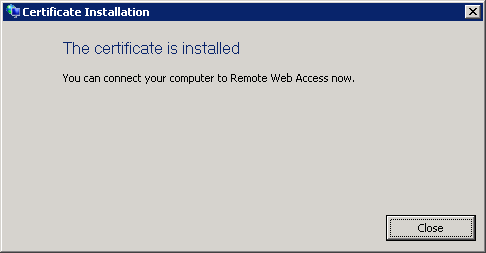
Once the certificate is installed, the user can access the RWA site without displaying a Certificate Error page.
4. Accessing the WSUS Website
Unlike the other Windows SBS 2011 websites,
users do not access the WSUS site using a web browser. Because the site
is a local network replacement for the Microsoft Updates servers on the
Internet, the Windows Update client on the network computers is
responsible for accessing it. The Group Policy settings that configure
the Windows Update clients contain a URL pointing to the Windows SBS
2011 server by name, with the port number 8530, to distinguish it from
the server’s other websites.