1. Types of Databases Available
Access 2010 sports two types of databases:
a standard database, and a web database. The standard database is
consistent with that of all the previous versions of Access. A standard
database can house all the tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and
modules that comprise your application. Microsoft designed it for use
on a single machine or on your computer network. The web database is
new to Access 2010. With a web database, your tables are stored on the
Internet. Furthermore, you can create queries, forms, and reports, all
of which reside on the Internet, rather than within the ACCDB file.
Access 2010 is the first version of Access that allows for true web
development.
2. Creating a New Database
Create a New Database
To create a new blank database, follow these steps:
1. | Select New from the File tab.
|
2. | Select Blank Database or Blank Web Database from the list of options on the right side of the screen (see Figure 1).
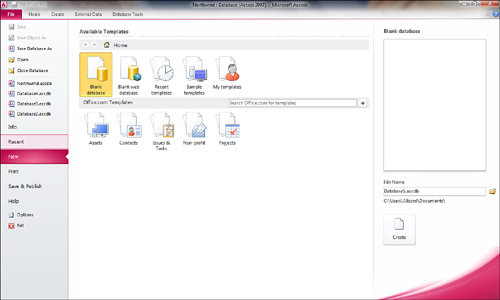
|
3. | Select a drive/folder where you will place the database.
|
4. | Type a filename for the database.
|
5. | Click the OK button.
|
Access creates an empty database file. It is your
responsibility to add the necessary tables, queries, forms, reports,
macros, and modules that comprise a functional application.
Database filenames must follow these rules:
Database names can contain up to 255 characters.
Database names can contain spaces, but you should avoid special characters such as asterisks.
Access assigns the extension .ACCDB to a databases that you create.