1. What Is Virtualization?
Virtualization has the capability for a physical piece of hardware
to run multiple virtual instances of an operating system. In a
traditional sense, every server deployed was associated with physical
hardware, had a single operating system installed, and the server
performed a specific function. When it was time to add a new server to
the environment, companies purchased a new piece of hardware, installed
the operating system, and then configured any applications or services.
With virtualization, companies no longer require new hardware for every
single new server because virtual machines can share a common set of
physical resources.
In virtualization, the physical hardware with the resources, such as
processing power, memory, and disk space, is referred to as the host, whereas any virtual instance of a server running on the host is considered a virtual machine guest.
Because a single physical machine can support running multiple virtual
machines, companies can now use a single piece of hardware to support
running multiple servers and each virtual machine running on a host
shares the resources physically installed on the host. For example, if
a host machine has 16 GB of RAM, only 16 GB of RAM is available to be
allocated to the virtual machine guests running on that host.
Note
Many products offer the capability
to do some form of dynamic memory management so that over-allocating or
dynamically moving physical memory between guests is possible, but the
bottom line here is that guest machines use the resources installed in
the host.
2. Hypervisor Types
The key to virtualization is the concept of a hypervisor,
which is a layer that sits between the host physical hardware and the
guest virtual machines. The hypervisor facilitates access for the
virtual machines to the physical hardware resources.
Virtualization hypervisors come in two distinct flavors. The first,
Type 1, allows virtualization to occur directly in an existing
operating system. Good examples of a Type 1 hypervisor are the
Microsoft Virtual PC or VMware Workstation products. These are
applications that run in an existing operating system on a workstation
or server, and they allow the user to run virtual machines in the
operating system. The hypervisor in these instances runs on top of the
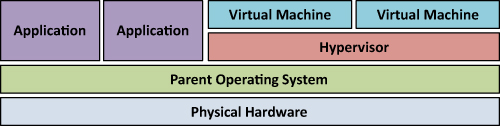
host operating system, as depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Type 1 Hypervisor
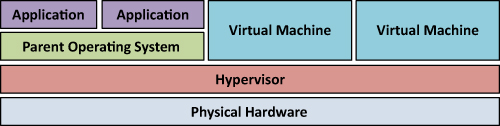
The second type of hypervisor, Type 2, is far more efficient than
Type 1 because it actually operates at a level directly above the
physical hardware, as shown in Figure 2.
This is the type of hypervisor product is used in Microsoft Hyper-V or
VMware vSphere products. Type 2 hypervisors are more efficient because
there is no need to have the hypervisor first pass through the host
operating system before addressing resources for the virtual machine
guests.
Figure 2 Type 2 Hypervisor
Note
It may be confusing to think of
Hyper-V as a Type 2 hypervisor for a Windows Server 2008 full
installation because an operating system is installed on the physical
host, but the reality is that the hypervisor layer is loaded prior to
the host operating system. It is completely abstracted from the Hyper-V
management console, but the host operating system is essentially a
virtual machine that runs on top of the hypervisor.