Heartbeat Discovery
Heartbeat
Discovery is a ConfigMgr capability that enables deployed ConfigMgr
clients to send DDRs to their management point. This enables clients to
keep the ConfigMgr database current with discovery-related data that
often changes, such as IP addresses. Heartbeat Discovery is the only
required discovery method and the only one that must be enabled.
Configure
a simple schedule, ensuring the schedule is configured to run more
frequently than the client rediscovery period of the Clear Install Flag
task in Site Maintenance. The Clear Install Flag task relies on
accurate data that is forwarded from Heartbeat Discovery. If a
heartbeat is not forwarded within the client rediscovery period, the
install flag is cleared, causing a new attempt at installing the client
and unnecessary utilization of your site and clients.
Network Discovery
Network
Discovery allows ConfigMgr administrators to collect discovery data by
IP subnet, domain, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) community,
SNMP device, or DHCP server (which must be a Microsoft-based DHCP
server).
Enable Network Discovery and then choose the type of discovery to perform:
Topology—
Discovers routers and IP subnets. Specify the Maximum hops option on
the SNMP tab to allow additional router hops to discover additional
systems.
Topology and client—
In addition to discovering topology as described in the previous
bullet, this type also discovers potential client computers using an IP
address. Specify one or more DHCP servers on the DHCP tab for Network
Discovery to query DHCP servers (Microsoft DHCP only) for clients that
have an IP address lease. Depending on the size of your network, you
may want to limit the number of hops to reduce network traffic.
Topology, client, and client operating system—
In addition to topology and client information, the client operating
system is also identified by using this network discovery type. Client
operating system information is obtained using SNMP, DHCP, the Windows
browser, and Windows networking calls.
Figure 3 shows Topology selected as the discovery type.
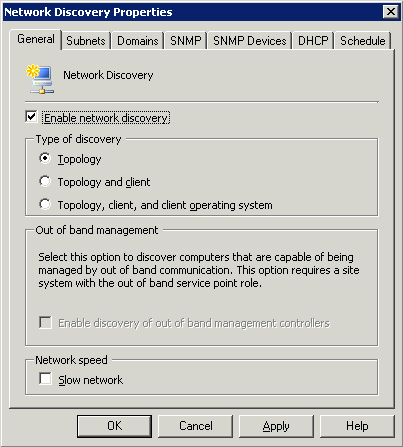
Figure 3
also shows the Out of Band (OOB) Management frame currently
disabled—you must have ConfigMgr Service Pack (SP) 1 installed to even
see this frame at all. You must configure the OOB service point and
configure a provisioning account before you can enable discovery of Out
of Band management controllers. Here are some points to keep in mind:
If
you are on a slow network, enable the check box on this dialog box to
reduce the number of SNMP sessions and increase the SNMP timeout.
Specify
subnets to discover by adding them to the Subnets tab. The desired
subnet will not be searched if it exceeds the number of hops specified
on the SNMP tab. In addition, the local subnet to the site server will
be searched by default.
Specify specific domains using the Domains tab. By default, local domain search is enabled.
Specify
all community names (they are case sensitive) in the SNMP community
names property of the SNMP tab. Take the time to identify all community
names used on your network, so that network discovery can search as
many routers as possible. Specify the maximum number of router hops
from the site server.
As with answers to many Microsoft-related questions, it depends. That answer seems to be a cop-out, but sometimes it is necessary. Here are some
pointers to keep you on track:
Heartbeat Discovery—
Always enable this method of discovery for every site that has assigned
clients. Unlike other discovery methods, Heartbeat Discovery is
executed at the client, and information is forwarded to the site. This
“heartbeat” updates the ConfigMgr site with updated client information.
Ensure the intervals for the Delete Inactive Client Discovery and
Delete Aged Discovery Data site maintenance tasks are set larger than
the heartbeat interval setting. Heartbeat Discovery does not discover
new clients, but keeps existing clients healthy in the ConfigMgr site.
Active Directory System Discovery—
If you have Active Directory, this will probably be your primary method
of discovery and client installation. In addition to discovering
computers, you can discover additional computer attributes from Active
Directory.
Active Directory System Group Discovery—
This discovery method queries Active Directory for group membership and
Organizational Unit information on computer systems that are existing
clients assigned to the ConfigMgr site. The discovery method will not
discover new systems, but will discover additional information about
existing systems.
Active Directory User Discovery—
This discovery method queries Active Directory for user resources and
includes objects such as user domain, AD container name, and username.
Additional user attributes can be queries, such as manager, telephone
number, and more. Because this is user discovery, client installation
does not occur. This discovery method is very valuable if you plan to
target users with software distribution.
Active Directory Security Group Discovery—
This discovery method queries Active Directory for groups. It is not
used for client installation, but can be used when targeting AD groups
for software distribution.
Network Discovery—
If all systems are in Active Directory, you may not need to use Network
Discovery. If you use workgroups, or also want to discover routers,
printers, and other network-connected devices, Network Discovery is for
you. Client installation will only target those systems discovered
using this method (not printers, routers, and such).