7. Mobile Devices
Mobile
Device Client Agent Properties is your one-stop-shop to configure those
mobile devices that ConfigMgr will manage. From this single dialog box,
you define the polling interval, inventory properties, software
distribution, and file collection. Figure 14 displays the default configuration of the Mobile Device Client agent.
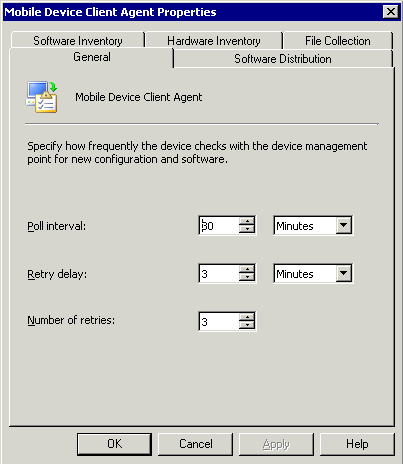
The mobile client performs operations similar to the ConfigMgr client. Table 1 lists several differences to consider.
Table 1. Mobile Client Nuances
| Mobile Client Setting | Additional Information |
|---|
| Polling Interval | For
a mobile client, consider a polling interval of 6 hours, because you
will not make changes as frequently on a mobile client as a workstation. |
| Retry Delay | If
the mobile client cannot connect to the management point at its polling
interval, you can specify an interval for retrying the connection. You
also specify the number of retry attempts. The polling interval must be
less than the retry delay multiplied by the number of retries. |
| Software Inventory | You may use wildcards, but use caution, because inventorying a large number of files may impact the performance of the device. |
| Hardware Inventory | Mobile
device hardware inventory is not extensible like the workstation
client. Data such as owner name, phone number, user name, certificates,
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number, battery status,
memory, and other device information is collected. See the ConfigMgr
integrated help for additional information. |
8. Remote Tools
You enable the Remote Tools Client agent to connect to remote systems so you can control the user’s desktop. Figure 15 displays the General tab of the Remote Tools Client Agent Properties dialog box.
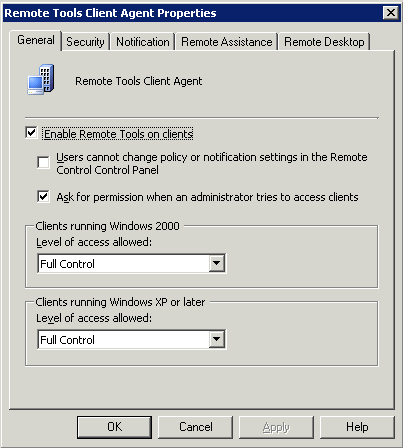
Check
the first box to enable Remote Tools. Use the configuration settings on
the General tab to manage the level of access. Some companies prefer
not to ask for permission for remotely accessing clients; other
companies require that a user is asked for permission before granting
remote access.
You can grant rights to
users and Active Directory groups to use remote control on a sitewide
level or on a collection level. For example, you could grant the Server
Operations group Remote Control rights to a collection containing
servers, and grant the Service Desk group Remote Control rights to a
collection containing workstations.
Use
the Notification tab to configure if and how you will notify an end
user a remote control session is active. This setting applies only to
Remote Tools.
You can also control the
Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop settings of ConfigMgr clients from
the respective tab on the Remote Tools Client Agent Properties dialog
box. The settings you configure are sitewide, and they override any
local policy configured on the client. Domain policy takes precedence
over these settings.
Note: About Remote Tools in ConfigMgr 2007
ConfigMgr
has a new version of the Remote Tools Client agent that uses the
Microsoft RDP protocol. This is the same protocol that supports Remote
Desktop and Remote Assistance. All ConfigMgr-supported operating
systems support the RDP protocol except Windows 2000 operating systems.
ConfigMgr uses an updated version of the SMS 2003 Remote Tools Client
agent on Windows 2000 operating systems in order to support remote
control.
The
biggest advantage to the new version of Remote Tools (for Windows XP,
Windows Server 2003, and newer) is that it is more secure.
Unfortunately, due to the enhanced security, you also lose the
functionality to manipulate the Ctrl+Alt+Delete screen. For Windows
2000, you still have this functionality by clicking the gold key on the
toolbar after initiating a Remote Tools session.
9. Network Access Protection
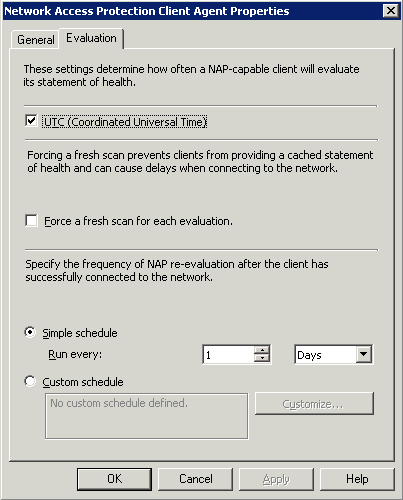
Enable
the check box on the General tab of the Network Access Protection
Client Agent Properties dialog box to configure Network Access
Protection (NAP). On the Evaluation tab, specify the frequency of NAP
reevaluation after the client has successfully connected to the
network. You can also force a fresh scan for each evaluation instead of
allowing clients to offer a cached Statement of Health, as displayed in
Figure 16.
Note: Statement of Health, Cached or Fresh?
You
may be trying to determine whether you should enable the check box to
force a fresh scan for each evaluation. This option is added for
environments that must ensure a
fresh compliance scan is performed at every evaluation cycle. Although
this option may be needed for some environments, requiring a new
Statement of Health to be generated at each scan can be resource
intensive, and may take a few minutes to complete on a client. Although
forcing a fresh scan for each evaluation is more secure, it will also
create a slower user experience, because the user may not be able to
access corporate network resources until the evaluation completes.