3. Working with EFS
Encrypting
files is easy. All a user has to do is right-click on any file or
folder, select Properties, click Advanced on the General tab, and check
the Encrypt contents to secure data option. If the user selected a
folder, then, when the user closes all of the dialog boxes, the system
will ask if all content should be encrypted. That's it. From now on,
the folder and the files contained within it will display in green in
Windows Explorer.
To
view the details of an encrypted file, the user needs to select it once
again, view its Properties, click Advanced on the General tab and now,
because the file is already encrypted, they will be able to click the
Details button. Clicking Details displays the Encryption dialog box
(see Figure 3).
This displays who has access to the file as well as who can recover the
file should an untoward event occur with the user's certificate. This
interface also gives you access to the backup of the user's keys if you
are using an internal CA to provide PKI keys.
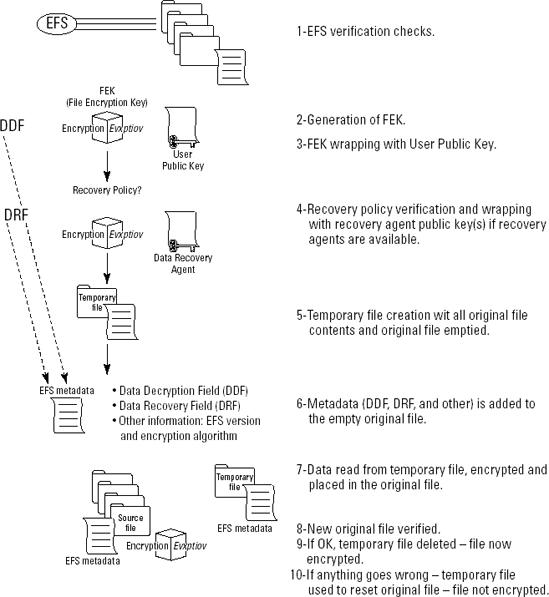
However,
since putting in place an encrypting file system structure can be
complex when you deal with it on a user per user basis, you should
control encryption at the Group Policy level so that you have one
single, structured EFS policy in place.
Implementing an EFS structure involves several activities:
Identifying information that may be at risk
Preparing a PKI for EFS use
Implementing EFS for data that may be at risk
Perform
each activity in turn. For the first activities, you may need to
request help from your Certificate Authority administrator.
3.1 Identifying potential EFS uses
The
first activity is relatively simple. In most organizations, the only
data that is at risk is the data that is in transit inside portable or
mobile computers. When the mobile system is lost and data is not
protected, then your organization's information can be at risk. In some
organizations, however, all data is considered at risk, and therefore
all data is encrypted at all time.
If you
choose to encrypt data that is located on mobile computers only, then
you will need to regroup these computers into an OU within Active
Directory to be able to more easily target them with an Encrypting File
System Group Policy Object. If you want to encrypt data on all systems,
then target your GPO to every PC in your network.
It
is also a good idea to create a Windows Security group to contain the
users you intend to assign EFS to. This helps identify them easily in
the event of issues.
3.2 Preparing the PKI for EFS
The
second activity is focused on using an existing PKI to prepare for EFS. But
keep the following in mind when you do put your PKI in place:
Use an Enterprise Edition of Windows Server — either 2003 or 2008 — as your Certificate Authority.
Obtain
an official certificate from a third-party Certificate Authority to
identify your organization and use this certificate as the root of your
CA. Doing this will automatically identify your organization and the
certificate it issues to others because most systems already trust
third-party CAs.
Use multiple levels of CAs to ensure redundancy for the infrastructure.
Validate
other uses for the CA. They support many more operations than just EFS.
For example, if you are using Exchange in your organization, then you
will need certificates for your Outlook Web Access Web site. This is
another area where a PKI could help.
Rely on user auto-enrolment to assign certificates.
Make sure that your users are well informed on the uses of PKI and the importance of protecting their certificates.
Implementing a CA structure can be a complex operation. Don't take it lightly.
NOTE
For information on how to put a PKI in place with Windows Server 2008, look up Windows Server 2008: The Complete Reference
by Ruest and Ruest from McGraw-Hill Osborne. For information on
integrating a third-party root certificate into your CA structure, look
up The Case for Outsourcing PKI under the Advanced PKI section at www.reso-net.com/articles.asp?m=8#c.
After
it is implemented, you should begin issuing EFS certificates to end
users. Windows includes a Basic EFS certificate template, but this
template does not include certain useful options you might want in
order to facilitate the management of these certificates. For this
reason, it is a good idea to make a duplicate of this template, rename
it to something such as Corporate EFS, and then customize it to your
needs. Customizations include at least five settings that are not on
the original template:
On the General tab of the certificate template's Properties, choose Publish certificate in Active Directory.
On the Request Handling tab of the template's Properties, choose Archive subject's encryption private key.
On the Request Handling tab of the template's Properties, choose Enroll subject without requiring any user input.
On
the Security tab of the template's Properties, add the group you
created earlier to grant access to this template. Grant the Read and
Enroll or Autoenroll rights.
On the Superseded Templates tab for the template's Properties, add the original Basic EFS template.
The
first setting makes it easier for users to share encrypted files
because they will be able to locate other user's certificates in AD.
The second creates the user's backup certificate. The third lets users
automatically generate the certificate. When users begin to use EFS,
the EFS certificate will automatically be generated by the CA. Use
Enroll rights to have the process issue the certificate on an as-needed
basis. Use Autoenroll to distribute certificates to anyone who has
access rights to them before they begin using EFS. The last option
makes sure that your new template is used when user certificates are
generated instead of the default template that is delivered with the CA.