|
If you suspect hardware as the source of your Internet connection problems, check the following:
Log on using an account with
Administrator privileges. On the Start menu, right-click Computer and
select Manage to open Computer Management. Select Device Manager. Look
for any yellow exclamation point (!) icons in the device list. If your
network adapter is marked with this trouble indicator, you must solve
the hardware problem before continuing. Also
within Computer Management, check the Event Viewer for any potentially
informative error messages that might indicate a hardware problem. Use ipconfig
on each of your computers to check that all the computers on your LAN
have the same gateway and network mask values, and similar but distinct
IP addresses. If your LAN has indicator lights on the network cards and hubs, open a Command Prompt window and type where x.x.x.x
is your network’s default gateway address. (This might be something
similar to 192.168.0.1.) This forces your computer to transmit data once
per second. Confirm that the indicator lights blink on your LAN adapter
and the hub, if you have one. This test might point out a cabling
problem. If your hub or LAN card’s
indicator doesn’t flash, you might have a bad LAN adapter, the wrong
driver might be installed, or you might have configured the card
incorrectly. You can stop the ping test by pressing Ctrl+C when you’re finished checking.
If you use a hardware connection-sharing router
for a broadband (DSL or cable) connection, your router might provide
further assistance. To access the router, follow these steps:
1. | Open a Command Prompt window (click Start, All Programs, Accessories, Command Prompt).
| 2. | Type the command ipconfig and press Enter.
| 3. | Note the gateway address. It will be something along the lines of 192.168.0.1.
| 4. | Open Internet Explorer. In the Address bar, type the URL //192.168.0.1, but enter the gateway address that you noted in the previous step.
| 5. | You
are prompted to enter the administrative username and password for your
router. Each manufacturer has a default name and password, which you
can find in the router’s user’s manual. You might also have changed it
when you installed it.
| 6. | Most
routers have a Status menu item that displays the status of the
router’s Internet connection. If it says that it can’t connect, you
might have an incorrect PPPoE username or password entered. Or it might
have dropped the connection. In this case, there might be a Connect
button you can click, or you might want to just power off and then power
on the router.
|
If you use a dial-up Internet connection, the next section can help you diagnose modem problems.
Identifying Modem Hardware Problems
Modems can have a greater variety of problems
than network adapters. You can take a few steps to determine what the
problem might be:
1. | Before
getting too frustrated, check the obvious one more time: Is a
functioning telephone line connected to the right socket on the modem?
Unless you’re using an ISDN modem, it also doesn’t hurt to plug in an
extension phone and listen as the modem dials and your ISP answers. You
must somehow put the extension on the “line” side of the modem, though,
because most modems disable the “telephone” jack when dialing. A duplex
telephone jack can help with this.
If dialing was actually taking place but you couldn’t hear it,
run the Phone and Modem Options (open the Control Panel and click
Hardware and Sound; then, click Phone and Modem Options). Select the
Modems tab, highlight the modem, and click Properties. Click Change
Settings, and then click Continue. Select the Modem tab and move the
volume slider up to its rightmost position. Click OK to save the change.
If you have a
voicemail system that uses a stutter dial tone to indicate that you have
messages waiting, your modem might not dial when the stutter is active.
If this is the case, open the Control Panel. In the Search box, type modem,
then click Phone and Modem. Select the Modems tab. Select your modem
and click Properties. Select the Modem tab and disable the Wait for Dial
Tone Before Dialing option, as shown in Figure 5.
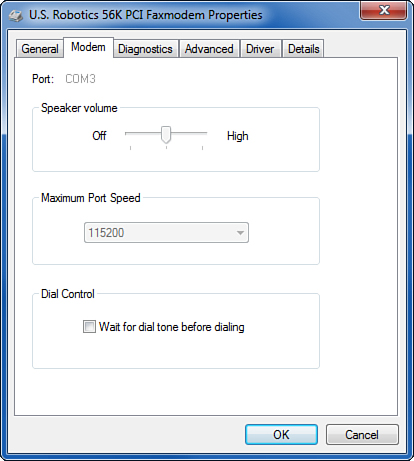
| 2. | If
you have an external analog or ISDN modem, be sure that it’s plugged in
and turned on. When you attempt to make a connection, watch for
flickering in the Send Data LEDs. If you don’t see flickering, your
modem cable might not be installed correctly.
| 3. | Check the Event Viewer for informative error messages that might indicate a hardware problem.
| 4. | In
the Start menu, right-click Computer, select Manage, and select Device
Manager. Look for any yellow exclamation point (!) icons in the device
list; if a modem or port is marked with this trouble indicator, you need
to solve the hardware problem before continuing. Double-click the line
that’s marked with the exclamation point and read the explanation of the
problem.
Note If you’d like to learn
more about troubleshooting hardware and resolving device conflicts, pick
up the latest edition of Scott Mueller’s Upgrading and Repairing PCs, published by Que. |
| 5. | On
the Options tab of the Dial-Up Connection Properties dialog box, check
Prompt for Phone Number and try to make the connection. This shows you
the actual number being dialed. Verify that the call-waiting code,
outside line-access codes, and area code are correct. These are set on
the connection’s General tab and in the Phone and Modem Options Control
Panel applet (in the Dialing Rules dialog box, select the proper
location and click Edit).
| 6. | If you have an analog or ISDN modem and dialing is taking place but no connection is made, open Control Panel and type modem
into the Search box. Click Phone and Modem. Select your modem and click
Properties. Click Change Settings. Select the Diagnostics tab and check
Append to Log. Close the dialog box and try to make the connection
again. Go back to the Properties dialog box and select View Log. This
log might indicate what is happening with the modem. Be sure to uncheck
Append to Log when you’re finished, or the file that stores this
information could grow to enormous proportions.
|
Identifying Modem Connectivity Problems
Modem problems are usually due to
incompatibility with your ISP’s equipment or to poor telephone line
quality. If your modem fails to make a connection or disconnects by
itself, you need to look for a few things:
If the ISP’s modem answers but you don’t establish a connection, your modem might be incompatible; call your ISP for assistance. If
your modem disconnects and you are told that there was a problem with
your username or password, try to connect again and check these entries
carefully. If you try two or three times and still can’t connect,
contact your ISP for help. Sometimes, ISPs get bought by other
companies, and the format of the required sign-on username can change as
a result. Create and view a log file of
modem activity and look for error messages indicating a
protocol-negotiation error. Your ISP can assist with this as well. If
your modem makes screeching sounds for approximately 15 seconds and
hangs up, your modem is probably incompatible with the equipment used at
your ISP, and you need an updated modem. Before you buy a new one, note
that some modems can be updated via software. Check the manufacturer’s
website for information. If your
connection works but the modem disconnects after a certain amount of
time, there are two possible causes. If your connection was sitting
idle, you might have run into the Windows inactivity timer. Click the
network icon in the taskbar, right-click the name of your dial-up
connection, and select Properties. View the Options tab. Check the entry
Idle Time Before Hanging Up. Increase the time or select Never. If this
problem recurs, you might enable the modem log and see whether it
provides an explanation. Your ISP might also have set up its equipment
to disconnect after a certain period of inactivity. If
you don’t think that idle time was the cause, your connection might
have been interrupted by call waiting. On the connection’s General tab,
check Use Dialing Rules, click the Dialing Rules button, and then click
Edit. Verify that To Disable Call Waiting is checked, and that the
proper call-waiting turn-off setting is selected (for example, *70).
Some newer modems can cope with call waiting and even alert you to a
call coming in. If you rely on call waiting, it might be time for an
upgrade. In this case, however, you’re probably better suited switching
to a cable or DSL connection, if one is available to you. If
none of these is the cause, you might simply have a scratchy telephone
line or a flagging older modem. This is an annoying problem that is
difficult to diagnose. Try changing modems.
If
your modem is making contact with your ISP but, despite a solid modem
connection, you still can’t use the Internet, see the next section for
tips on diagnosing Internet connectivity problems.
|