Microsoft introduces a number of new capabilities in
Configuration Manager 2007. The next sections focus on the new and
improved features.
Branch Distribution Points
While
functioning similar to standard DPs, branch distribution points provide
greater control over network traffic, which is necessary for branch
offices that may have limited network bandwidth availability.
Branch
distribution points allow not only for manual content provisioning, but
also provide configurable settings for scheduling and throttling
network traffic to help minimize network impact.
Branch
distribution points allow on-demand package distributions, where
packages are downloaded to the branch distribution point only when
specifically requested by a client computer.
Branch
distribution points are limited to only being able to handle 10
concurrent connections, due to limitations in Microsoft desktop
operating systems.
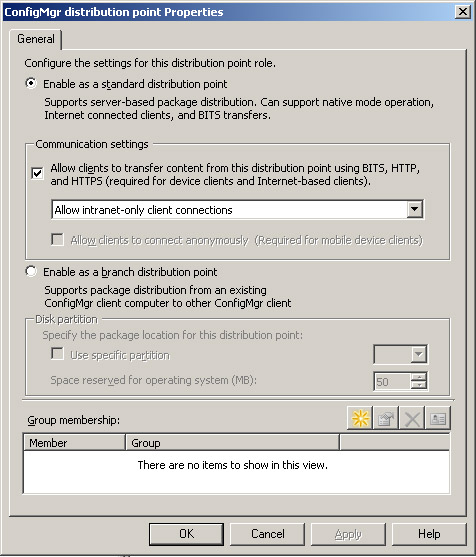
Figure 1
shows the General Properties page for a DP; there is a radial button
midway down the page to enable the DP as a branch distribution point.
Software Update Point
The SUP installs as a site
system role in the Configuration Manager console. Each site must have
an active SUP before you can enable software updates. You can install a
second SUP for communications from Internet-based client computers. You
must create the software update point site system role on a server that
has Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) 3.0 already installed and
configured.
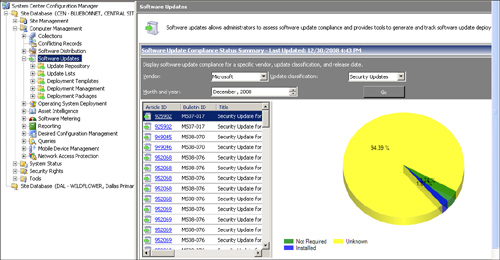
The software update point provides communication with WSUS and
synchronizes with the WSUS database to retrieve the latest software
update metadata from Microsoft Update, as well as locally published
software updates. Once this is configured via the Configuration Manager
console, the administrator does not need to perform any patch management
in the WSUS console. Instead, all patch management configuration and
administration occurs in the ConfigMgr console. Figure 2 shows the integration between Configuration Manager and WSUS.
Fallback Status Point
The primary purpose of the fallback status point is to resolve client health issues. Client health
describes the overall percentage of clients regularly checking into
their designated management points, downloading policy, uploading
inventory, and executing specified actions such as running an
advertisement to install a package such as Microsoft Office.
The FSP in
Configuration Manager 2007 always communicates with clients using HTTP,
which uses unauthenticated connections and sends data in clear text,
even when the site is in native mode. This makes the fallback status
point vulnerable to attack, particularly when used with IBCM. To help
reduce the attack surface, always dedicate a server to running the FSP
and do not install other site system roles on that server in a
production environment.
Install an FSP in the site if all the following scenarios exist:
You want client computers to report any failures to the site database, particularly when they cannot contact an MP.
You want to utilize the Configuration Manager 2007 client deployment reports that use data sent by the FSP.
You
have a dedicated server for this site system role and have additional
security measures to help protect the server from attack.
The
benefits of using an FSP outweigh any security risks associated with
unauthenticated connections and clear–text transfers over HTTP traffic.
Caution: Fallback Status Point Security Risk
Do not install an FSP in
the site if the security risks of running a website with unauthenticated
connections and clear–text transfers outweigh the benefits of
identifying client communication problems.
PXE Service Point
PXE is a
technology allowing individuals to boot a computer from the network
instead of a local disk. You can use this capability in situations where
the disk needs to be written to in a way where no files can be in use,
such as deploying an operating system.
The PXE service point must
be configured to respond to PXE boot requests by Configuration Manager
2007 clients so that those clients can interact with the ConfigMgr
infrastructure to determine the appropriate installation actions to
take.
Other Site Systems
Other site systems
new to ConfigMgr 2007 include the state migration point and branch
distribution point.
Operating System Deployment
OSD
in ConfigMgr is very different from the OSD Feature Pack on SMS 2003.
ConfigMgr 2007 exposes a brand-new task sequencer, which sometimes is
thought to be from BDD 2007 because it was available in the Business
Desktop Deployment (BDD) Solution Accelerator released slightly earlier.
The task sequencer from ConfigMgr was actually integrated into the BDD
Solution Accelerator and Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT). This
integration allows for interoperability between OS deployments made in
BDD/MDT and ConfigMgr.
ConfigMgr also now
provides the ability to build a complete reference PC, Sysprep, and
image it all using a single unattended task sequence. This new
capability provides administrators a mechanism to ensure the build
process across all systems, regardless of platform or image, is
consistent.
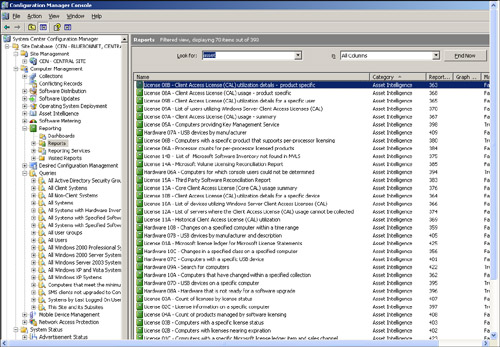
Asset Intelligence
First
introduced in SMS 2003 SP 3, Microsoft enhanced Asset Intelligence
significantly in Configuration Manager 2007. The Asset Intelligence
reports include nine new License Management reports, three new Hardware
reports, and six new Software reports.
Besides tracking
installed software, auto-start software, and browser helper objects, new
Software reports provide information about recently used executables.
In addition to the Hardware reports that track USB devices, processor
age, and readiness for upgrade, these new reports identify computers
that have software or hardware changes since the last inventory cycle.
New Client Access License reports, added to the existing License Ledger
reports, complete the ability to compare license usage with Microsoft
License Statements. Figure 3 lists some of the Asset Intelligence reports included with ConfigMgr 2007.
Device Management
Mobile
device management has changed substantially since SMS 2003. ConfigMgr
device management enables discovering, inventorying, and reporting on
the following mobile device categories:
ConfigMgr 2007 also adds support for the following mobile devices:
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC 2003
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC 2003 Second Edition
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC Phone Edition 2003
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC Phone Edition 2003 Second Edition
Windows Mobile Smartphone 2003
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC 5.0
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC Phone Edition 5.0
Windows Mobile 5.0 Smartphone
Windows CE 4.2 (ARM processor only)
Windows CE 5.0 (ARM and x86 processors)
Windows Mobile 6 Standard
Windows Mobile 6 Professional
Windows Mobile 6 Classic
The R2 release adds support for Windows Mobile 6.1.
SMS 2003 required
connecting mobile devices to a host device running the SMS 2003 client.
In ConfigMgr, mobile devices can be managed over Ethernet, wireless, or
via IBCM. You can manage mobile devices when they have a standard
Internet connection.
Internet-Based Client Management
IBCM
allows you to manage ConfigMgr clients that are outside your network
firewall. This configuration has a number of advantages, including the
reduced costs of not having to run virtual private networks (VPNs) and
being able to deploy software updates in a timelier manner.
Because of the
higher security requirements of managing client computers on a public
network, IBCM requires the site to be in native mode. Native mode
ensures an independent authority mutually authenticates connections to
the management point, software update point, and distribution points,
and that data to and from these site systems is encrypted using Secure
Sockets Layer (SSL). IBCM in essence allows ConfigMgr administrators to
manage their client systems wherever they are (home, hotel, and so on)
without them having to VPN in.
DCM and NAP
Desired
Configuration Management and Network Access Protection, both new in
Configuration Manager 2007.
SQL Support
ConfigMgr 2007
requires a minimum of SQL Server 2005 with Service Pack 2 for the site
database. Microsoft also supports using SQL Server 2005 SP 3 and SQL
Server 2008.
The following caveats apply to using SQL Server 2008 with Configuration Manager 2007:
There is no
support for a clean installation of SQL Server 2008 with ConfigMgr 2007
RTM. You need to first install SQL Server 2005, then upgrade the
database, and apply hotfix 955229.
With ConfigMgr 2007 SP 1, Microsoft supports a clean installation of SQL Server 2008; hotfix 955262 is required.
TCP/IP is the only
protocol now used for SQL Server to communicate with ConfigMgr; there is
no longer a reliance on Named Pipes. The default port SQL uses is 1433,
which you can change using the SQL Server Configuration Manager
utility.
In most cases,
Microsoft recommends having SQL Server and ConfigMgr on the same server
when you install a primary site. Alternatively, Microsoft now recommends
that if you are going to use a remote SQL Server, to install an
additional network card in both the SQL Server and the ConfigMgr server
and dedicate each card to communicate with one another, similar to a
heartbeat network on a cluster.
SQL Server has
supported using instances (which are multiple installations of SQL in
parallel on the same server) since SQL Server 2000. Microsoft now
supports the installation of the ConfigMgr 2007 database on a SQL named
instance.
ConfigMgr
also supports SQL replications, where you can point the MP or SLP roles
at a SQL replica to improve performance in low-bandwidth scenarios.
Client Support
Microsoft does not
support the Configuration Manager client on any operating system prior
to Windows 2000 Service Pack 4. Installing the Configuration Manager
client explicitly is not supported on the following operating system
versions:
Windows 95
Windows 98
Windows Millennium Edition
Windows XP Media Center Edition
Windows XP Starter Edition
Windows XP Home Edition
Windows XP Professional, with less than Service Pack 2 applied
Windows Vista Starter Edition
Windows Vista Home Basic Edition
Windows Vista Home Premium Edition
Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Windows NT Server 4.0
Windows 2000 Server, Service Pack 3 and earlier
Windows 2003 Server, with no service pack installed
Windows CE 3.0
Windows Mobile Pocket PC 2002
Windows Mobile Smartphone 2002