Before you can delete records, you must select them.
The following sections cover the process of selecting records and then
the process of deleting records.
Selecting One or More Records
To select one record, you just click the gray record selector button to the left of the record within the datasheet.
To select multiple records,
you click and drag within the record selector area. Access selects the
contiguous range of records in the area over which you click and drag.
As an alternative, you can click the gray selector button for the first
record you want to select, hold down the Shift key, and then click the
gray selector button of the last record that you want to select. When
you do this, Access selects the entire range of records between them. Figure 1 shows the Customers table with three records selected.
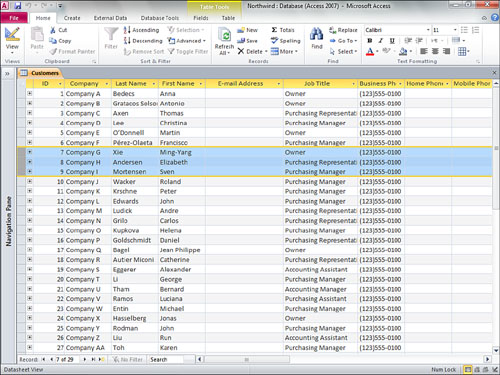
If you want to select a single
record when the cursor is within the record, you can simply choose
Select from the Find group on the Home tab, and then choose Select. To
select all records, choose Select from the Find group on the Home tab,
and then choose Select All.
Deleting Records
When you know how to select records, deleting them is quite simple. You just follow these steps:
1. | Select the records you want to delete.
|
2. | Press the Delete key. The dialog box in Figure 2 appears, asking whether you’re sure you want to delete the records.
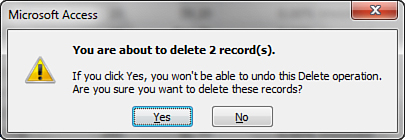
|
3. | Click the Yes button. Access deletes the records.
|
The process of deleting a
record is not so simple if you have established referential integrity
between the tables in a database and the row that you are attempting to
delete has child rows. You can think
about the fact that customers generally have orders associated with
them, and those orders have order detail records associated with them.
The relationship between the Customers table and the Orders table
prohibits the user from deleting customers who have orders. Here’s how
you delete a customer who has orders:
1. | Select the records you want to delete.
|
2. | Press the Delete key. The dialog box in Figure 3 appears, telling you that the records cannot be deleted because the table includes related records.
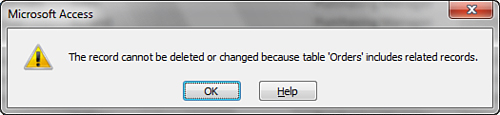
|
3. | Click OK to close the dialog box.
|
Access provides a referential integrity
option with which you can cascade a deletion down to the child table (a
table related to a parent table, such as orders related to customers).
This means, for example, that if you attempt to delete an order, Access
deletes the associated order detail records. If you establish
referential integrity with the cascade delete option, the deletion
process works like this:
1. | Select the records you want to delete.
|
2. | Press the Delete key. The dialog box in Figure 4 appears, asking if you’re sure you want to delete the records.
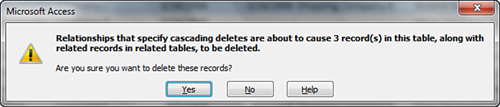
|
3. | Click Yes to complete the deletion process.
|
After you have selected
records, they appear in black, and you can copy them, delete them, or
modify them as a group. Remember that deleting records is a permanent
process. You cannot undo record deletion.
Finding and Replacing Records
When
you are working with records in a large data table, you often need a
way to locate specific records quickly. By using the Find feature, you
can easily move to specific records within a table. After you have found
records, you can also replace the text within them.
Find a Record That Meets Specific Criteria
The Find feature enables you to search in a datasheet for records that meet specific criteria. Here’s how it works:
1. | Select the field containing the criteria for which you are searching.
|
2. | Click the Find button in the Find group on the Home tab of the Ribbon. The Find and Replace dialog box appears (see Figure 5).
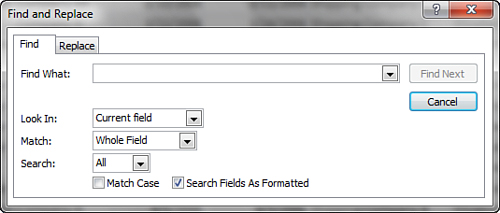
|
3. | Type the criteria in the Find What text box.
|
4. | Use the Look In drop-down list box to designate whether you want to search only the current field or all fields in the table.
|
5. | Use
the Match drop-down list box to designate whether you want to match any
part of the field you are searching, the whole field you are searching,
or the start of the field you are searching. For example, if you type Federal
in the Find What text box and you select Whole Field in the Match
drop-down list box, you find only entries where Ship Via is set to
Federal. If you select Any Part of Field, you find Federal Shipping,
Federal Express, United Federal Shipping, and so on. If you select Start
of Field, you find Federal Shipping and Federal Express, but you do not
find United Federal Shipping.
|
6. | Use
the Search drop-down list box to designate whether you want to search
only up from the current cursor position, only down, or in all
directions.
|
7. | Use the Match Case check box to indicate whether you want the search to be case sensitive.
|
8. | Use
the Search Fields as Formatted check box to indicate whether you want
to find data only based on the display format (for example, 17-Jul-96
for a date).
|
9. | Click the Find Next button to find the next record that meets the designated criteria.
|
10. | To continue searching after you close the dialog box, use the Shift+F4 keystroke combination.
|
Replacing Data in a Table
There may be times when you
want to update records that meet specific criteria. You can use the
Replace feature to automatically insert new information into the
specified fields. Here’s how:
1. | Click within the field that contains the criteria you are searching for.
|
2. | Click the Replace button in the Find group on the Home tab of the Ribbon. The Find and Replace dialog box appears.
|
3. | Select the Replace tab (see Figure 6).
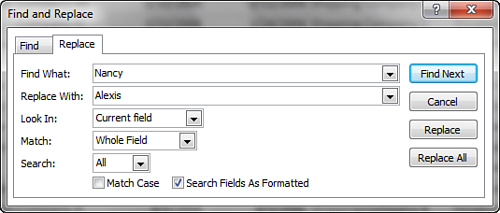
|
4. | Type the criteria in the Find What text box.
|
5. | Type the new information (the replacement value) in the Replace With text box.
|
6. | Choose
values for the Look In drop-down list box, Match drop-down list box,
Search drop-down list box, Match Case check box, and Search Fields as
Formatted check box.
|
7. | Click the Find Next button. Access locates the first record that meets the criteria designated in the Find What text box.
|
8. | Click
the Replace button. Access replaces the text for the record and finds
the next occurrence of the text in the Find What text box.
|
9. | Repeat
step 8 to find all occurrences of the value in the Find What text box
and replace them. As an alternative, you can click the Replace All
button to replace all occurrences at once.
|
You should use Replace All with quite a bit of caution. Remember that the changes you make are permanent.
Although Replace All is a viable option, when you use it you need to
make sure you have a recent backup and that you are quite certain of
what you are doing. In fact, I usually do a few replaces to make sure
that I see what Access is doing before I click Replace All.
|
|
10. | Click Cancel when you’ve finished.
|
|
If you are searching a very
large table, Access can find a specific value in a field fastest if the
field you are searching on is the primary key or an indexed field.
|
When
using either Find or Replace, you can use several wildcard characters. A
wildcard character is a character you use in place of an unknown
character. Table 1 describes the wildcard characters.
Table 1. Wildcard Characters You Can Use When Searching
| Wildcard Character | Description |
|---|
| * | Acts as a placeholder for multiple characters |
| ? | Acts as a placeholder for a single character |
| # | Acts as a placeholder for a single number |