Group Policy Preferences help you configure, deploy, and manage
operating system and application settings that you cannot manage by
using Group Policy. Examples include mapped drives, scheduled tasks,
and Start menu settings. Using Group Policy Preferences is often a
better alternative than logon scripts for configuring these settings.
Group Policy Preferences are built into the Group Policy Management
Console.
Networks customarily have two types of settings: enforced
settings (Group Policy) and optional settings (preferences). Enforced
settings can’t be changed by users. Preferences, on the other hand,
can be changed by users. By specifically deploying preferences, you can create configurations
that are more suitable for your organization than the operating
system’s default settings. Deploying preferences is usually done through logon scripts or
default user profiles.
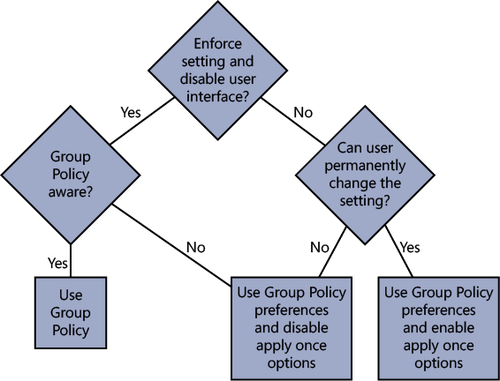
So what are the differences between Group Policy Preferences and Group Policy? The primary
difference is that Group Policy is enforced and Group Policy
Preferences are not. Table 1 shows the other
key differences.
Table 1. Group Policy vs. Group Policy preferences
| GROUP POLICY SETTINGS | GROUP POLICY PREFERENCES |
|---|
| Settings are enforced. | Preferences are not enforced. |
| User interface is disabled. | User interface is not disabled. |
| Adding policy settings requires application
support and constructing administrative
templates. | Preference items for files and registry settings
are easily created. |
| Requires Group Policy–aware
applications. | Supports non-Group Policy–aware
applications. |
| Filtering is based on Windows Management
Instrumentation (WMI) and requires writing WMI
queries. | Supports item-level targeting. |
| Alternative user interface is provided for most
policy settings. | Uses a familiar, easy-to-use interface for
configuring most settings. |
Figure 1
shows a decision tree for choosing between Group Policy settings and
Group Policy Preferences.
To view Group Policy Preferences, start Group Policy Management
from the Administrative Tools menu and follow these steps:
Navigate to Group Policy Objects. Right-click Default Domain
Controllers Policy and select Edit.
Under Computer Configuration, expand Preferences, expand
Windows Settings, and then expand Control Panel Settings.
Under User Configuration, expand Preferences, expand Windows
Settings, and then expand Control Panel Settings.
As you can see in Figure 2, the Computer
Configuration and User Configuration lists are very similar. However,
even when the names are identical, the properties might differ. The
following preferences do not overlap: Applications, Drive Maps,
Internet Settings, Regional Options, and Start Menu under User
Configuration; and Network Shares and Network Options under Computer
Configuration.