Quality of Service (QoS) can be used in networks
where the media traffic used by Lync Server 2010 servers and clients
should have a higher priority than other traffic using the same
infrastructure. This is done by having the Lync servers and endpoints
tag their media traffic packets with a specific Differentiated Services
Code Point (DSCP) value. Routers within the network are then configured
to prioritize traffic based on the DSCP values included with packets.
DSCP marking in Lync Server 2010 is done by using the
policy-based QoS first introduced with Windows Server 2008 and Windows
Vista. These policies are controlled through Windows Group Policy and
can mark traffic with DSCP codes based on application names and port
ranges. Because these policies can be centrally managed and controlled
by the organization, it should be acceptable to trust the markings sent
from client endpoints. Using a separate port range for each type of
traffic enables the policy-based QoS to tag the traffic appropriately.
For example, audio traffic using one port range can be assigned a DSCP
code with higher priority than the port range used for video or
application sharing.
Note
Network equipment is typically configured to ignore
or not trust DSCP markings from computers on the regular data network.
Because Lync is a softphone and operates using the same VLAN as PCs, the
markings from machines on the data VLAN must be trusted to use QoS with
Lync.
Server Configuration
Lync servers operate similarly to clients and tag
media traffic through the use of policy-based QoS in Group Policy. Each
media type has one of the following default port range assigned:
These port ranges can then be matched through
policy-based QoS and assigned a DSCP marking. The default port range for
application sharing overlaps with both audio and video. If application
sharing is tagged differently than either traffic, a separate port range
must be configured. Port ranges for each media type can be configured
using the Set-CsConferenceServer and Set-CsMediationServer cmdlets.
For example, to separate application sharing into its own port range, run the following command:
Set-CsConferenceServer –AppSharingPortStart 32768
This changes application sharing to use ports 32,768–49,151 while keeping the same amount of ports available.
Client Configuration
QoS tagging of the media is performed by the Lync
client itself, so it must be provisioned in a way that it understands
what ports to use for each type of traffic. By default, no tagging is
done and all traffic uses the port range 1,024–65,535. The Lync client
supports using different port ranges for the following types of traffic
and recommends a minimum number of ports for each modality. Using port
ranges that are below the recommended minimums increases the chance for a
media request to fail.
Audio (20 ports required)
Video (40 ports required)
Application sharing (4 ports required)
File transfer (4 ports required)
First, to enable separate port ranges for each media type, run the following command:
Set-CsConferencingConfiguration –ClientMediaPortRangeEnabled $true
Next, define a unique port range for each type of
traffic. As an example, the ports used on the client side can be the
same as on the server. The sample numbers used here are well beyond the
minimum number of ports required and are used only to show how the
default port ranges can be moved. The port ranges used should be limited
to the recommended sizes for ease of management and troubleshooting.
Set-CsConferencingConfiguration –ClientAudioPort 49152 –ClientAudioPortRange
8348 –ClientVideoPort 57501 –ClientVideoPortRange 8034 –ClientAppSharingPort
32768 –ClientAppSharingPortRange 16383 –ClientFileTransferPort 24733
–ClientFileTransferPortRange 8034
Creating a QoS Policy
After modifying the Lync clients and servers to use
specific port ranges, QoS policies must be created to add the
appropriate DSCP value to traffic originating from each port range. The
steps required to use policy-based QoS through Group Policy are similar,
but the port ranges used for servers and clients will likely differ.
Create at least two separate policies: one for servers and one for
clients. To create a new policy, perform the following steps:
1. | Open a new Group Policy object.
|
2. | Expand Computer Configuration, Windows Settings, and then click Policy-Based QoS.
|
3. | Right-click Policy-Based QoS and select Create new policy.
|
4. | Enter a name for the policy, such as Lync Audio.
|
5. | Enter a DSCP value, such as 46 and click Next.
|
6. | To limit the tagging only to Lync clients, select Only applications with this executable name and enter communicator.exe. Click Next.
|
7. | Allow the policy to apply to any source IP address and any destination IP address.
|
8. | In the Select the protocol this QoS policy applies to, select TCP and UDP.
|
9. | In the Specify the source port number section, select From this source port number or range and enter the range used for audio traffic, such as 49152:57500.
|
10. | Click Finish to complete the policy.
|
Repeat these steps for each type of media using a unique port range, which should be tagged differently. Figure 1 demonstrates what a policy with separate audio and video settings looks like.
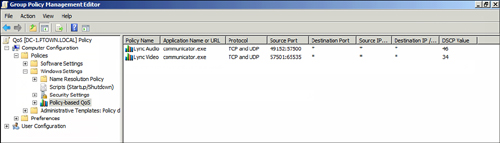
Note
The A/V Edge service behaves a bit differently.
First, because it typically is not part of the domain, it might be
necessary to create the policies locally on each server. Second, the
port range used to define each service should be specified as a destination
port instead of source port. This ensures traffic, which the Edge
server uses to communicate to a Front End pool, is marked correctly.
Windows XP QoS
Because QoS policies can be created only on Windows
Vista or later operating systems, the process for enabling QoS on
Windows XP is slightly different. Windows XP QoS marking is also not as
flexible as policy-based QoS and can only mark audio traffic as
SERVICETYPE_GUARANTEED and video as SERVICETYPE_CONTROLLEDLOAD.
First, verify the QoS packet scheduler is installed on the client. Secondly, run the following command on a Lync server:
Set-CsMediaConfiguration –EnableQoS $true
Before the Lync client attempts to tag packets, the DSCP values should be modified using Group Policy.
1. | Open a new Group Policy object.
|
2. | Expand Computer Configuration, Administrative Templates, Network, QoS Packet Scheduler, and click DSCP value of conforming packets.
|
3. | Double-click Guaranteed service type.
|
4. | Select Enabled and enter a DSCP value such as 46.
|
Repeat these steps for the Controlled load service type to tag video media.
Lync Phone Edition QoS
The final client type that can use QoS settings is
the Lync Phone Edition client, which can run on third-party partner
hardware. Lync Phone Edition settings are determined through in-band
signaling to the devices. In addition to a DSCP value for audio traffic,
the Lync Phone Edition clients also support 802.1p. To set the Lync
Phone Edition QoS settings, use the following command on a Lync server:
Set-CsUcPhoneConfiguration –VoiceDiffServTag 46 –Voice8021p 5