3.4 Implementing an EFS recovery solution
Every
organization planning to use EFS should devise a proper recovery
policy. As seen earlier, recovery policies are used to assign the
public keys of designated recovery agents to the data recovery field
(DRF) of an encrypted file or folder. This allows the recovery agent to
decrypt encrypted data in the event of a key loss or a user
reassignment.
By default, a standalone
machine will not have a recovery policy. That's because Windows Vista
no longer requires the recovery policy to be in place before users can
have access to the encryption capabilities it offers. In a domain, the
recovery policy is enabled through the same policy which enables EFS.
Recovery
agent private keys are very valuable because they are automatically
included in each and every encrypted document and can therefore decrypt
anything in your organization. Protect these keys as much as possible,
removing them from machines and importing them only when a data
recovery operation is required. Removing them is easily done. Keys can
be stored on many types of removable storage, such as smart cards,
floppy disks, CD-ROMs, DVDs, or even USB keys. Make sure that the
removable storage is stored in a safe place that is immune to tampering
or theft.
To begin, you need to deploy
recovery agent certificates to the people you've designated to manage
data recovery in the encrypting file system. This can be done by using
the Certification Authority console, but there is a potential issue
with using this console. As a best practice, you should make your data
recovery agent certificates last much, much longer than the
certificates you issue users. This ensures that your recovery
certificates are always valid even if user certificates must be updated
on a regular basis. By default, certificates you issue with the console
will have the same duration as the Certificate Authority itself. Then,
when they expire, you will need to maintain these older certificates to
be able to recover files that were encrypted using the older DRA
certificate. Using longer certificate duration avoids this issue.
By
default, the cipher command can generate DRA certificates that have
duration of 100 years. This should be long enough to recovery pretty
well any file in your organization. To do so, use the following command
to generate your certificates:
Cipher /r: Filename
Run
this command within the security context of each user that will become
a DRA. You'll need at least two DRAs in your organization. Each time
the command is run, the new DRA will have to enter a password to
protect the certificate files. Two files will be generated using the
name you input as the file name. The .CER file only includes the
certificate and is used to load the certificate into the EFS recovery
policy. The .PFX file includes the certificate and the private key and
is the file used to recover data.
After
the recovery agent certificates have been issued, the recovery policy
can be implemented. Use the following procedure. You need Group Policy
Modification access rights.
Begin by launching the Group Policy Management Console.
Locate the GPO which contains your EFS policy.
This can be the User Profile Management policy if you are assigning it
to all PCs or the EFS Policy if you are only assigning it to mobile
systems.
Right-click on the policy to select Edit.
Choose Computer Configuration =>
Policies =>
Windows Settings =>
Security Settings =>
Public Key Policies =>
Encrypting File System.
Right-click on Encrypting File System and select Add Data Recovery Agent. This launches the Add Recovery Agent Wizard.
Click Next. Click Browse Folders because you generated certificates with the cipher command instead of the directory.
Locate the .CER files containing the DRA certificates.
You will get a warning because Windows is unable to determine if the
certificate is revoked once again because it was self-generated.
Click Yes to install the certificate.
Repeat for each DRA certificate to load.
Review your changes and click Finish or click Back to modify your settings.
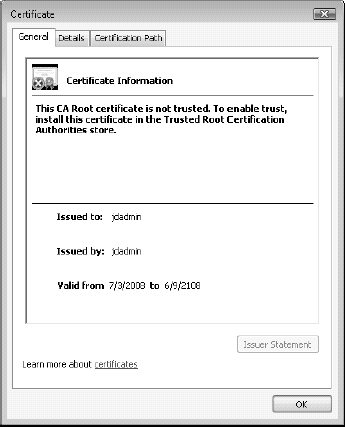
Recovery
certificates will now be displayed in your policy. You can right-click
on each certificate and open them or view their properties. The
Properties dialog box lets you add a friendly name and a description to
the certificates. When you open the certificate, you will see that
because it is self-generated, it is not trusted by your organization.
You will also note that it has a duration of 100 years (see Figure 5).
Now
you should add these certificates to the Trusted Root Certification
Authorities store within the GPO to make them trustworthy.
Within the same GPO, move to Computer Configuration =>
Policies =>
Windows Settings =>
Security Settings =>
Public Key Policies =>
Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Right-click Trusted Root Certification Authorities and select Import. This launches the certificate import wizard.
Click Next, and then click Browse.
Despite the information in this dialog box, you can use either the .PFX
or the .CER files generated earlier with the cipher command. Only one
file can be loaded at a time.
Locate the file and click Next. Select the .CER file because using the .PFX file will require a password to support the import of the private key.
Make
sure that Place all certificates in the following store is selected and
the Trusted Root store is indicated and click Next. Review your changes
and click Finish. Click OK when Windows tells you the import was
successful.
Repeat for each other DRA certificate.
Now
your certificates will be trusted by the users impacted by this GPO.
From now on the DRA certificates will be added to all DRF fields of
each encrypted file. Because the recovery policy is distributed by
Group Policy, it automatically overrides any existing local policy.
Should a member machine not be able to contact a domain controller to
refresh its recovery policy, it will use a locally cached version of
the policy to encrypt files.
In a
workgroup, assigning a standard recovery agent is a bit more complex.
That's because in a workgroup each machine has its own security
accounts manager (SAM) database that is separate from all others. So to
standardize the recovery agent, you first need to create one-on-one
machine, export it to external storage and re-import it on the same
machine. Make sure that you assign a strong password to the exported
certificate. The export/re-import operation is necessary to have a
separate copy of the certificate on removable storage. After this is
done, you have to go to each machine and create the recovery agent,
export it but then you re-import the agent that was created on the
first machine. This automatically standardizes the agent on all members
of the workgroup.
All is done through the Certificates console. Remember to keep the offline copy of the DRA well protected.
After
the recovery policy is in place, it is relatively easy to recover
files. If a single file is recovered, the recovery agent only needs to
open it normally. Once opened, the file is in clear text and can be
saved normally. If multiple files need to be decrypted, the recovery
agent can do so through the file system, either by using the Windows
Explorer and addressing the files' properties or through the cipher
command.